Trapezoidal-block embankment structure
A trapezoidal block and embankment technology, applied in the field of embankment structure of embankments, can solve the problems of limited ability to resist wave action, large amount of concrete, and insufficient ability to resist wave action.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] Embodiment 1: A trapezoidal block embankment structure (without wave dissipation and pressure relief holes) is placed on the built slope embankment to form a guide embankment.
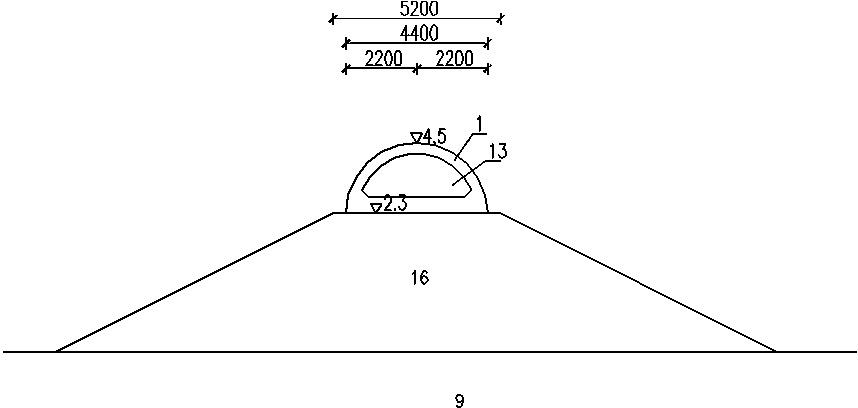
[0060] 1) The design conditions of a certain guide embankment are: the existing slope embankment 16 is a throw-filled large rock structure, the minimum particle size of the rock is 0.6m, the top elevation is 2.3m, and the top width is 5.2m. It is necessary to increase the elevation of the dike crest to 4.5m on the basis of the existing slope embankment 16, the elevation of the beach surface in front of the embankment is -2m, the design low water level is 0.08m, the design high water level is 4.11m, and the wave H 1% =3.5m, T=7.6s, L=58m.
[0061] 2) If prior art semicircular caissons are placed on the built slope embankment 16 to form a guide embankment, see figure 1 , figure 2 , prefabricated and placed a semicircular caisson 1 on the top of the existing slope embankment 16 (as a foundation...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Embodiment 2: A trapezoidal block embankment structure (wave dissipation and pressure relief holes connecting up and down) is placed on the built slope embankment to form a guide embankment.
[0077] The design conditions of a guide embankment are: the existing slope embankment 16 is a throw-filled large rock structure, the minimum particle size of the rock is 0.6m, the top elevation is 2.3m, and the top width is 5.2m. It is necessary to increase the elevation of the dike crest to 4.5m on the basis of the existing slope embankment 16, the elevation of the beach surface in front of the embankment is -2m, the design low water level is 0.08m, the design high water level is 4.11m, and the wave H 1% =3.5m, T=7.6s, L=58m.
[0078] see Figure 15 , Figure 16 , on the top of the existing slope embankment 16 (as the foundation bed), the trapezoidal blocks 3 with a cross-sectional direction of a whole block are placed longitudinally and continuously one by one, arranged and con...
Embodiment 3
[0082] Embodiment 3: Trapezoidal block embankment structure (without wave dissipation and pressure relief holes).
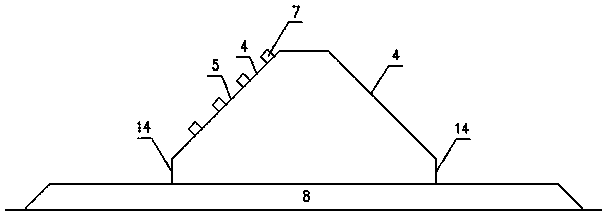
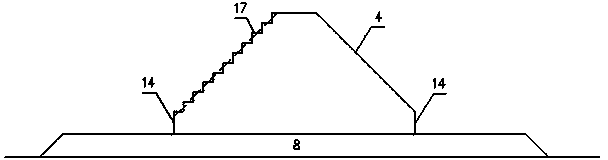
[0083] see Figure 12 , Figure 13 , Figure 14 , trapezoidal block embankment structure (without wave-dissipating and pressure-relief holes), which is formed by placing trapezoidal blocks 3 in the cross-sectional direction as a whole on the riprap foundation bed 8, and connecting them one by one in the longitudinal direction. The trapezoidal blocks 3 It is a block whose cross-sectional direction is approximately trapezoidal, and the overall shape is approximately trapezoidal prism, and the angle between the slope surface 4 on both sides of the trapezoidal block and the horizontal plane is not greater than 60°. The connection method of longitudinally adjacent trapezoidal blocks 3 is vertical plane contact connection, or vertical tongue-and-groove tenon joint, the seam width is generally not greater than 5cm, or vertical plane plus rubber water-stop contact conn...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com