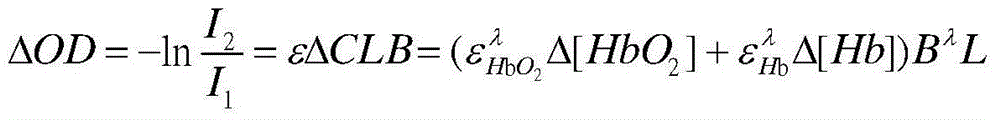Quick near-infrared brain-computer interface method
A brain-computer interface, near-infrared technology, applied in mechanical mode conversion, computer components, input/output of user/computer interaction, etc. lower problem
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
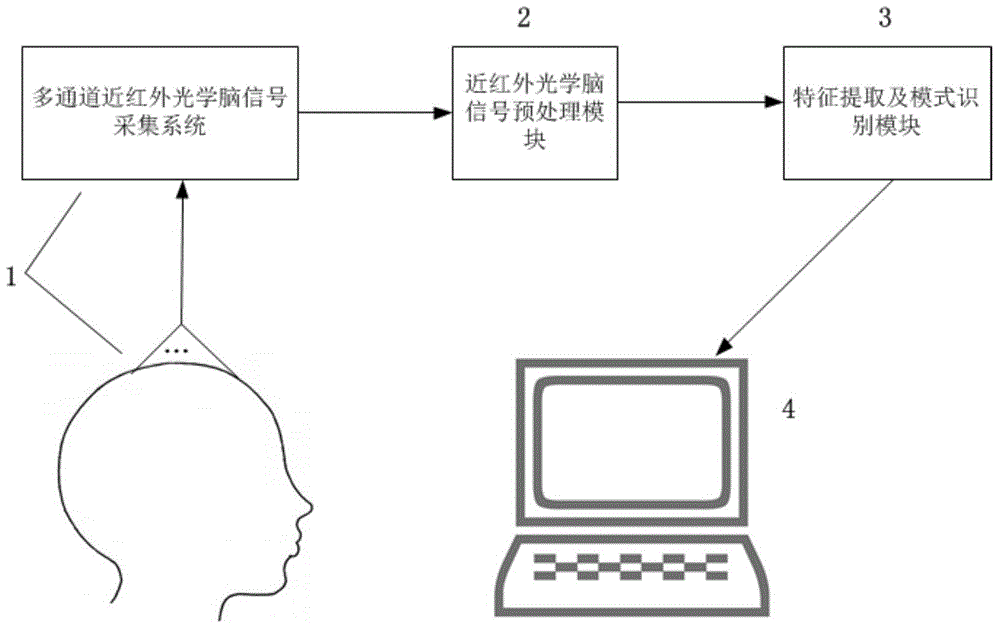
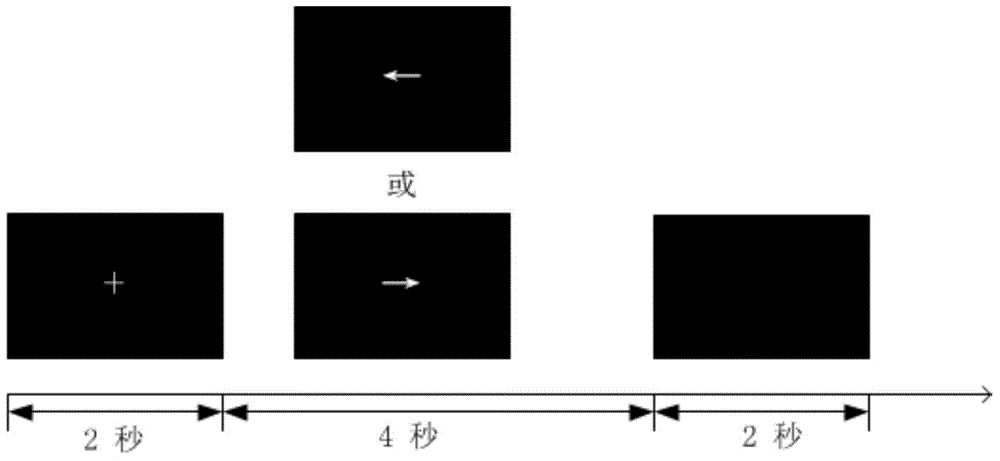
[0038] like figure 2 As shown, the user sits directly in front of the brain-computer interface task presentation interface 4, and completes the motor imagery task according to the interface prompts. The timing of each task is as follows: figure 2 shown. 2 seconds before each task, a "+" appears on the screen to remind the user that the task is about to start; in the next 4 seconds, an arrow pointing to the left or right appears randomly on the screen, and the user imagines the corresponding left or right side according to the direction of the arrow The movement of body parts; the screen is black for the last 2 seconds, and the user stops imagining and remains in a calm state of rest. The total duration of the entire task was 8 seconds, and the imagery task for each body part appeared randomly 50 times. After the multi-channel fast event-related near-infrared optical brain signal is collected by the multi-channel near-infrared optical brain signal acquisition system 1 when ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com