Method for preparing porous glass ceramics by waste glass through low-temperature melting and high temperature foaming
A porous glass-ceramic and high-temperature foaming technology, which is applied in glass manufacturing equipment, glass molding, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of inability to control the mechanical and thermal conductivity of porous glass-ceramic, poor uniformity of pore size, opening and closing Pore mixing and other problems, to achieve the effect of environmental protection, energy saving, high value-added utilization, controllable pore size, and controllable porosity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
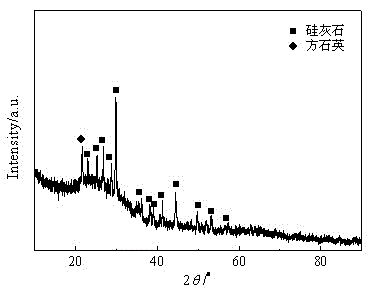
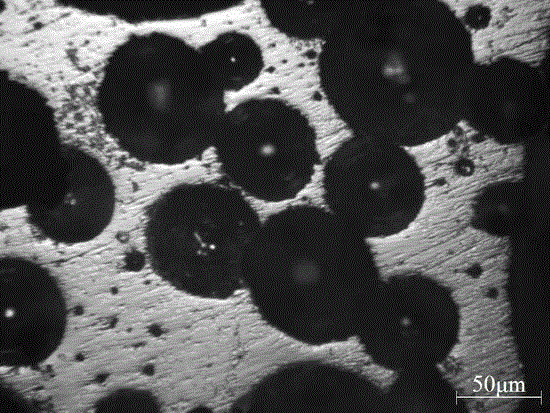
[0026] Crush and finely grind architectural glass plates into 45-120 micron glass powder, add 5% boric acid, 2% cryolite, 1% SiC and 3% CaCO 3 , after ball milling and mixing evenly, the mixed powder is evenly spread in a porcelain boat coated with alumina powder, and directly put into a rapid heating furnace that has been heated to 800°C. After constant temperature for 30 minutes, heat up to 980°C for 30 minutes , then lower the temperature to 650 ° C, keep the temperature constant for 60 minutes, and cool to room temperature with the furnace to obtain porous glass-ceramics. The results of crystal structure and optical microstructure analysis show that the main crystal phase in porous glass-ceramics is wollastonite and a small amount of cristobalite, and contains a large amount of glass phase (attached figure 1 ), the pore size is 50-100 microns (attached figure 2 ).
Embodiment 2
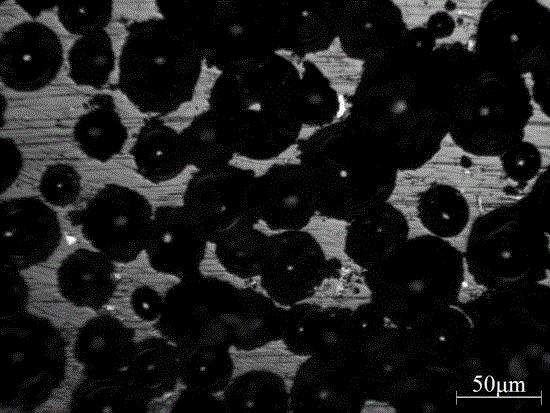
[0028] Crush and finely grind the glass plate of the fluorescent tube into a glass powder of 45-120 microns, add boric acid with a mass content of 8%, 4% V 2 o 5 and 5% CaCO 3 , after ball milling and mixing evenly, the mixed powder is evenly spread in a porcelain boat coated with alumina powder, and directly put into a rapid heating furnace that has been heated to 750°C. After 30 minutes of constant temperature, the temperature is raised to 900°C for 10 minutes. , then lower the temperature to 650 ° C, keep the temperature constant for 60 minutes, and cool to room temperature with the furnace to obtain porous glass-ceramics. The crystal structure test analysis shows that the sample is wollastonite containing a large amount of glass phase, and the pore size is 20-50 microns (attached image 3 ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com