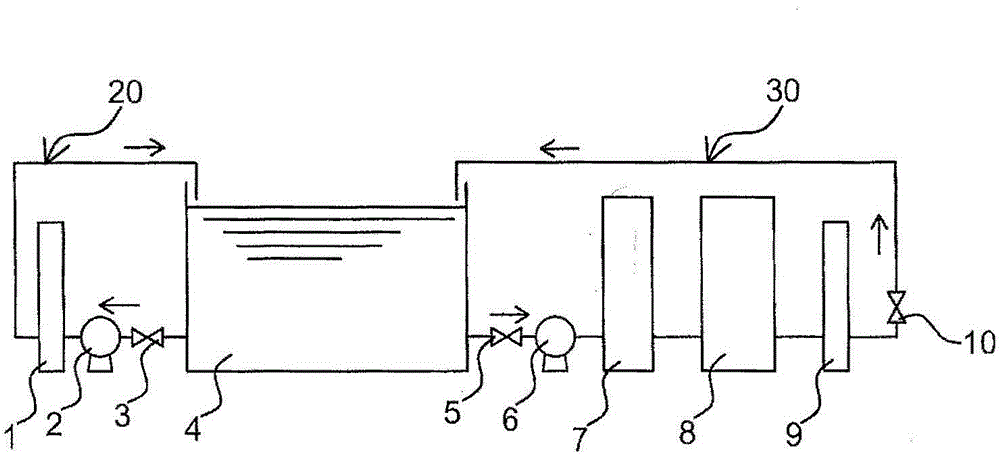
Eliminating device for rare earth impurity in nickel plating solution
A technology of nickel electroplating solution and rare earth impurities, applied in the direction of electrolysis process, electrolysis components, cells, etc., can solve the problems of inefficiency, equipment, complicated operation, etc., and achieve the effect of stable quality and plating treatment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example 1
[0098] A plating solution having a composition of 250 g / L of nickel sulfate, 50 g / L of nickel chloride, and 45 g / L of boric acid and pH 4.5 was heated to 50° C., and nickel plating was performed on the surface of the R—Fe—B based sintered magnet. R-Fe-B-based sintered magnets use a variety of magnets whose composition is adjusted within the following ranges according to the required magnetic properties, namely Nd: 15-25mass%, Pr: 4-7mass%, Dy: 0-10mass%, B: 0.6 mass%~1.8mass%, Al: 0.07~1.2mass%, the balance is Fe, Cu and Ga below 3mass%. However, the composition of the magnets used in one batch is the same composition.
[0099] It should be noted that the respective compositions and amounts of rare earth impurities dissolved in the plating solution depend on the combination of magnets used for plating, the treatment method such as barrel plating or rack plating, and the composition of the plating solution. different.
[0100] After several days of plating treatment, the nick...
experiment example 2
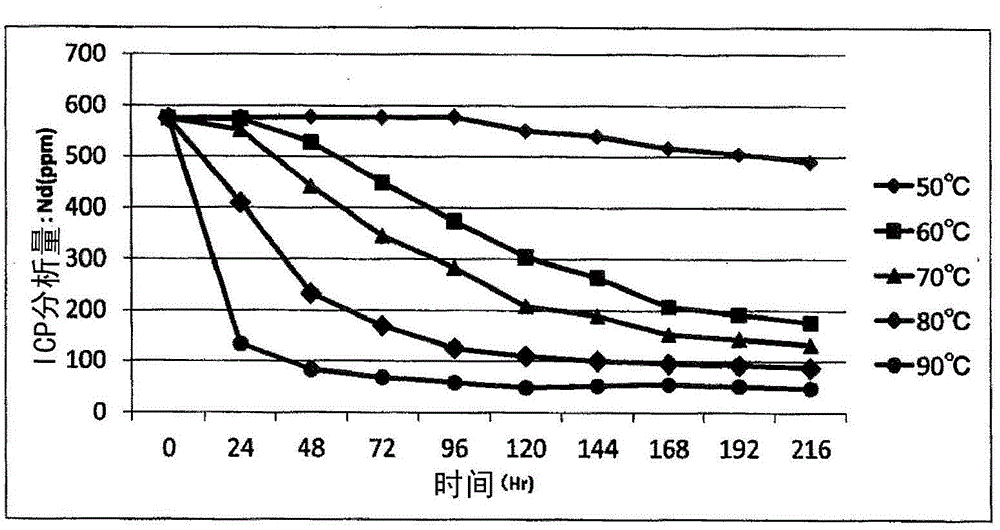
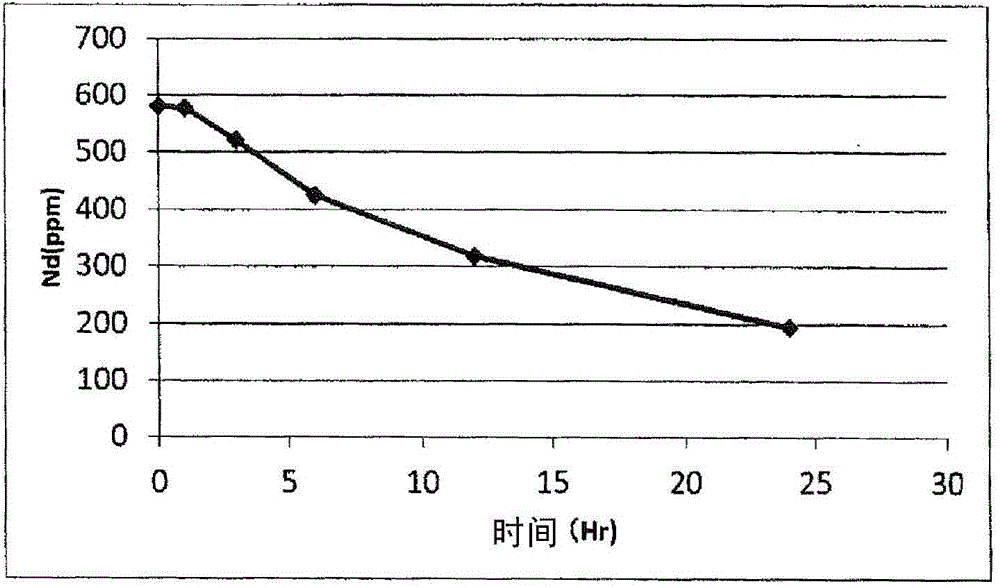
[0109] With the composition of nickel sulfate 250g / L, nickel chloride 50g / L, boric acid 45g / L, the plating solution of pH4.5 is heated to 50 ℃, in R-Fe-B base sintered magnet (using the same as embodiment 1 The composition range of magnets) is nickel-plated on the surface. After several days of plating treatment, the Nd impurity in the nickel plating solution was analyzed and found to be 576 ppm.
[0110] The heating temperature is set to 6 conditions from 50°C to 95°C (wherein 50°C to 90°C, there are 5 conditions in increments of 10°C), and the plating solution is taken to 3 liters at each condition in a beaker and heated. Stir with a magnetic stirrer (magnetic stirrer) while heating. Water was added during heating to keep the concentration of the plating solution constant. In addition, a sufficient amount of plating solution for ICP emission analysis was taken at certain time intervals, and the taken plating solution was cooled and filtered with filter paper, and then the...
experiment example 3
[0119] In Experimental Example 1 and Experimental Example 2, the plating solution after heat treatment was cooled and filtered with filter paper, and the deposited precipitate was recovered from the plating solution.
[0120] The precipitate was dried with a constant temperature bath. The properties are powder (solid).
[0121] The precipitates were analyzed using an energy dispersive X-ray analyzer (EDX), as follows:
[0122] Nd: 32.532, Pr: 11.967, Dy: 1.581, Al: 0.402, Ni: 7.986, C: 0.319, O: 45.213 (mass%).
[0123] It was confirmed that the rare earth impurities in the plating solution were precipitated from the plating solution in the form of powder (solid) by heat treatment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com