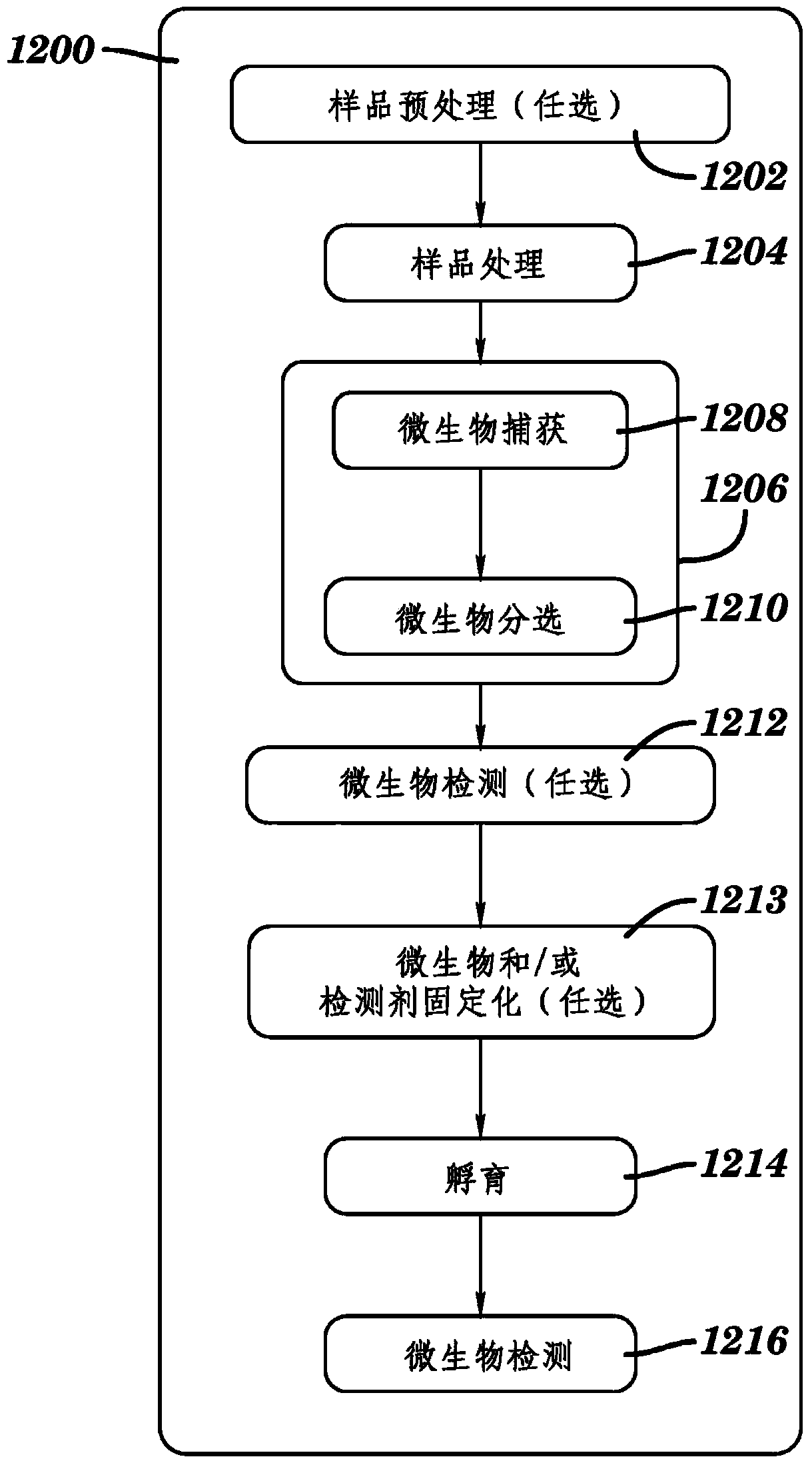
Rapid antibiotic susceptibility testing
一种抗生素、药敏的技术,应用在抗生素药敏性的快速测试领域
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0438] Example 1 - Rapid Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing Based on Magnetic Sorting and Microscopy
[0439] Bacteremia, a condition also known as bacterial sepsis or blood poisoning, which describes a bacterial infection of a patient's blood, is a major killer in the United States and worldwide. Worldwide, there are 18 million cases of sepsis each year, resulting in more than 6 million deaths; in the United States alone, there are 750,000 cases a year, resulting in more than 200,000 deaths. When doctors suspect a patient has bacteremia, they must act quickly: Because bacteria can divide so rapidly, every hour lost before the right treatment is given can make a substantial difference in patient outcomes. So doctors must quickly answer two questions: whether the patient does have bacteremia, and if so, what antibiotics to prescribe. Unfortunately, existing methods for answering these questions (blood culture) take two days or more to get an answer, which often proves to be too...
Embodiment 2
[0450] Example 2 - Rapid Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing Based on Magnetic Sorting and ELISA
[0451] The inventors developed methods for the rapid isolation, detection and determination of antibiotic susceptibility for bacteremia or other microbial infections using magnetic sorting and ELISA / metabolic readout. This provides a technique for detecting bacteremia and determining the antibiotic resistance profile of causative agents in hours or less.
[0452] In general, the method involves: (i) extracting and concentrating pathogens from blood using functionalized magnetic beads; (ii) dividing pathogens into subsamples and incubating with antibiotic-supplemented medium (not for ELISA). Yeast extract-containing media, or other media for luciferase-based assays); and (iii) luciferase detection assays using ELISA assays (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays) or ATP production method (e.g. BACTITER-GLO from Promega (Cat No. G8230) TM microbial cell viability assay) to detect patho...
Embodiment 3
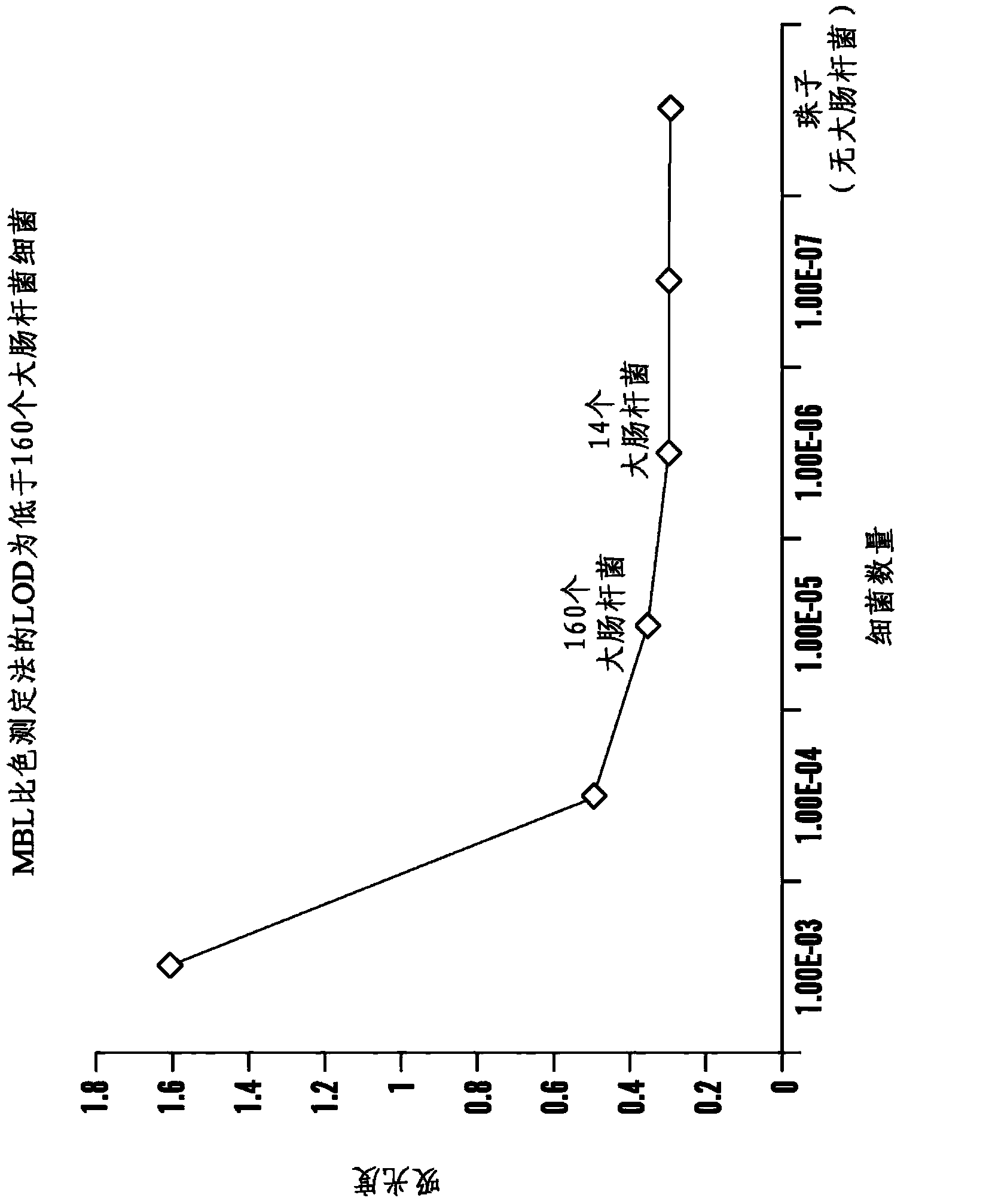
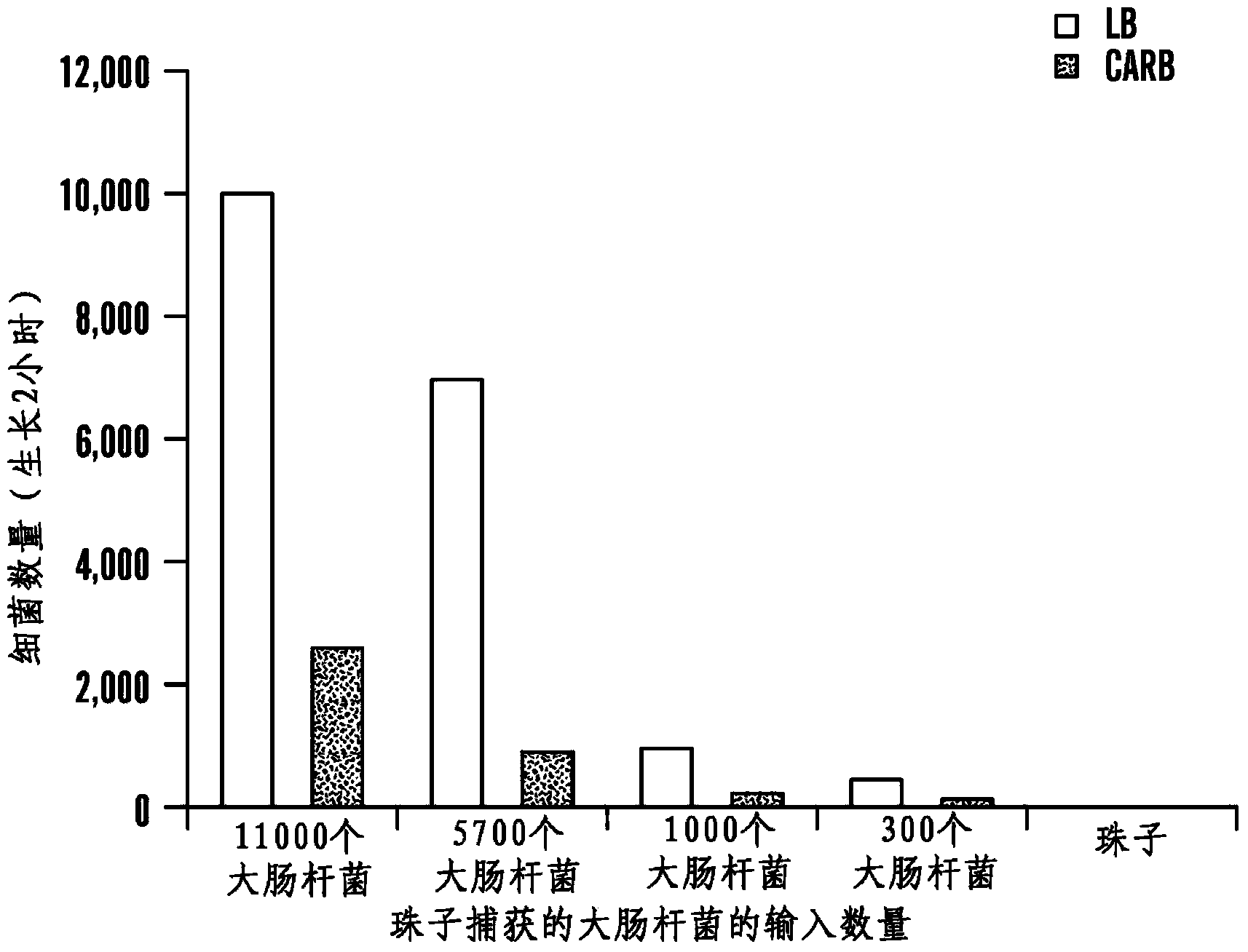
[0464] Example 3 - Plate Capture / Natural Growing Bacteria Can Produce Artificially Low Counts
[0465] Determine capture efficiency of Akt-FcMBL beads by plate count:
[0466] -5 μl Akt-FcMBL beads + 10 μl S. aureus or E. coli (1 mL TBST-Ca 2+ middle);
[0467] -Hula 10min;
[0468] - in TBST-Ca when on magnet 2+ 1 wash in medium.
[0469] count:
[0470] - Number of bacteria added (input), washed bead supernatant (uncaptured) and bead fraction (captured).
[0471] like Figure 8 As shown, plating bead fractions yields an artificially low readout of bacterial counts. Therefore, non-plated readouts (eg Fc-MBL ELISA, metabolic assays - ATP luminescence) may be more useful for measuring growth of bacteria isolated with Akt-FcMBL beads.
[0472] Without wishing to be bound by theory, the FcMBL beads bound all bacteria. However, they clump together so that standard techniques of plating and colony counting may not be feasible for quantification of captured pathogens, with ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com