Five-freedom-degree auxiliary lens adjusting mechanism of astronomical telescope working in extreme environment
A technology for astronomical telescopes and adjustment mechanisms, applied to telescopes, optics, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as difficult control, mutual interference, and small lateral load of six-bar mechanism, and achieve the effects of improving motion accuracy, easy control, and convenient calculation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
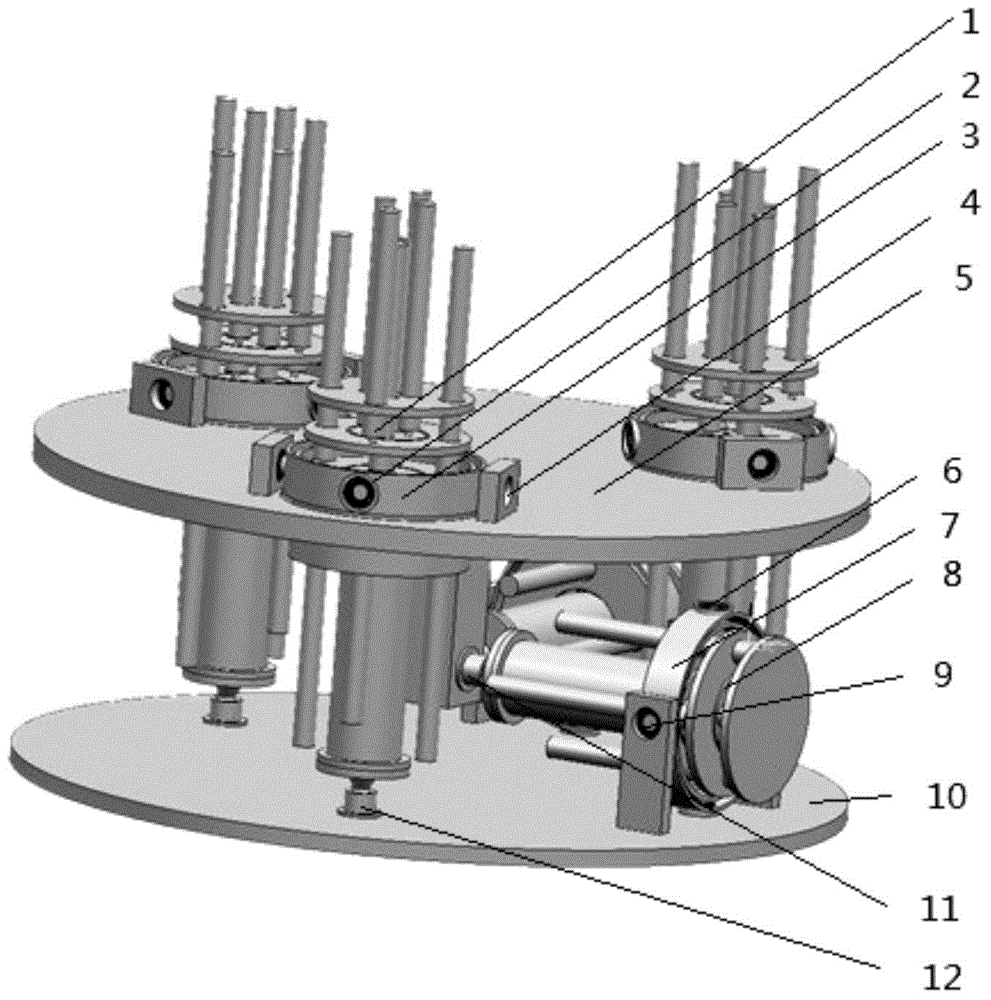
[0018] Example 1, figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the mechanism of an embodiment of the present invention, including a static platform, a moving platform, a first piezoelectric ceramic drive rod, a second piezoelectric ceramic drive rod, a third piezoelectric ceramic drive rod, and a fourth piezoelectric ceramic drive rod , the fifth piezoelectric ceramic driving rod.
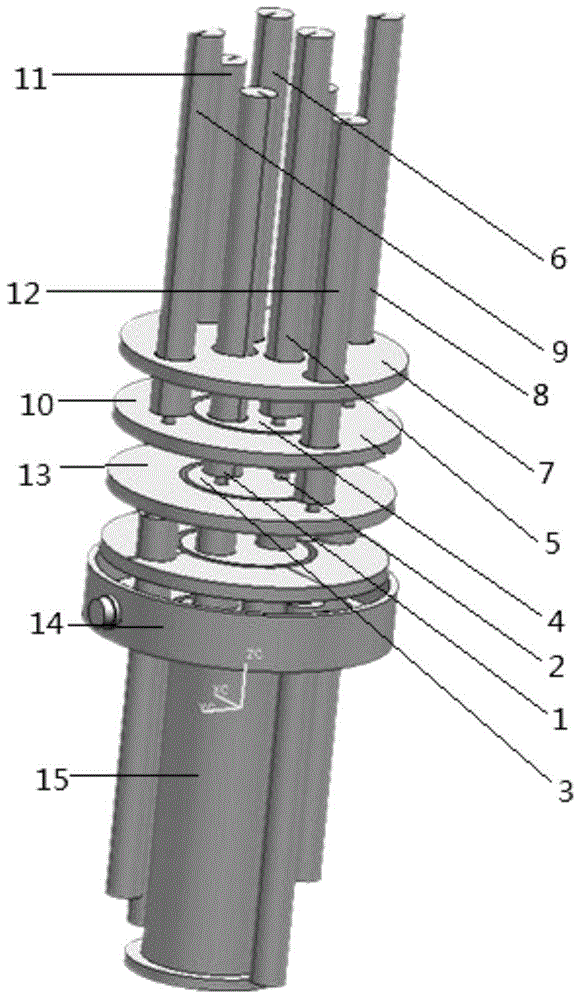
[0019] One end of the first piezoceramic drive rod group 1 is connected to an engagement mechanism 3 through a pair of bearings 2, and the engagement mechanism 3 is connected to a static platform 5 through another pair of bearings 4 perpendicular to the bearings 2, and the first piezoceramic drive The other end of the rod group is connected with the moving platform 10 through a ball joint 12 . The piezoelectric ceramic driving rod is extended and shortened to drive the moving platform to move.
[0020] Similarly, the second piezoelectric ceramic driving rod group, the third piezoelectric ceramic drivin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com