Bacterium for degrading herbicides and application thereof
A herbicide and fungicide technology, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve problems such as slow natural degradation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Example 1. Isolation and identification of Rhizobium sp. 198-L-30CGMCC No. 9864
[0045] 1. Isolation of herbicide-degrading bacteria 198-L-30
[0046] 1. Add 10g of soil sample (collected from farmland contaminated by herbicides in Heihe, Heilongjiang, China) into 100ml of sterile water, shake culture for 30min to make a turbid solution. Take 1ml of the above turbid solution and add it to a test tube containing 9ml of sterile water and mix well (at this time, the dilution is recorded as 10 -1 ), then draw 1ml from this test tube and add it to another test tube containing 9ml of sterile water and mix well, and so on to make 10 -2 , 10 -3 , 10 -4 , 10 -5 Bacterial suspensions of different dilutions. Take 0.1ml of each dilution and evenly spread it on a nitrogen-free solid medium plate, and incubate at a constant temperature of 28°C for 2-3 days. After the colonies are formed, the strains are purified on a nitrogen-free solid medium plate.
[0047] 2. The preliminary screening...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Example 2. Quantitative determination of Rhizobium sp. 198-L-30CGMCC No.9864 degradation ability
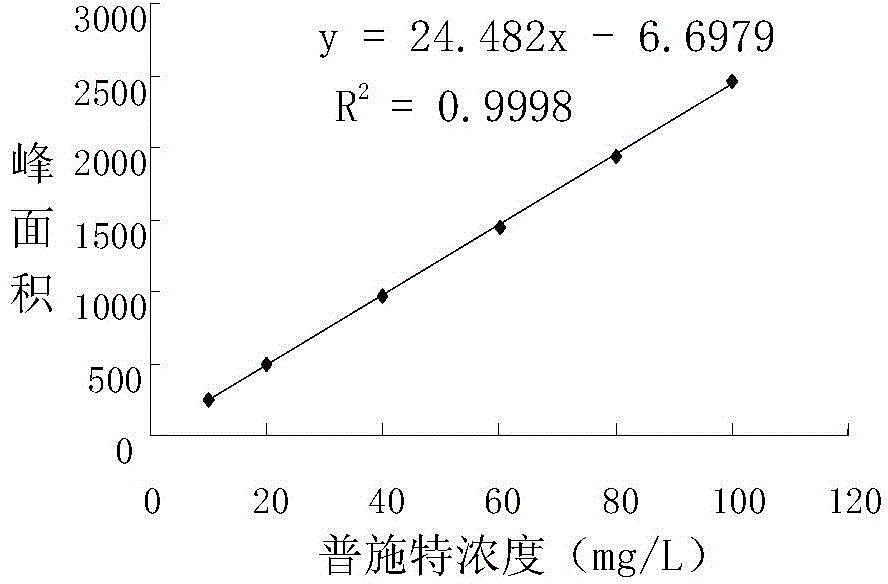
[0068] 1. Drawing of the standard curve of Pusite determination
[0069] Accurately weigh 10.0 mg of Pusite standard (product of Fluka) into a 10mL volumetric flask, dissolve it with a small amount of methanol, place the volumetric flask in an ultrasonic bath and shake for 10min, then dilute to 10mL with methanol, shake well, and mix 1000mg / L Pu Shite mother liquor. Continue to dilute with methanol to prepare 20, 40, 60, 80, 100 mg / L series of Pu Shite standard solutions. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was used to determine the peak area of different concentrations of Pursite standards, and the peak area was repeated 3 times. Use the Pste concentration as the abscissa and the peak area as the ordinate to draw the Pste standard curve, such as figure 1 Shown.
[0070] The detection conditions are as follows:
[0071] Detection system: Agilent 1100Series. Column...
Embodiment 3
[0081] Example 3. Quantitative determination of the ability of Rhizobium sp. 198-L-30CGMCC No. 9864 to degrade acetochlor
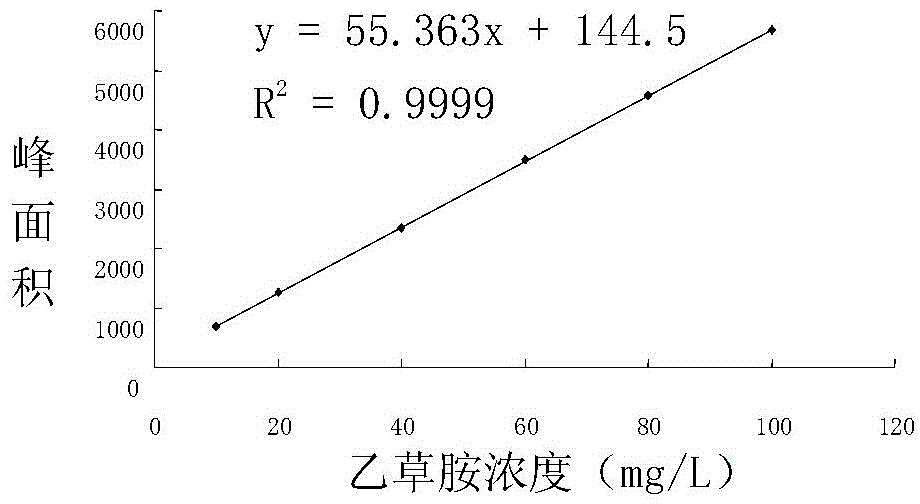
[0082] 1. Production of standard curve for acetochlor determination
[0083] Accurately weigh 10.0 mg of acetochlor standard (product of Fluka) into a 10 mL volumetric flask, dissolve it with a small amount of methanol, place the volumetric flask in an ultrasonic bath and shake for 10 minutes, then dilute to 10 mL with methanol, shake well, and mix 1000mg / L acetochlor mother liquor. Then it was diluted with methanol to obtain standard solutions with concentrations of 10, 20, 40, 60, 80, and 100 mg / L. High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was used to determine the peak areas of the standards of acetochlor at different concentrations, repeated three times. Using the concentration of acetochlor as the abscissa and the peak area as the ordinate, draw a standard curve of acetochlor, such as figure 2 Shown.
[0084] The detection conditions are as follows: ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com