Method for removing blue-green algae by using microbubble hydrodynamic cavitation enhanced coagulation
A hydraulic cavitation and micro-bubble technology, applied in the field of water treatment, can solve problems such as filter bed blockage, affecting water quality of water purification plants, and increased coagulant consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Embodiment 1 (hydraulic cavitation directly removes algae)
[0026] The implementation steps of this embodiment:
[0027] (1) First prepare a device for generating microbubbles using a gas-liquid mixing pump.
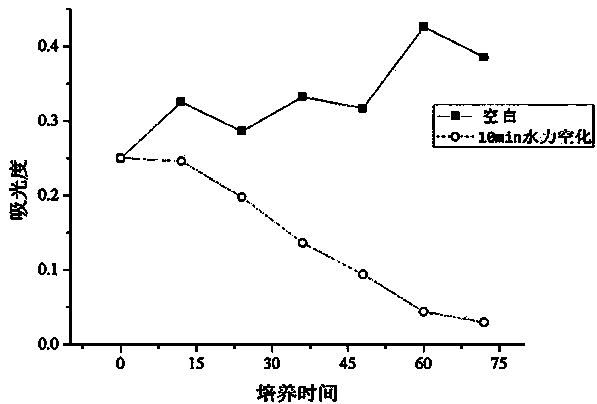
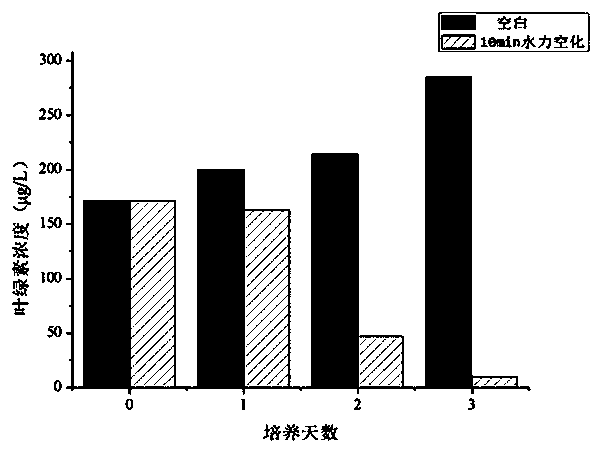
[0028] (2) Add algal liquid with an algae density of about 2×109 cel / L into the water tank, turn on the device, and act for 10 minutes, then place the treated algae liquid and the blank control group without hydrodynamic cavitation into light The incubator is normally cultivated, the density of algae is measured every 12 hours, and the chlorophyll content is measured once a day.
[0029] After the microbubble hydraulic cavitation treatment, the algae density continued to decrease during the 72-hour observation period. After 72 hours, the algae density was only 7.3% of the original, and the removal rate was as high as 92.7%. Without hydrocavitation The algae density of the control algae liquid did not change substantially.
[0030]
Embodiment 2
[0031] Example 2 (hydraulic cavitation enhanced coagulation algae removal)
[0032] The implementation steps of this embodiment:
[0033] (1) First prepare a device for generating microbubbles using a gas-liquid mixing pump.
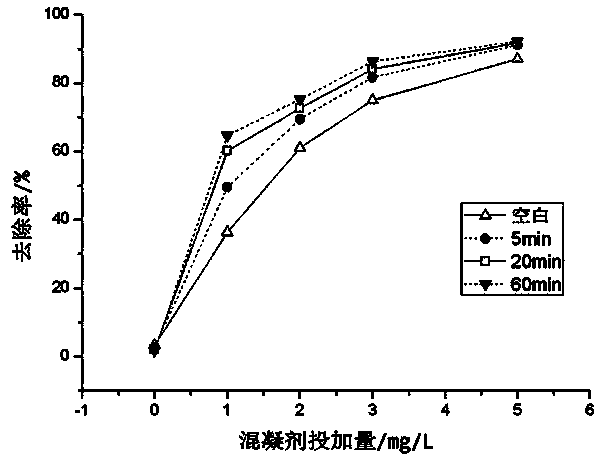
[0034] (2) Add algae liquid with an algae density of about 2×109 cel / L into the water tank, turn on the device, and act for a certain period of time, and then conduct coagulation and sedimentation experiments on the treated algae liquid and the blank control algae liquid respectively. Polyaluminum chloride (PAC) is selected, and the dosage is 0mg / L, 1mg / l, 2mg / L, 3mg / L, 5mg / L respectively. Coagulation conditions: rapid stirring at 150r·min-1 for 2min, slow stirring at 50r·min-1 for 10min, after 30min of static settling, sampling at 2cm below the liquid surface and determination of algae density.
[0035] In order to obtain the best working condition of hydraulic cavitation enhanced coagulation, the single factor variable method was adopted to examine t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| clearance rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com