Method and device for stabilizing 1529 nm optical fiber communication laser frequency
A fiber optic communication and laser technology, applied in lasers, laser parts, phonon exciters, etc., can solve the problems of limitation, frequency stability improvement, frequency modulation noise effect, etc., and achieve the effect of compact structure and high frequency stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
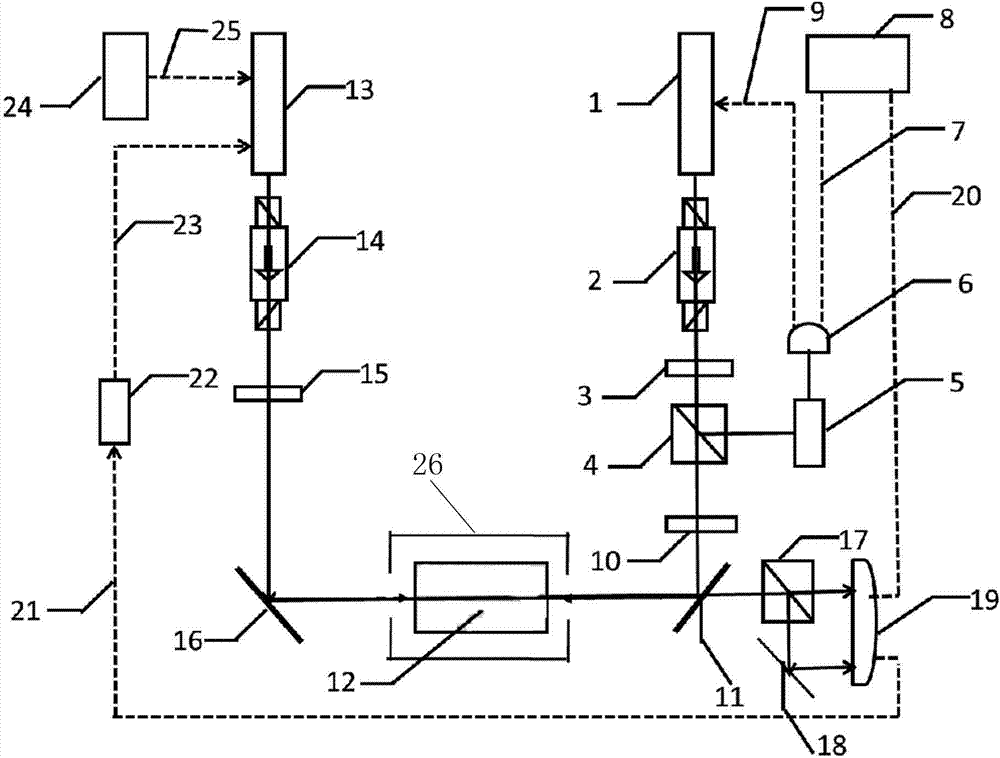
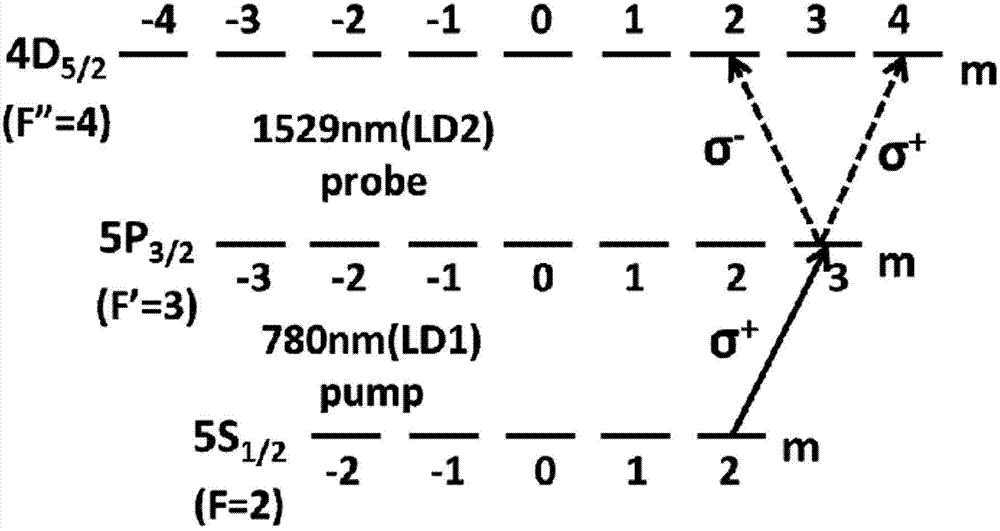
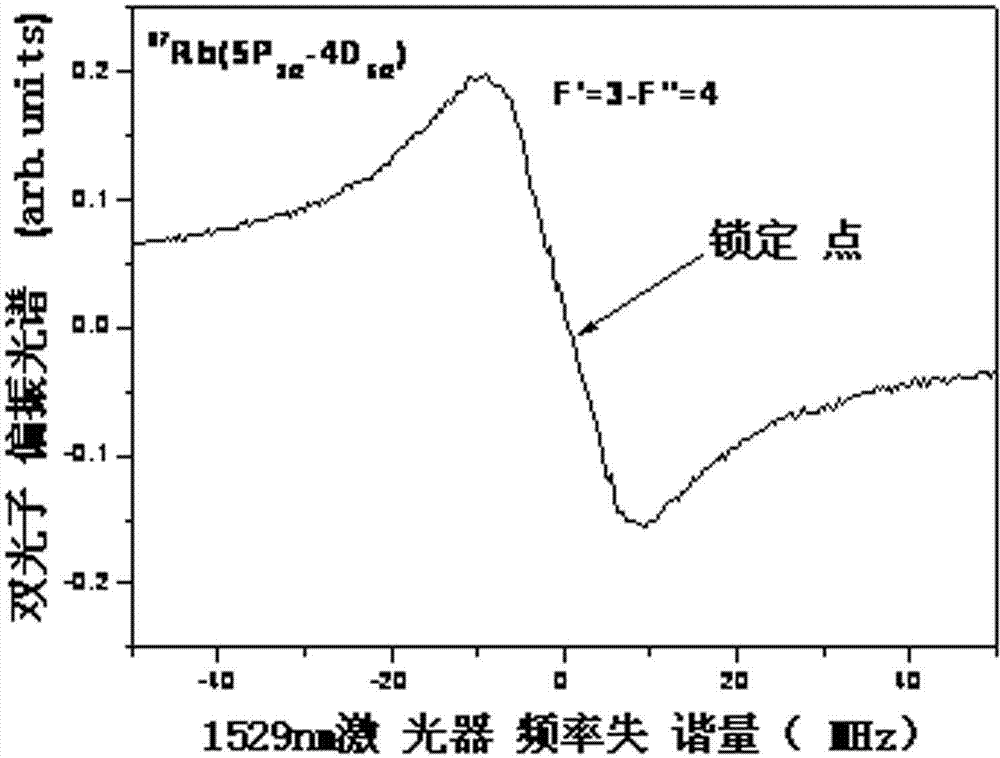
[0027] A method for stabilizing the frequency of a 1529nm optical fiber communication laser, comprising the following steps: (a) locking a beam to the hyperfine energy level 5S of rubidium 87 atoms using polarization spectrum 1 / 2 (F=2)-5P 3 / 2 (F’=3) The 780nm laser on the transition line is converted to σ + Circularly polarized light is then introduced into the rubidium bubble 12 filled with rubidium 87 vapor; (b) a beam of linearly polarized laser output by the 1529nm semiconductor laser 13 is introduced into the rubidium bubble 12, and the 1529nm laser is in the rubidium bubble 12 and 780nm Laser reverse coincidence; (c) Make the output frequency of 1529nm semiconductor laser 13 at 5P 3 / 2 (F'=3)-4D 5 / 2 (F”=4) Scan within a small range of the transition. During the scanning process, the 1529nm linearly polarized light emitted from the rubidium bubble 12 is divided into two beams of light with vertical polarization directions, and the intensity signals of the two beams are...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Light intensity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Outer diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com