Pedestrian navigation device and method based on inertial sensor
An inertial sensor and pedestrian navigation technology, applied in navigation, navigation through speed/acceleration measurement, measurement devices, etc., can solve the problems of low algorithm accuracy, limitations, and high computational complexity, and achieve high application value and accuracy The effect of high and low computational complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0053] The technical solution of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
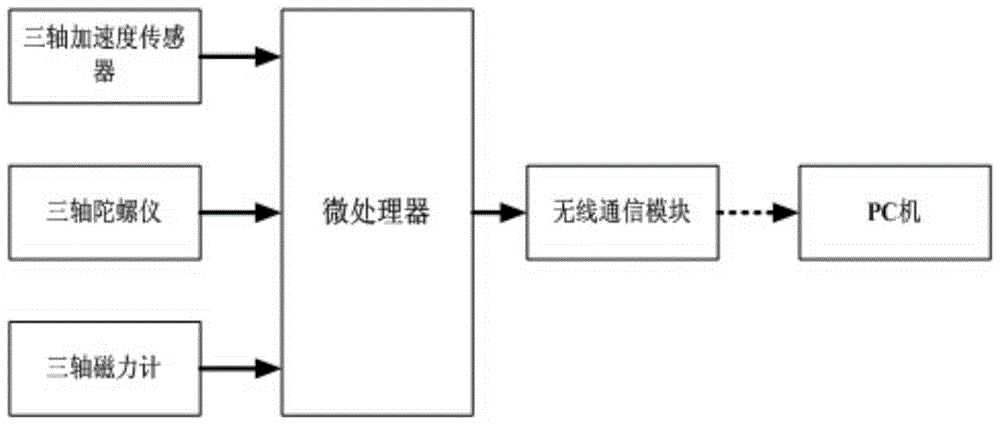
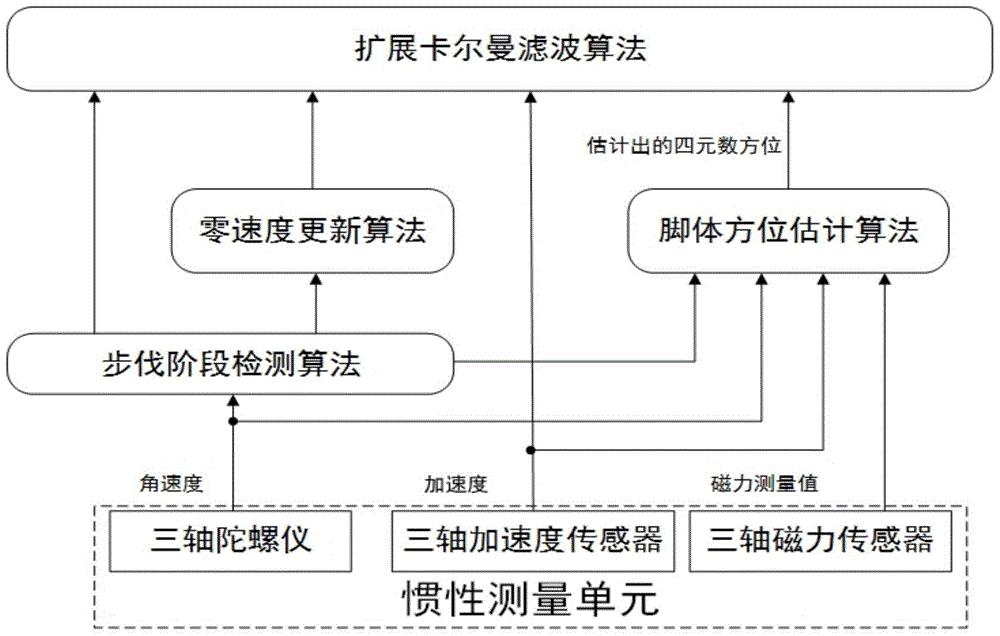
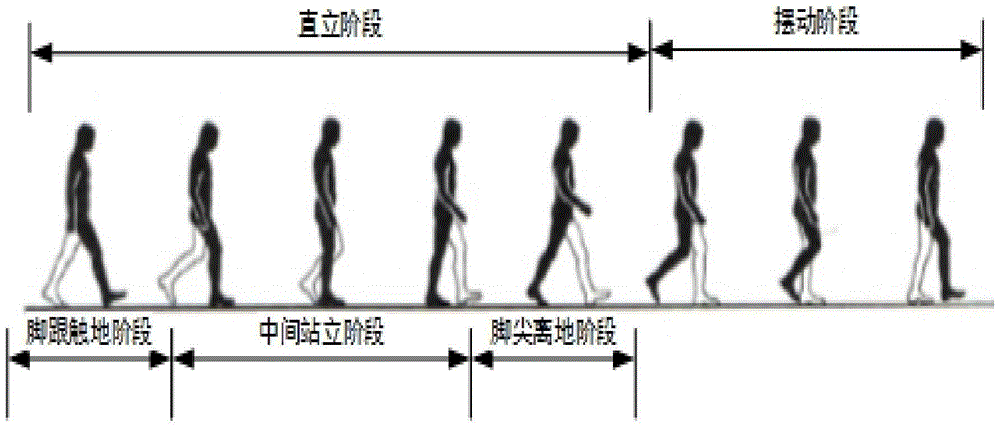
[0054] Such as figure 1 The system structure block diagram of the present invention is shown. A pedestrian navigation device based on inertial sensors includes a microprocessor and a three-axis acceleration sensor, a three-axis gyroscope, a three-axis magnetometer, and a wireless communication module connected to it. The micro-processing The receiver receives the data collected by the three-axis acceleration sensor, the three-axis gyroscope and the three-axis magnetometer, and uploads these data to the PC through the wireless communication module. In this embodiment, the three-axis acceleration sensor uses Freescale’s MMA7361, the three-axis gyroscope uses InvenSense’s 500 series, the three-axis magnetometer uses Honeywell’s HMC5842, and the wireless communication module uses ZigBee / IEEE 802.15.4 technology. The low power consumption radio fre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com