Method for improving grade of low-grade iron ore
A low-grade iron ore, a technology for improving the grade, applied in the direction of improving the process efficiency, etc., can solve the problems of high reduction temperature, long reduction time, and easy ring formation cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
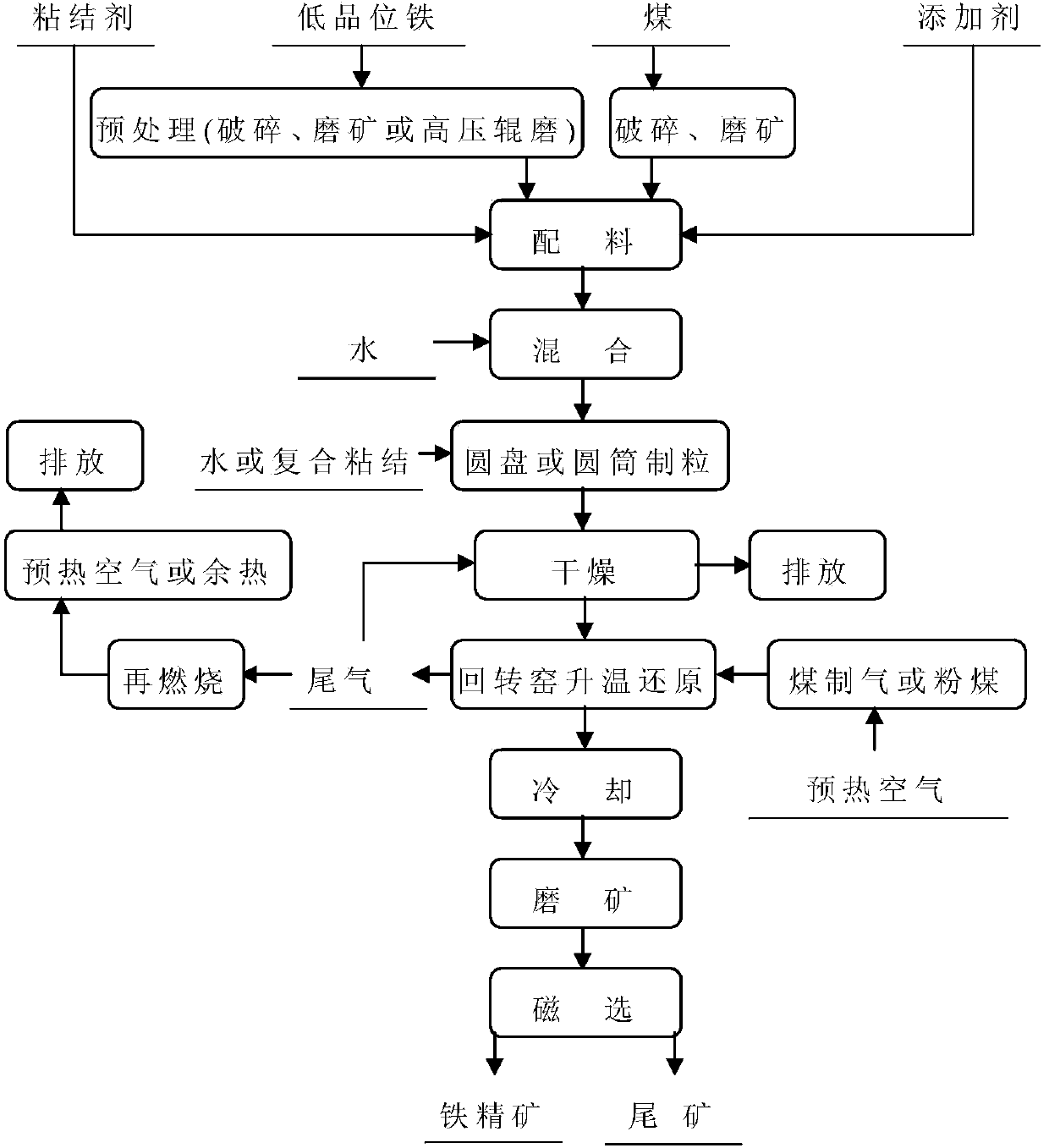
[0042] Low-grade iron ore internal coal blending and additive granulation coal-based medium-temperature rapid reduction-magnetic separation method, the mass percentage of low-grade iron ore and coal less than 0.074mm after pretreatment is 52.32%, and the internal blending coal C / Fe ratio is 0.3 , additive NaCl accounted for 3.0% of the mass percentage of iron ore and bentonite accounted for 1.5% of the mass percentage of iron ore were mixed, disc granulated into small balls with a diameter of 3-8mm; after the granulated balls were dried, the rotary tube was used The time for the preheating temperature of the charge in the furnace to rise from 200°C to 920°C is 35 minutes; the rotary tube furnace is used to reduce and roast at 920°C for 20 minutes; the reduced roasted ore is ball milled for 20 minutes, the grinding concentration is 50%, and the magnetic field strength is 1.8KA / m magnetic separation; the result obtained is that the recovery rate of magnetic iron concentrate is 6...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Low-grade iron ore internal coal blending and additive granulation coal-based medium-temperature rapid reduction-magnetic separation method, the mass percentage of low-grade iron ore and coal less than 0.074mm after pretreatment is 65.01%, and the internal coal blending C / Fe ratio is 0.4 , additive NaCl accounted for 3.0% of the mass percentage of iron ore and bentonite accounted for 1.5% of the mass percentage of iron ore were mixed, disc granulated into small balls with a diameter of 3-8mm; after the granulated balls were dried, the rotary tube was used The time for the preheating temperature of the charge in the furnace to rise from 200°C to 950°C is 35 minutes; the rotary tube furnace is used to reduce and roast at 950°C for 20 minutes; the reduced roasted ore is ball milled for 20 minutes, the grinding concentration is 50%, and the magnetic field strength is 1.8KA / m magnetic separation; the result obtained is that the recovery rate of magnetic iron concentrate is 7...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Low-grade iron ore internal coal blending and additive granulation coal-based medium-temperature rapid reduction-magnetic separation method, the mass percentage of low-grade iron ore and coal less than 0.074mm after pretreatment is 71.41%, and the internal coal blending C / Fe ratio is 0.4 , additive NaCl accounted for 3.0% of the mass percentage of iron ore and bentonite accounted for 1.5% of the mass percentage of iron ore were mixed, disc granulated into small balls with a diameter of 3-8mm; after the granulated balls were dried, the rotary tube was used The time for the preheating temperature of the charge in the furnace to rise from 200°C to 950°C is 35 minutes; the rotary tube furnace is used to reduce and roast at 950°C for 10 minutes; the reduced roasted ore is ball milled for 20 minutes, the grinding concentration is 50%, and the magnetic field strength is 1.8KA / m magnetic separation; the result obtained is that the recovery rate of magnetic iron concentrate is 6...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com