Distribution network cable single-phase ground fault distance measuring method utilizing transient main frequency component
A technology of fault distance measurement and phase-to-grounding, applied in the direction of the fault location, etc., can solve the problems of difficult signal extraction, weak steady-state residual current, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0054] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with accompanying drawing:
[0055] The present invention comprises the following steps:
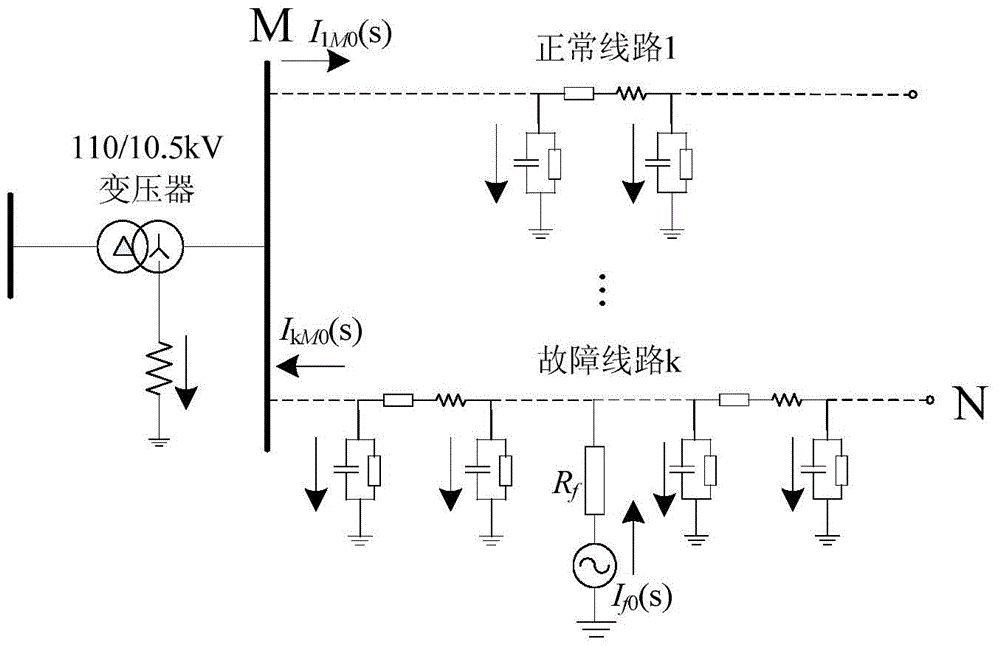
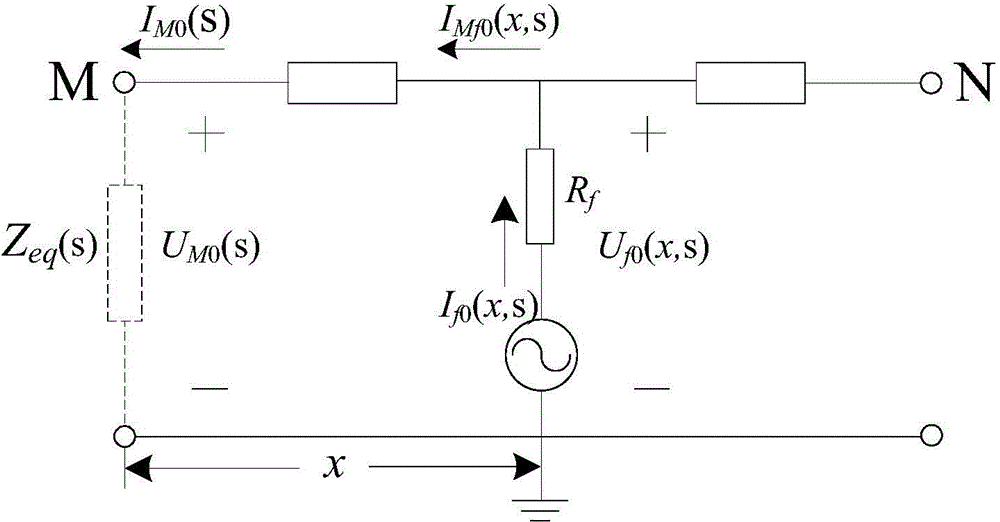
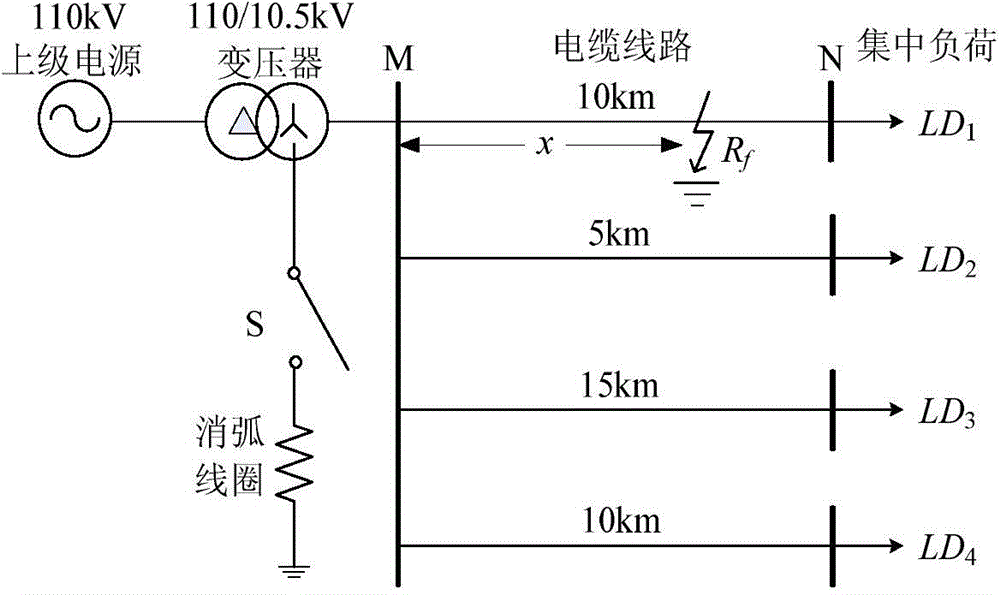
[0056] Step (1), sampling the three-phase transient current signal i at the head end (M end) of the faulty cable line MA (t), i MB (t), i MC (t) and the three-phase transient voltage signal u MA (t), u MB (t), u MC (t). The sampling frequency of the data is 10kHz, and the time window is the half cycle (10ms) after the fault;
[0057] Step (2), calculate the 0-mode component u of the voltage at the head end of the faulty cable line M0 (t) and the 0-mode component i of the current M0 (t):
[0058] ①. In step (1), the first-end three-phase transient voltage signal sequence value u of the faulty cable line obtained by sampling MA (t), u MB (t), u MC (t) Perform Karenbuaer phase-mode transformation to obtain the 0-mode component u of the voltage at the head end of the faulty cable line M0 (t), the specifi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com