A method and device for detecting abnormal chromosome structure
A technology for chromosomes and chromosome fragments, applied in the fields of genomics and bioinformatics, can solve problems such as probe design limitations, and achieve the effect of improving effectiveness and reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0019] According to one embodiment of the present invention, a method for detecting abnormal chromosome structure is provided, comprising the following steps:
[0020] Step1. Obtain the whole genome sequencing results of the target individual.
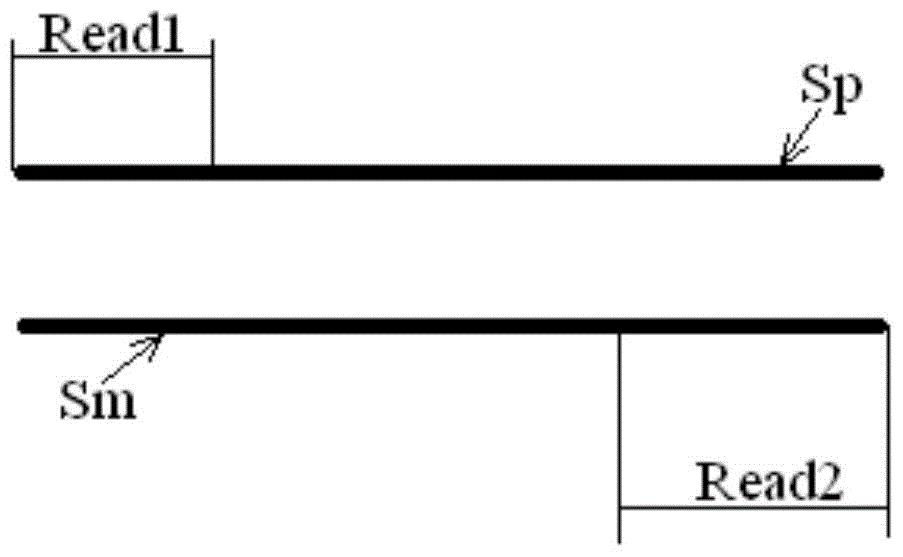
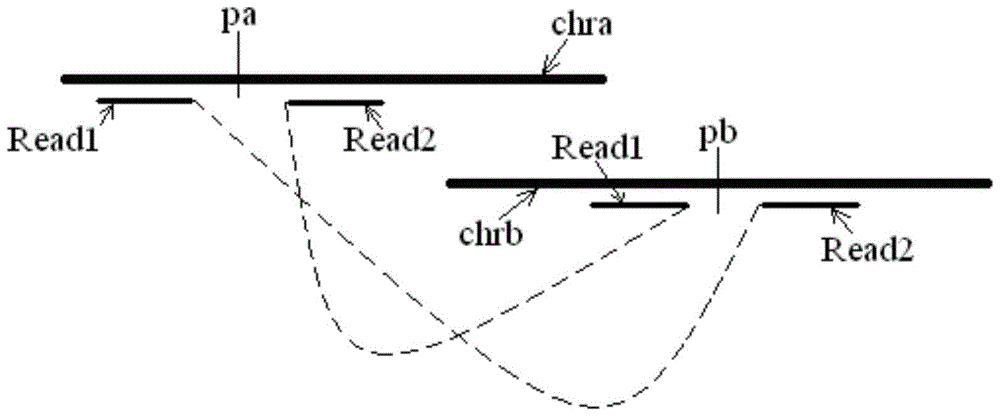
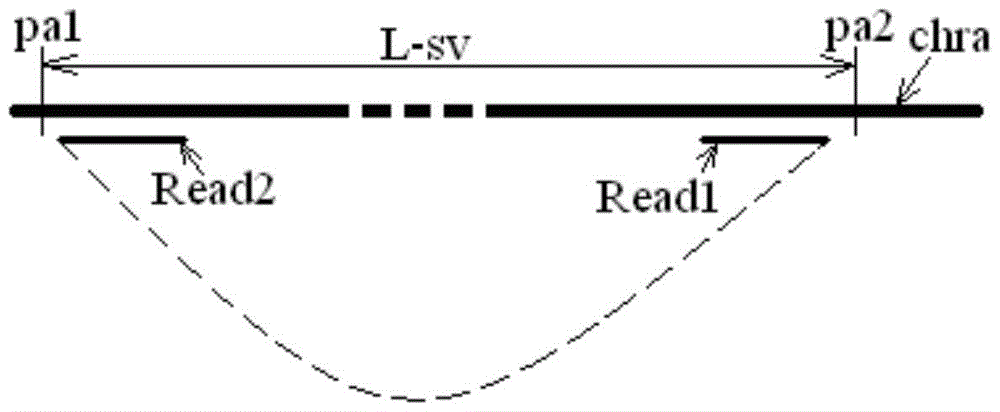
[0021] The sequencing results include paired read length pairs (also called "reads") Reads, each pair of Reads consists of two read length sequences, which are located at both ends of the measured chromosome segment, and each pair of Reads comes from the positive strand of the corresponding chromosome segment and negative strands, or, each pair of Reads comes from both the positive and negative strands of the corresponding chromosome segment.
[0022] The measured chromosome fragments are usually obtained by fragmenting the chromosome samples from the target individual, and the corresponding library (library) is prepared according to the selected sequencing method. The optional sequencing method includes but is not li...
experiment example 1
[0084] This case is a family study of cat-calling syndrome. The two target individuals in this example belong to a family, where "FA" means father and "SON" means son.
[0085] 1. Perform genome-wide low-multiplier sequencing on the two target individuals, in which the sequencing depth of "FA" is 2.2, and the sequencing depth of "SON" is 3.1.
[0086] 2. Then use the SOAP comparison software to compare the sequencing results of the two target individuals with the reference sequence HG19, and obtain two files FA.sin and SON.sin.
[0087] 3. Perform clustering, filtering and analysis processing on the two files FA.sin and SON.sin, and obtain the result clusters and related parameters output as follows:
[0088] "FA":
[0089] The numbers of the two chromosomes where the paired result cluster is located: chr12, chr5
[0090] The position range of the two ends of the paired result cluster: 14779615-14780233, 23314785-23314205
[0091] Spans at both ends of the paired result cl...
experiment example 2
[0108] This example is a congenital heart disease study. The target individual in this example is a patient with congenital heart disease, denoted by "XX".
[0109] 1. Sequence the entire genome with a low multiplier for the target individual, and the sequencing depth is 2.7.
[0110] 2. Then use the SOAP alignment software to compare the sequencing results with the reference sequence HG19 to obtain XX.sin.
[0111] 3. Perform clustering, filtering and analysis processing on XX.sin to obtain the result clusters and related parameters output as follows:
[0112] "XX":
[0113] The numbers of the two chromosomes where the paired result cluster is located: chr14, chr14
[0114] The position ranges of the two ends of the paired result cluster are 73557040-73557288, 73670432-73670682
[0115] Estimated repeat length: 113392
[0116] Spans at both ends of the paired result cluster: 248, 250
[0117] Number of Reads supporting the pair of result clusters: 4
[0118] Compactnes...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com