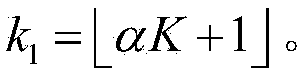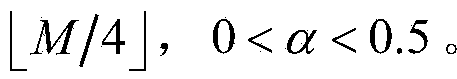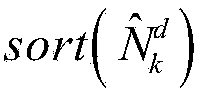Method for estimating jump cycle and take-off time of frequency hopping signal
A frequency-hopping signal and take-off time technology, applied in the field of signal processing, can solve the problems of parameter estimation performance degradation, large noise influence, and huge calculation amount
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0097] Embodiment 1: First, perform parameter initialization, set short-time window length M=128, short-time window moving step L=32, α=0.25 of α-TM algorithm, and calculate the total number of short-time windows The number of initialization window moves i=1.
[0098] Then, using the time-frequency ridge line of the frequency hopping signal at the beginning of each hop, the peak frequency transient and the peak-to-average power ratio are extremely small at the same time, and the initial time of each hop is estimated. The actual and estimated values of are shown in Table 1:
[0099] Table 1
[0100] actual value
[0101] Finally, the hopping cycle estimation value of the frequency hopping signal is estimated by using the α-TM algorithm The relative error is | N ^ h - N h | / N h =...
Embodiment 2
[0102] Embodiment 2: First, perform parameter initialization, set short-time window length M=256, short-time window moving step L=64, α=0.25 of α-TM algorithm, and calculate the total number of short-time windows The number of initialization window moves i=1.
[0103] Then, using the time-frequency ridge line of the frequency hopping signal at the beginning of each hop, the peak frequency transient and the peak-to-average power ratio are extremely small at the same time, and the initial time of each hop is estimated. The actual and estimated values of are shown in Table 2:
[0104] Table 2
[0105] actual value
[0106] Finally, the hopping cycle estimation value of the frequency hopping signal is estimated by using the α-TM algorithm The relative error is | N ^ h - N h | / N h =...
Embodiment 3
[0107] Embodiment 3: First, perform parameter initialization, set short-time window length M=128, short-time window moving step L=32, α=0.3 of α-TM algorithm, and calculate the total number of short-time windows The number of initialization window moves i=1.
[0108] Then, using the time-frequency ridge line of the frequency hopping signal at the beginning of each hop, the peak frequency transient and the peak-to-average power ratio are extremely small at the same time, and the initial time of each hop is estimated. The actual and estimated values of are shown in Table 3:
[0109] table 3
[0110] actual value
400
1000
1600
2200
2800
3400
4000
estimated value
416
992
1600
2208
2816
3392
4160
[0111] Finally, the hopping cycle estimation value of the frequency hopping signal is estimated by using the α-TM algorithm The relative error is | N ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com