Substrate and base plate separation process, sacrificial layer and flexible display device and production process thereof
A flexible display and sacrificial layer technology, applied in the manufacture of semiconductor/solid-state devices, electric solid-state devices, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problem of easily damaged electronic devices, high temperature resistance of viscous materials, poor drug resistance, limited type of substrate application scope, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of low cost, no impact on device performance, fast device performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] A substrate and substrate separation process for the preparation of a flexible display device, comprising the following steps:
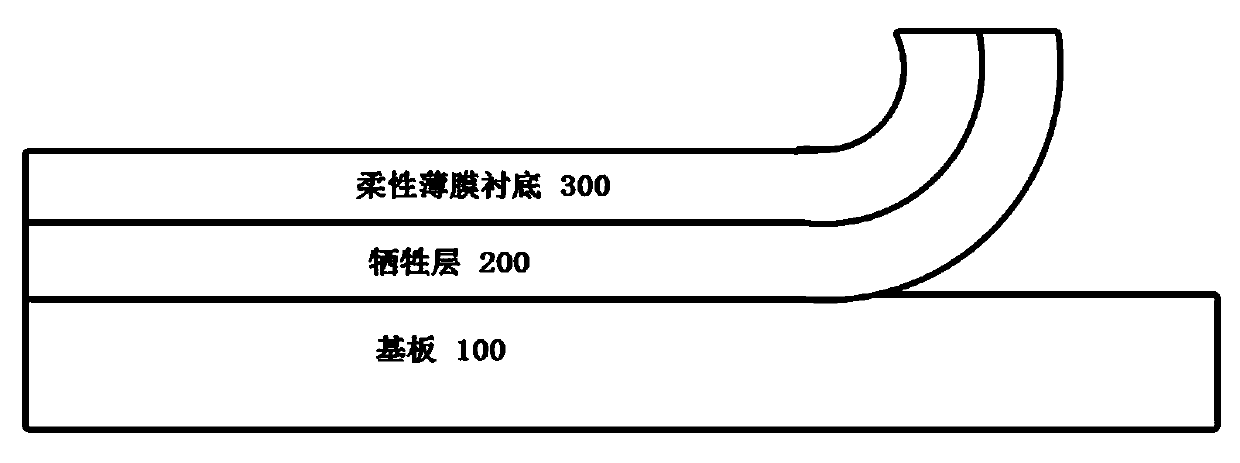
[0055] (1) Prepare a sacrificial layer 200 on the substrate 100, and the sacrificial layer 200 is a carbon thin film.
[0056] The substrate 100 is a hard material, which can be made of glass, metal, plastic and fiber, or it can be a substrate 100 based on the above materials with a buffer layer.
[0057] Wherein, the simple carbon film is any one or more than one of amorphous carbon film, carbon nanotube film, graphene film, fullerene film or diamond-like film.
[0058]The thickness of the sacrificial layer 200 is 1nm-1000nm, and the sacrificial layer 200 is prepared by any one of chemical vapor deposition, physical vapor deposition or solution processing.
[0059] (2) Prepare the flexible film substrate 300 on the sacrificial layer 200 .
[0060] The material of the flexible film substrate 300 can be polyimide (Polyimide, PI), polyethylen...
Embodiment 2
[0071] A substrate and substrate separation process for the preparation of a flexible display device, other features are the same as in Embodiment 1, the difference is that it also has the following features:
[0072] Step (2) of this embodiment prepares a flexible film substrate 300, so that the flexible film substrate 300 completely covers the sacrificial layer 200 to form a partial covering body 400, and the prepared structure is as follows figure 2 shown. The flexible film substrate 300 should completely cover the sacrificial layer 200 , the area of the flexible film substrate 300 is larger than that of the sacrificial layer 200 , and the flexible film substrate 300 is in direct contact with the substrate 100 outside the edge of the sacrificial layer 200 . This structure can improve the adhesion of the flexible film substrate 300 and the sacrificial layer 200 to the substrate 100, and reduce the chance of accidental dissociation of the flexible substrate during the devi...
Embodiment 3
[0081] A substrate and substrate separation process for the preparation of a flexible display device, other features are the same as in Embodiment 1, the difference is that it also has the following features, the process specifically includes the following steps:
[0082] (1) Prepare the sacrificial layer 200 on the substrate 100 to form the first body 500 .
[0083] (2) Prepare the flexible film substrate 300, so that the flexible film substrate 300 completely covers the outer surface of the first body 500 to form a fully covered body 600, such as Figure 5 shown.
[0084] (3) Electronic components are prepared on the flexible film substrate on the side close to the sacrificial layer 200, and the flexible film substrate on the side close to the sacrificial layer 200 refers to Figure 5 Side A in . (4) Detaching the flexible film substrate 300 from the substrate 100 to obtain a finished flexible display device.
[0085] Step (4) specifically includes, such as Image 6 as s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com