Control device and method for ac rotary electrical machine, and electrical power steering device
A technology of rotating motors and control devices, which is applied in the field of control and can solve problems such as the inability to maintain smooth rotation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
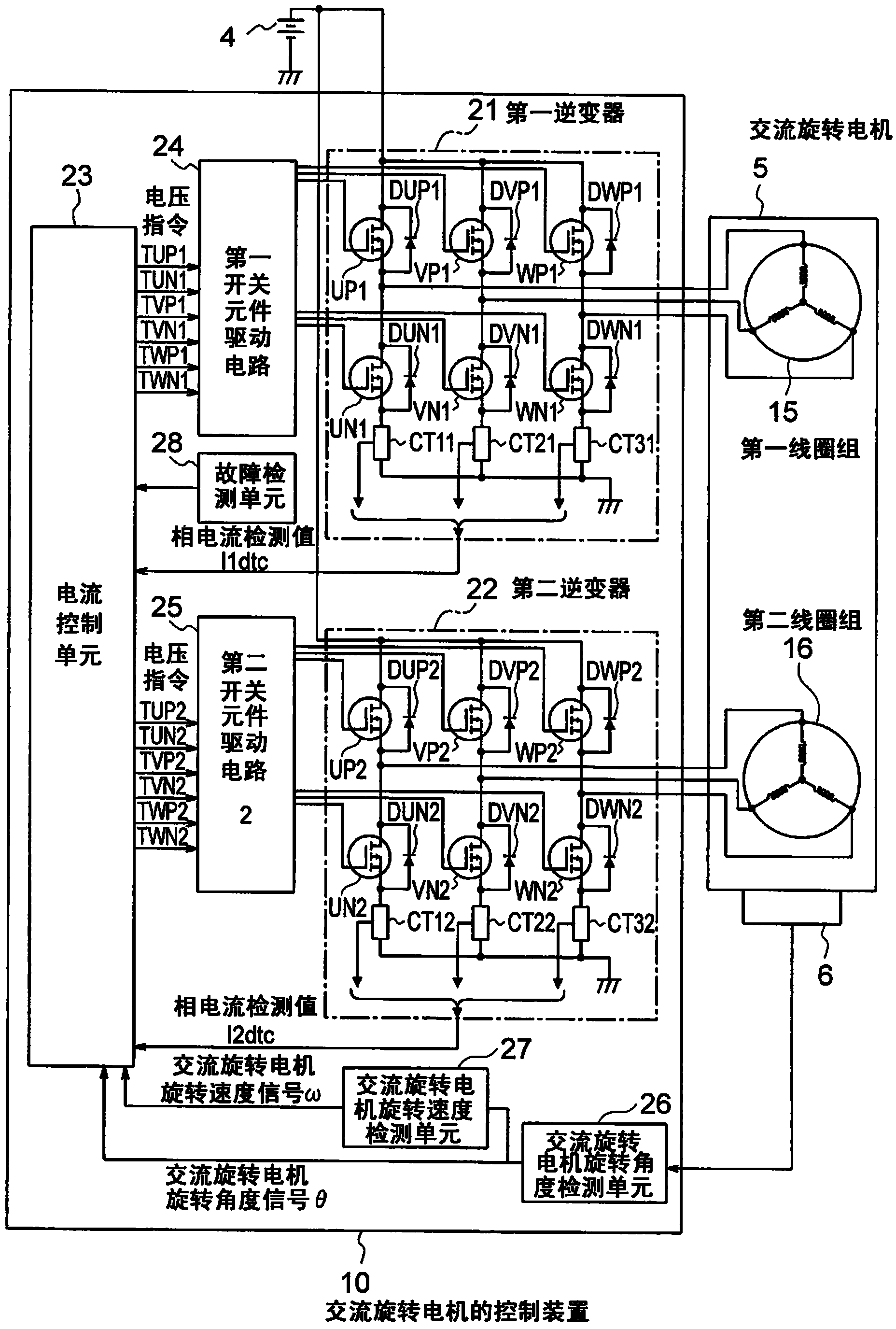
[0037] figure 1 It is a schematic block diagram showing an example of the overall configuration common to each embodiment of the control device for the AC rotating electric machine of the present invention. In addition, in addition to the control device 10 for the AC rotating electric machine, a power source 4, an AC rotating electric machine 5, and an AC rotating electric machine rotation angle sensor 6 that detects the rotation angle of the AC rotating electric machine 5 are also described.
[0038] The AC rotating electrical machine 5 includes a first coil group 15 composed of three phases: U1 phase, V1 phase, and W1 phase, and a second coil group 16 composed of three phases: U2 phase, V2 phase, and W2 phase. Each coil group is individually Combine phases with star connection. These multiple coil groups constitute a stator (not shown), and the AC rotating electric machine 5 is constituted by the stator, a rotor (not shown), and a rotating shaft fixed to the rotor. In addition...
Embodiment approach 2
[0062] The overall structure of the control device of the AC rotating electrical machine in the second embodiment of the present invention is figure 1 the same. Taking a case where a short-circuit fault occurs on the low potential side of the W1 phase of the first coil drive system as an example, the operation of this embodiment will be described. Here, when both the first inverter 21 and the second inverter 22 are normal, the first coil group 15 and the second coil group 16 generate the same output torque.
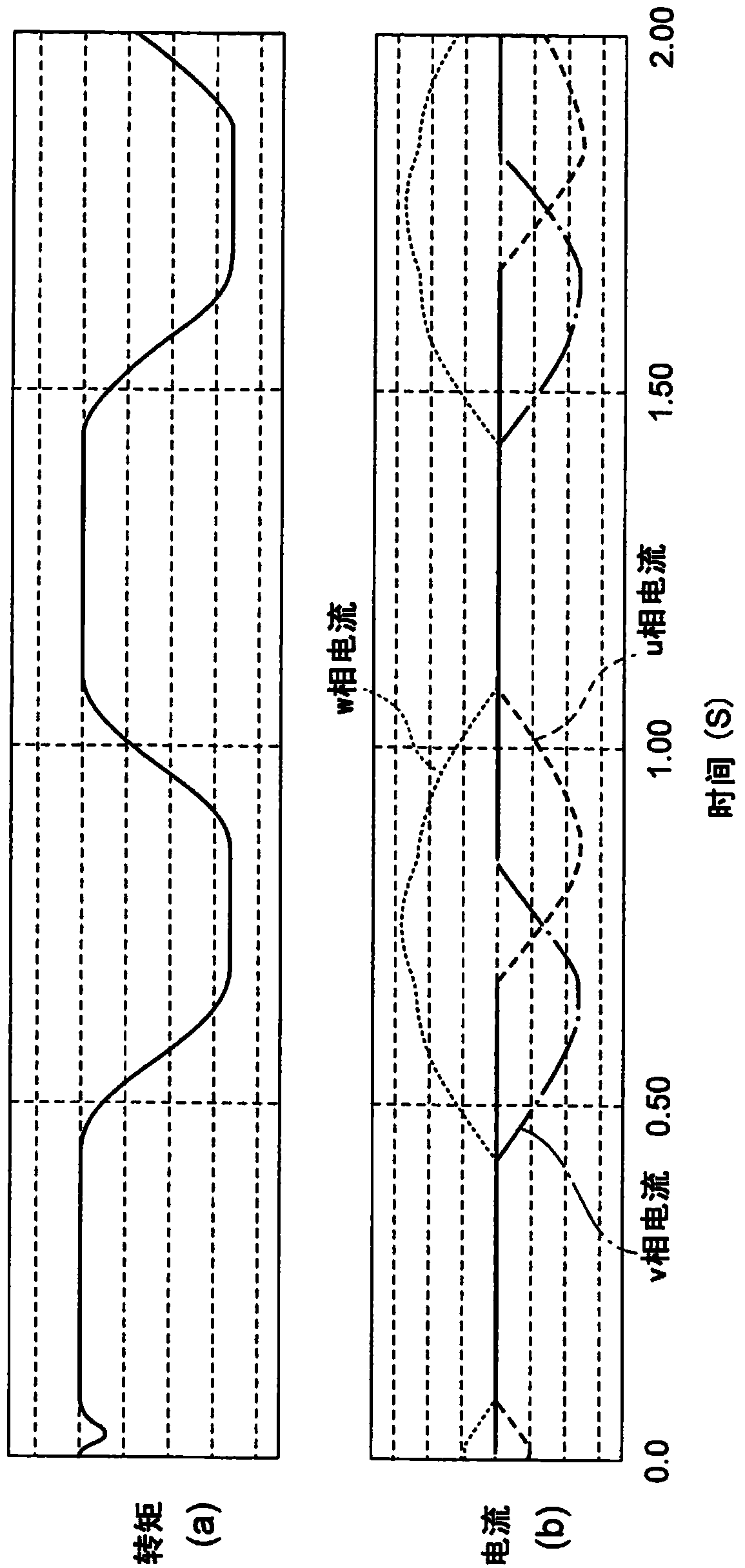
[0063] At this time, the switching element WN1 located in the first inverter 21 is always in an on state. When switching elements other than WN1, namely UP1, UN1, VP1, VN1, and WP1 are turned off, an induced voltage will be generated in the first coil group 15. As a result, the first coil group 15 will flow Figure 7 (b) That kind of current. Figure 7 (a)(b) is a diagram showing the relationship between the elapsed time, torque and current when a short-circuit fault occurs ...
Embodiment approach 3
[0068] The overall structure of the control device of the AC rotating electric machine in the third embodiment of the present invention is figure 1 the same. The operation of this embodiment will be described by taking the case where an open fault occurs on the high potential side of the W1 phase of the first coil drive system as an example. Here, when both the first inverter 21 and the second inverter 22 are normal, the first coil group 15 and the second coil group 16 generate the same output torque.
[0069] At this time, the switching element WP1 located in the first inverter 21 is always in the off state. When the switching elements other than WP1, that is, UP1, UN1, VP1, VN1, and WN1 are turned off, no current flows through the first coil group 15 and no braking torque is generated.
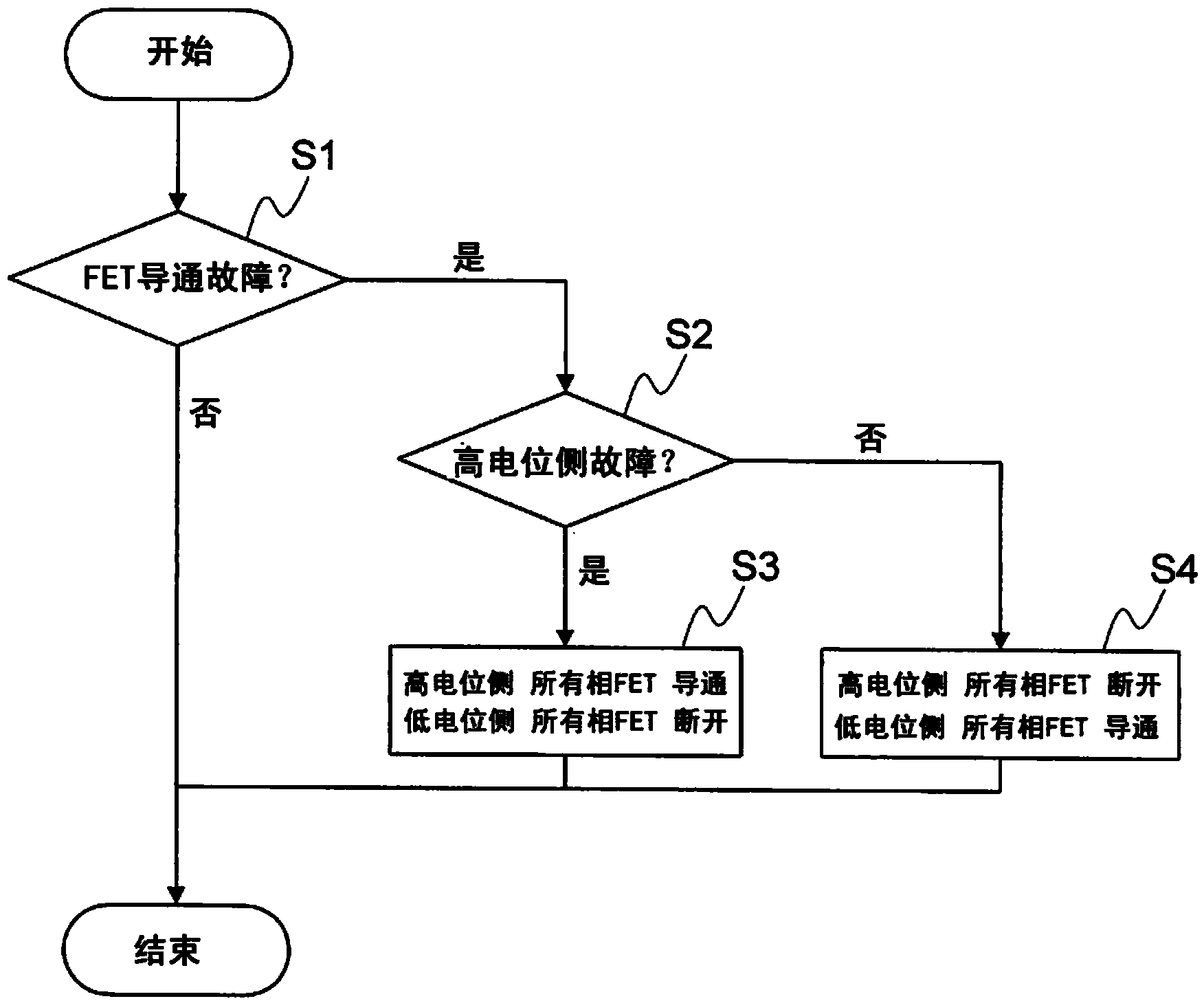
[0070] Figure 8 Shows the operation flowchart of the control of the current control unit 23. The current control unit 23 implements Figure 8 The control of the control flow shown produces a co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com