Thread division method for avoiding unrelated dependence on many-core processor structure
A technology of many-core processors and threads, applied in the field of microprocessor architecture design, to achieve the effects of reducing synchronization overhead, improving effective utilization, and improving overall parallel performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
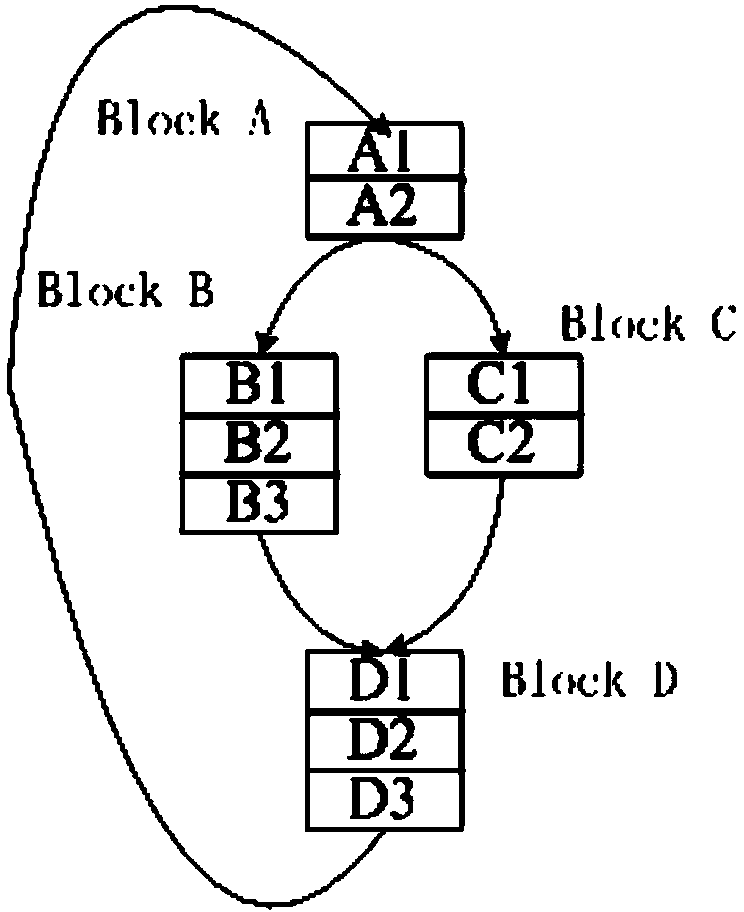
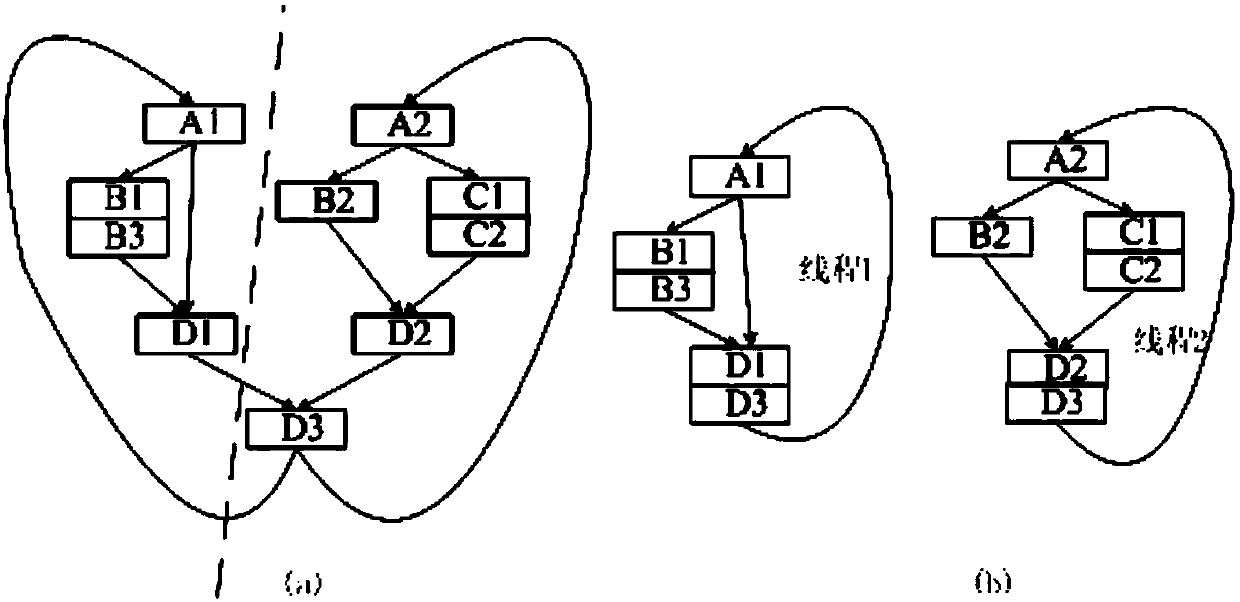
[0055]LLVM is a compilation framework tool that provides compilation analysis and optimization of the entire program life cycle. Its architecture is mainly divided into three parts: LLVM intermediate representation - LLVM virtual instruction set (LLVA); integrated library for program analysis, optimization and code generation; and tools based on the above integrated library, including assembler , linker, debugger, etc. The LLVM intermediate representation provides explicit control flow graphs and explicit data flow graphs, which can effectively support the construction of control flow graphs and data flow graphs required by our proposed method. And LLVA is independent of the target machine, which makes it not dependent on a specific machine architecture and has better versatility. The steps of the many-core thread division method implemented on LLVM to avoid irrelevant dependencies are as follows:
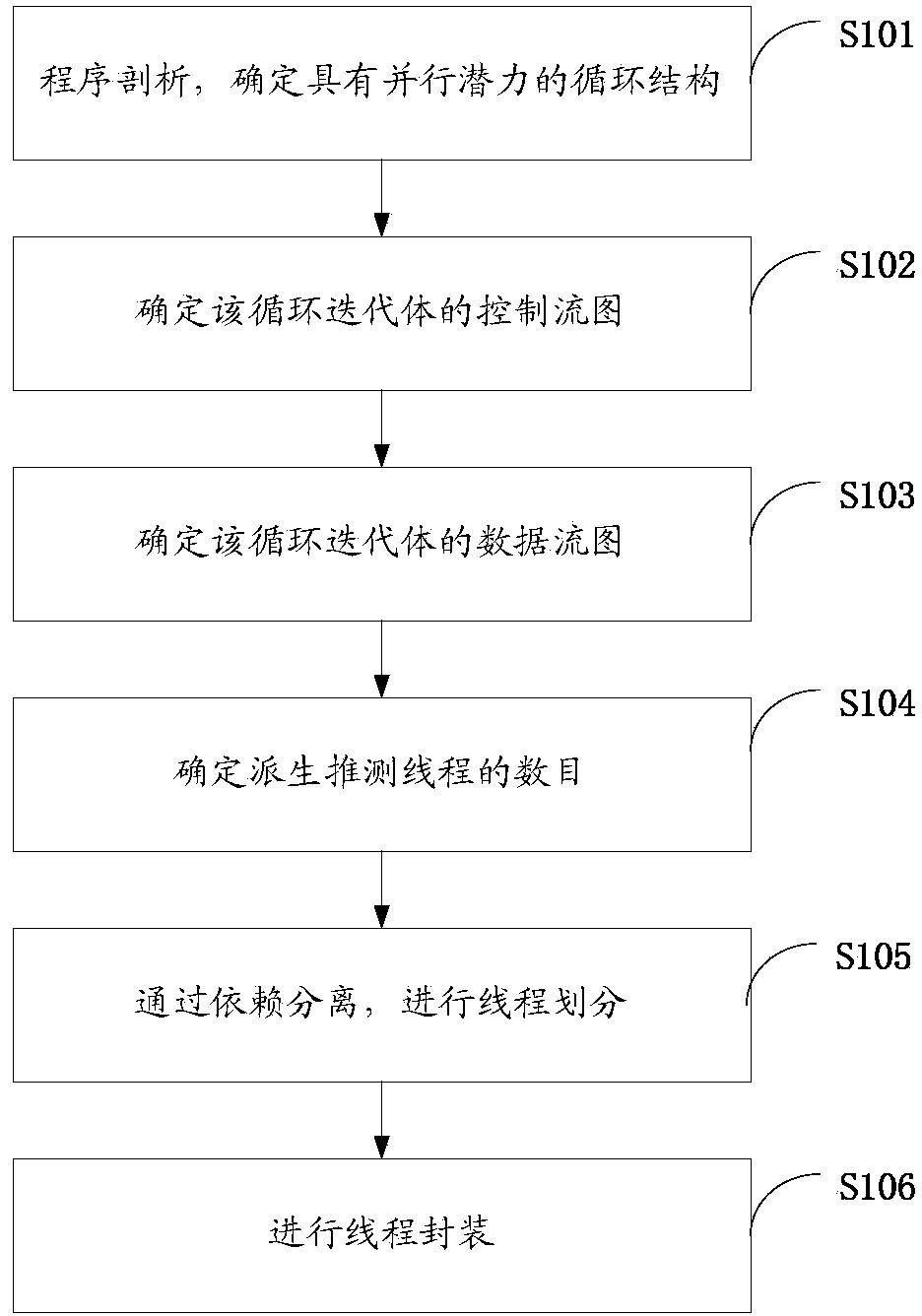
[0056] Step 1, program analysis, to determine the loop structure with parall...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com