Culture media for stem cells
A culture medium and stem cell technology, applied in cell culture medium, cell culture active agent, pancreatic cells, etc., can solve the problem of not establishing a long-term culture system to maintain the differentiation potential phenotype and genome integrity of human epithelial stem cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0773] To address the need for improved media and methods for human epithelial stem cells, the inventors investigated signal transduction pathways known to be disrupted in certain cancers, such as colorectal cancer. It is postulated that these pathways affecting the final cell type in cancer also play a role in determining the final cell type under in vitro cell culture conditions.
[0774] In a first screening experiment, a series of vitamins, hormones and growth factors were tested in combination with standard stem cell media. Gastrin and nicotinamide were identified as producing significantly improved culture conditions. Incorporating these factors into standard culture conditions, a second screening experiment was performed in which certain small molecule inhibitors associated with relevant signal transduction pathways were tested, such as ERK, p38, JNK, PTEN, ROCK, and Hedgehog. In the prior art, there is no reasonable way to predict what effect each of these additional ...
Embodiment 2
[0808] Example 2 - Culturing Mouse Pancreatic Organoids
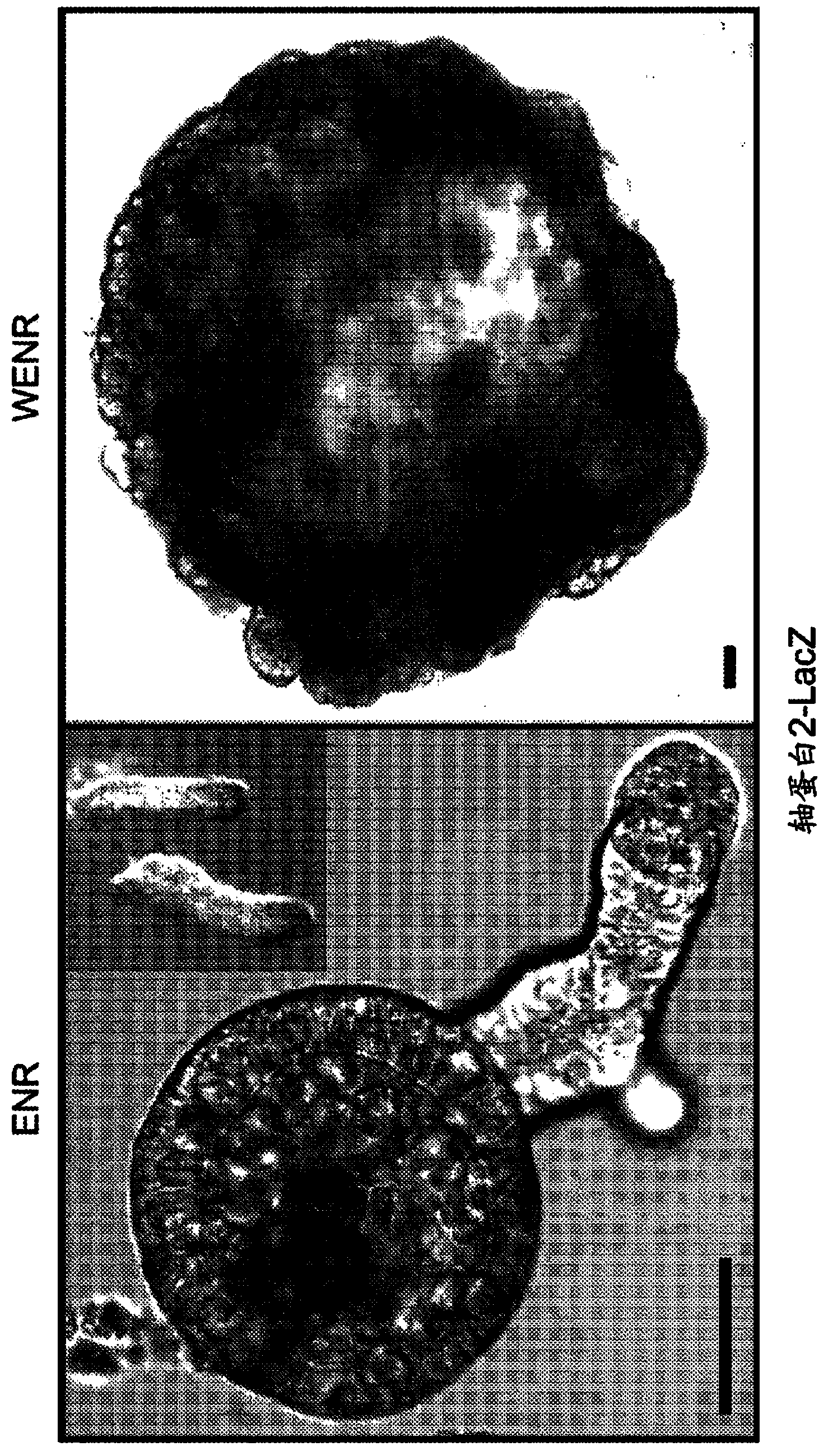
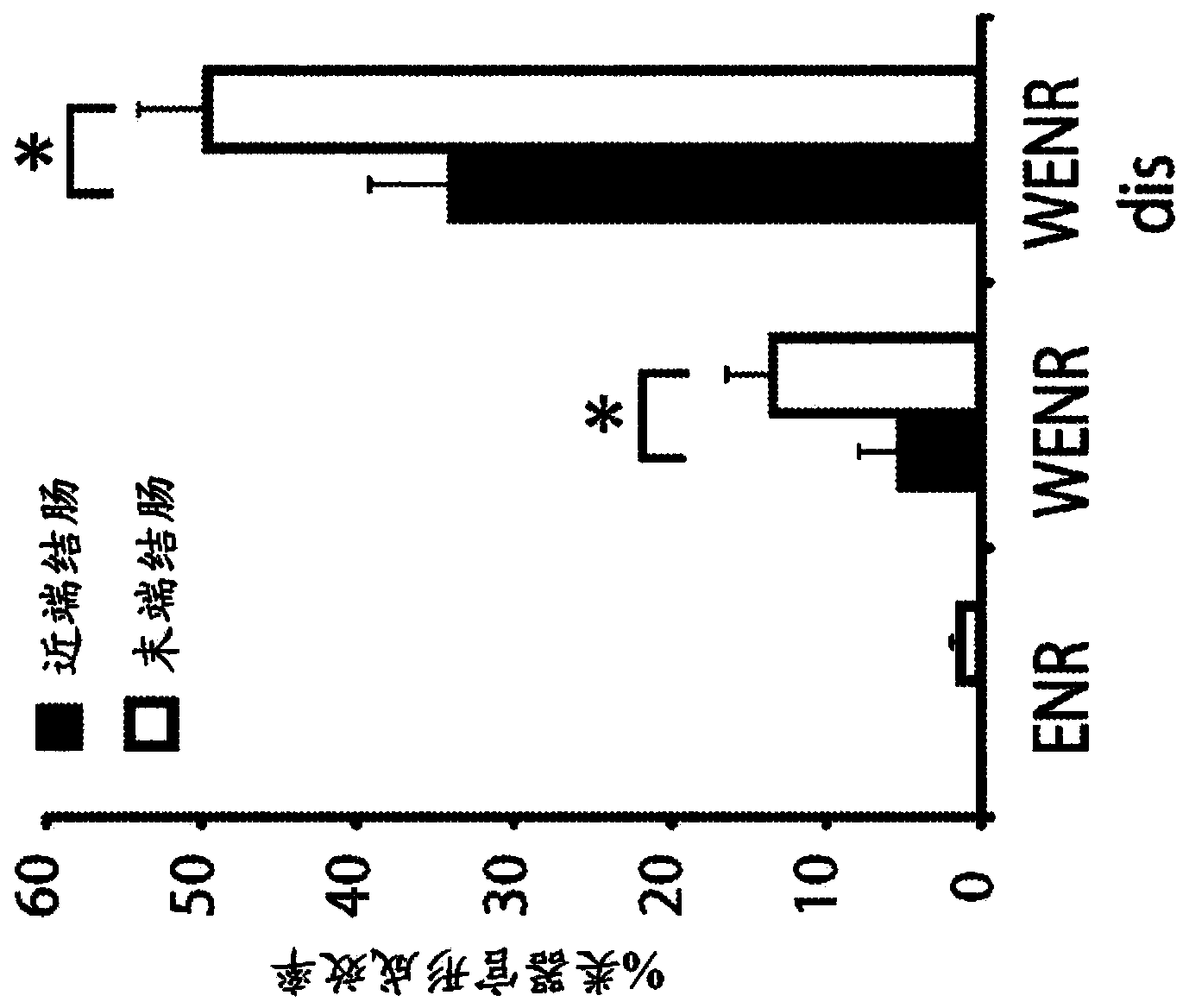
[0809] The use of TGF-β inhibitors was also tested in the culture medium of mouse pancreatic organoids. The expansion medium used was DMEM / F12 medium (supplemented with P / S, Glutamax, 10mM Hepes, B27, N2 and N-acetylcysteine), EGF (50ng / ml), R-spondin (10% ), Noggin (100ng / ml), FGF10 (100ng / ml), A8301 (TGF-β inhibitor, 500nM) and gastrin (10μM). This is slightly different from the above HISC medium used in Example 2 in that no Wnt agonist (Rspondin instead) or nicotinamide was present and FGF10 was added. However, these media share many key components (ENR + gastrin + TGF-beta inhibitor) and in both cases the addition of a TGF-beta inhibitor is advantageous. Pancreatic organoids grown in these conditions will be expanded up to >3 months and passaged at least 5 times.
[0810] Microarray experiments were performed on pancreatic organoids grown in the expansion medium described above, and the results were compared to a...
Embodiment 3
[0814] Example 3 - Effect of Noggin on Expansion Medium
[0815] To study the effect of the BMP inhibitor Noggin in the expansion medium, the inventors compared the mRNA levels of early endocrine markers and ductal markers in pancreatic organoids (which had been cultured in EGFRA medium from which not cultured in the presence of Noggin) were compared to the expression levels of the same markers in organoids that had been cultured in EGFRAN medium (ie, usually in the presence of Noggin). The inventors also compared the mRNA levels of these markers in pancreatic organoids by adding Noggin to or removing Noggin from the culture, respectively. Specifically, one sample of pancreatic organoids was cultured in EGFRA medium, then Noggin was added, and the organoids were cultured for an additional 2 or 4 days. Another sample of pancreatic organoids was cultured in EGFRAN medium, then Noggin was removed, and the organoids were cultured for an additional 2 or 4 days. Gene expression wa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com