Method for fixing soil heavy metals so as to protect groundwater
A technology for heavy metals and groundwater, applied in the field of fixing heavy metals in soil to protect groundwater, can solve the problems of poor water solubility and diffusivity of lime, improper treatment of leaching liquid, groundwater pollution, etc., and achieve the effects of low cost, low cost and environmental friendliness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] The method for fixing heavy metals in soil to protect groundwater according to the present invention is specifically: using potassium hydroxide (KOH) fixative to apply on the surface of heavy metal contaminated soil, and through irrigation and natural diffusion to achieve vertical penetration distribution, thereby forming Vertical alkaline fixation belt (medium alkaline fixation belt or high alkaline fixation belt) or formation of alkaline fixation belt (medium alkaline fixation belt or high alkaline fixation belt) in the lower layer of the soil to fix soil heavy metals to protect groundwater The purpose; wherein the amount of the potassium hydroxide fixative is 0.5-2kgm -2 .
[0026] The potassium hydroxide (KOH) selected in the present invention is a water-soluble alkaline substance with good diffusibility and can form a wide range of alkaline bands. The medium alkaline soil can fix heavy metals and reduce the mobility of heavy metals and plants. Effectiveness.
[0027] B...
Embodiment 2
[0031] The difference from Example 1 is that the sugarcane field ridges and furrows are tested to obtain the effect of applying KOH on soil pH at different depths. The specific conditions are as follows:
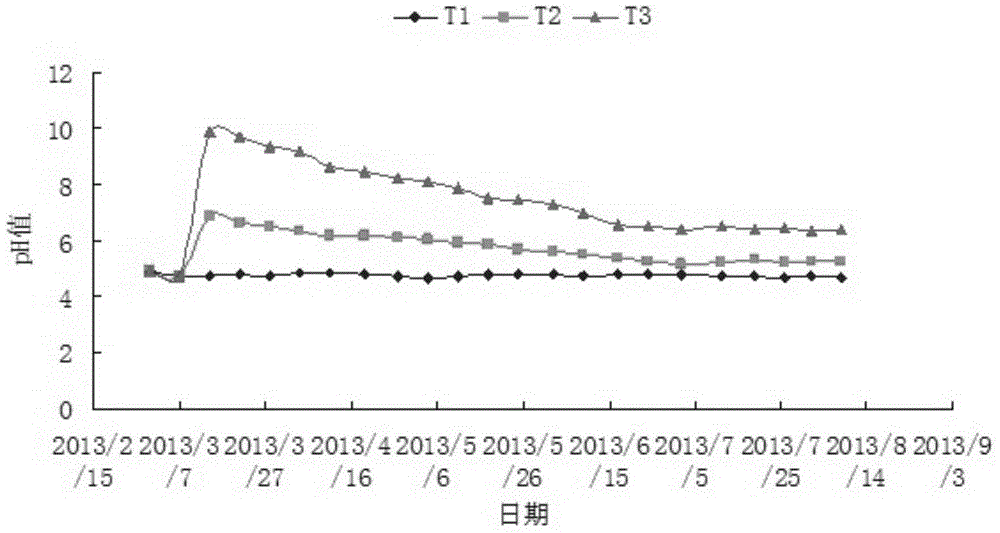
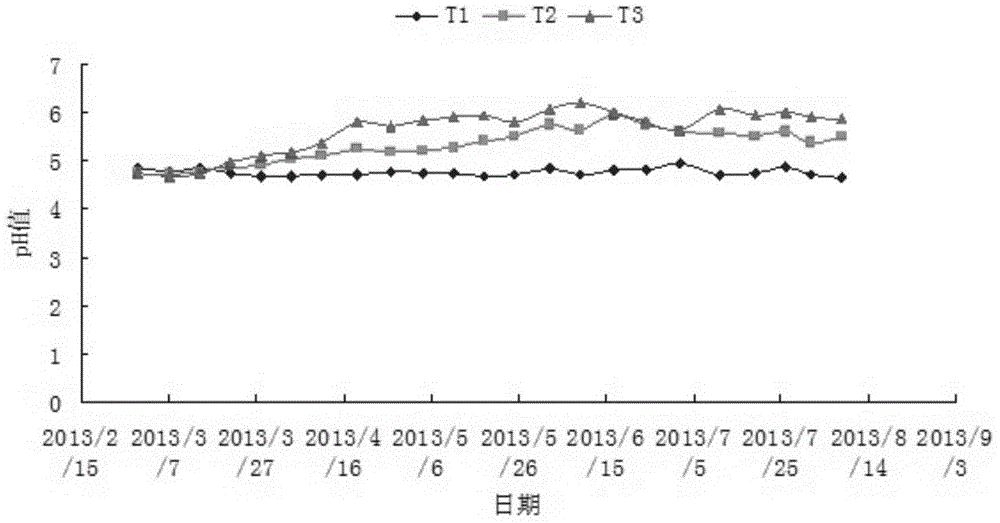
[0032] The experiment was conducted in a sugarcane field polluted by heavy metals. Choose 5 furrows in the sugarcane field, the ridge height is 45cm, the furrow length is 18m, and the width is 40cm. Sprinkle KOH 1kgm evenly in each furrow. -2 ; Another 3 ditches were selected without any treatment, as a blank control, irrigation water was introduced to make the test field in a flooded state for a period of time, and then the sugarcane was managed according to normal field management. During the test, soil samples are collected once a month, namely, 3 points are randomly selected in the ditch, the surface sampling depth is 0-20cm, and the deep soil samples (20-40cm) are collected with soil drills. The mixed soil samples at multiple points are about 1kg soil. kind. Take it back ...
Embodiment 3
[0035] The difference from Example 1 is the study of the influence of the diffusion of alkaline substances on the formation of alkaline barrier walls on groundwater. The details are as follows:
[0036] The test field is located in a farmland polluted by acid mine wastewater. The annual average temperature is 20.6°C and the annual average rainfall is 1694mm. It has a mid-subtropical monsoon climate. The basic physical and chemical properties of soil and heavy metal content are shown in Table 1 below.
[0037] Table 1 Basic physical and chemical properties of soil
[0038]
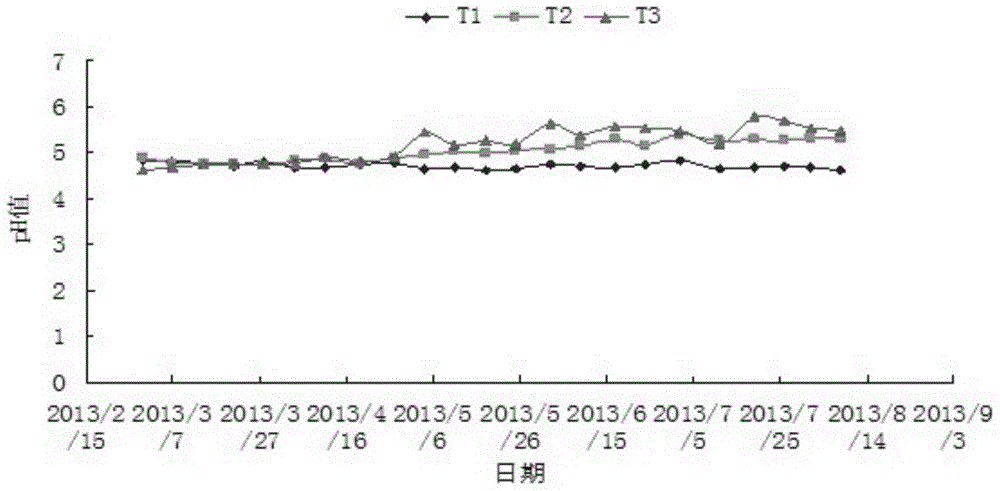
[0039] On November 7, 2012, 4 small wells with a diameter of 20cm and a depth of 1.5m were drilled around 2m from the main groundwater sampling well, such as image 3 As shown, 10kg KOH and 5kg lime are added to each small well, and water is added to diffuse the alkaline substances, hoping to form an alkaline barrier wall. The other main sampling well was not processed and served as a control well. On March 21, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com