Oxygen-bearing Re-(Fe, TM)-B based sintering magnetic body and manufacturing method thereof
A technology of sintered magnets and oxygen content, which is applied in the manufacture of inductors/transformers/magnets, magnets, magnetic objects, etc., and can solve the problems of reduced corrosion resistance of magnets
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
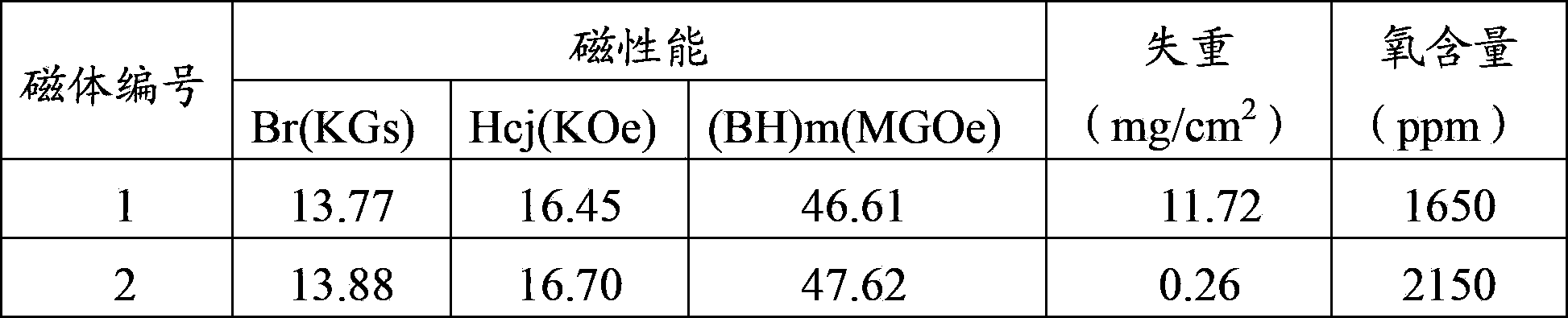
[0019] The design composition is (NdPr) 30 Fe 66.03 Al 0.1 Ga 0.5 Cu 0.1 co 1.0 Zr 0.25 B 1.02 (mass percentage, the total amount of rare earth is 31%), in order to improve the coercive force, there are two methods, one is to add 1% of pure metal Dy in the smelting process, called magnet 1; the other is Add 1% Dy2O3 powder less than 325 mesh before the jet mill after medium crushing, called magnet 2. The magnetic properties of the two alloys were measured after smelting, coarse crushing, medium crushing, jet milling, mixing, magnetic field forming, vacuum sintering, and aging treatment (test method: measure the blank with a magnetization characteristic automatic measuring instrument, standard: China National Standard of the People's Republic of China (GB / T 13650-2000) - Sintered NdFeB Permanent Magnets), Weight Loss Experimental Test and Oxygen Content Analysis. The test results are shown in Table 1:
[0020] Table 1: Magnetic properties, weight loss, and oxygen conte...
Embodiment 2
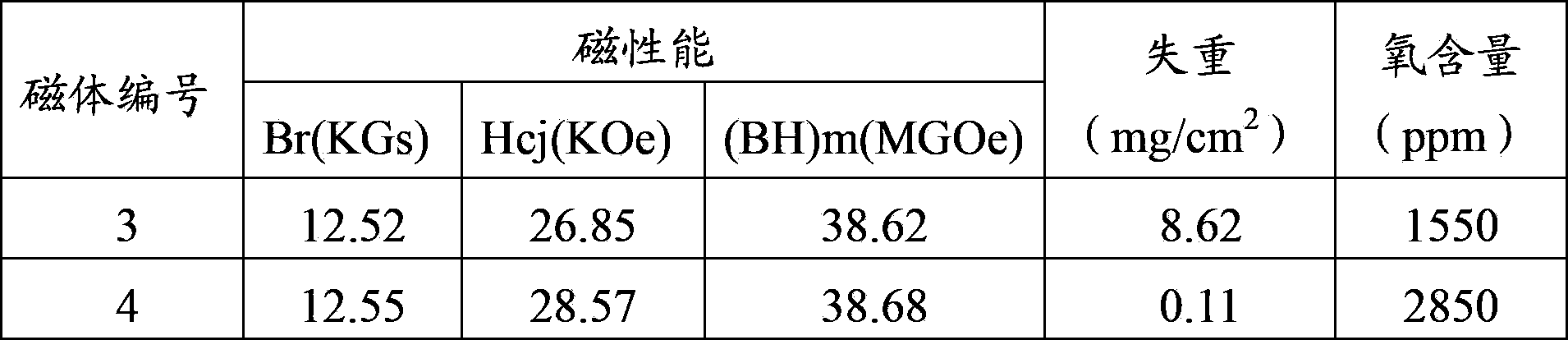
[0025] The composition is designed as (NdPr) 25.5 Dy 4.0 Fe 65.99 Al 0.2 Nb 0.5 Ga 0.4 Cu 0.15 co 1.0 Zr 0.25 B 1.01 (mass percentage) formula, in order to improve the coercive force, there are two methods, one is to add 1.0% pure metal Tb in the smelting process, called magnet 3; Add 1.0% Tb4O7 powder less than 325 meshes, lower the content of metal Nb from 0.5% to 0.1%, and increase the content of metal Fe from 65.99% to 66.34%, which is called magnet 4. The two alloys were smelted, roughly crushed, medium crushed, jet milled, mixed, formed in a magnetic field, vacuum sintered, aged, and then subjected to magnetic property measurement, weight loss test and oxygen content analysis. The test results are shown in Table 2:
[0026] Table 2: Magnetic properties, weight loss, and oxygen content tests of magnets
[0027]
[0028] Weight loss test conditions: 120 ℃, 100% humidity, 2 atmospheres of continuous storage for 96 hours; sample size: φ10*10 cylinder.
[0029]...
Embodiment 3
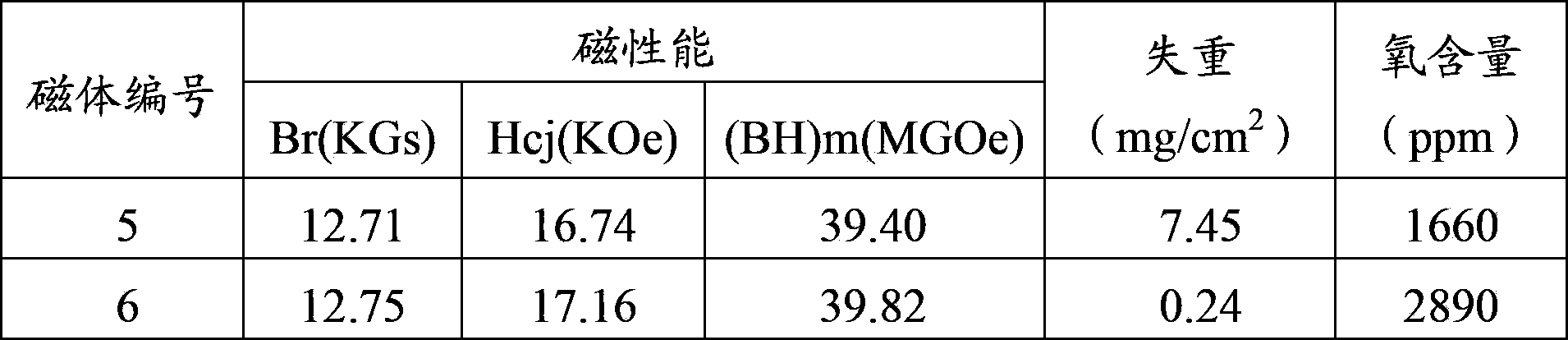
[0031] The composition is designed as (NdPr) 30.5 Fe 64.43 Al 0.85 Nb 0.5 Cu 0.2 co 0.75 Zr 0.25 B 1.02 (mass percentage, the total amount of rare earth is 32%), in order to improve the coercive force, there are two methods, one is to add 1.5% pure metal Nd in the smelting process, called magnet 5; the other is Add 1.5% Nd less than 325 mesh before jet mill after intermediate crushing 2 o 3 Powder, called magnet 6. The two alloys were smelted, roughly crushed, medium crushed, jet milled, mixed, formed in a magnetic field, vacuum sintered, aged, and then subjected to magnetic property measurement, weight loss test and oxygen content analysis. The test results are shown in Table 3:
[0032] Table 3: Magnetic properties, weight loss, and oxygen content tests of magnets
[0033]
[0034] Weight loss test conditions: 120 ℃, 100% humidity, 2 atmospheres of continuous storage for 96 hours; sample size: φ10*10 cylinder.
[0035] It can be seen from Table 2 that: with 1....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com