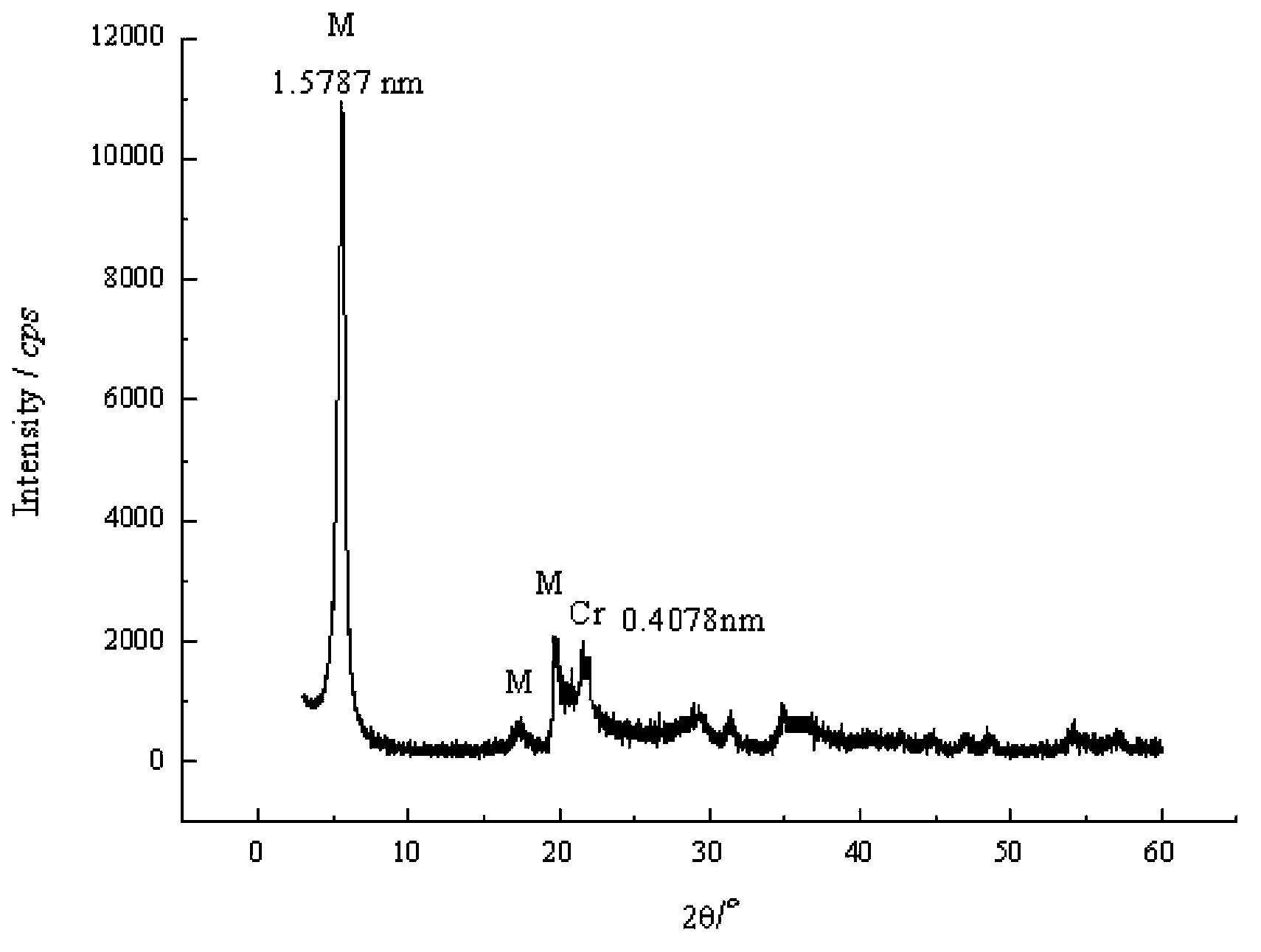
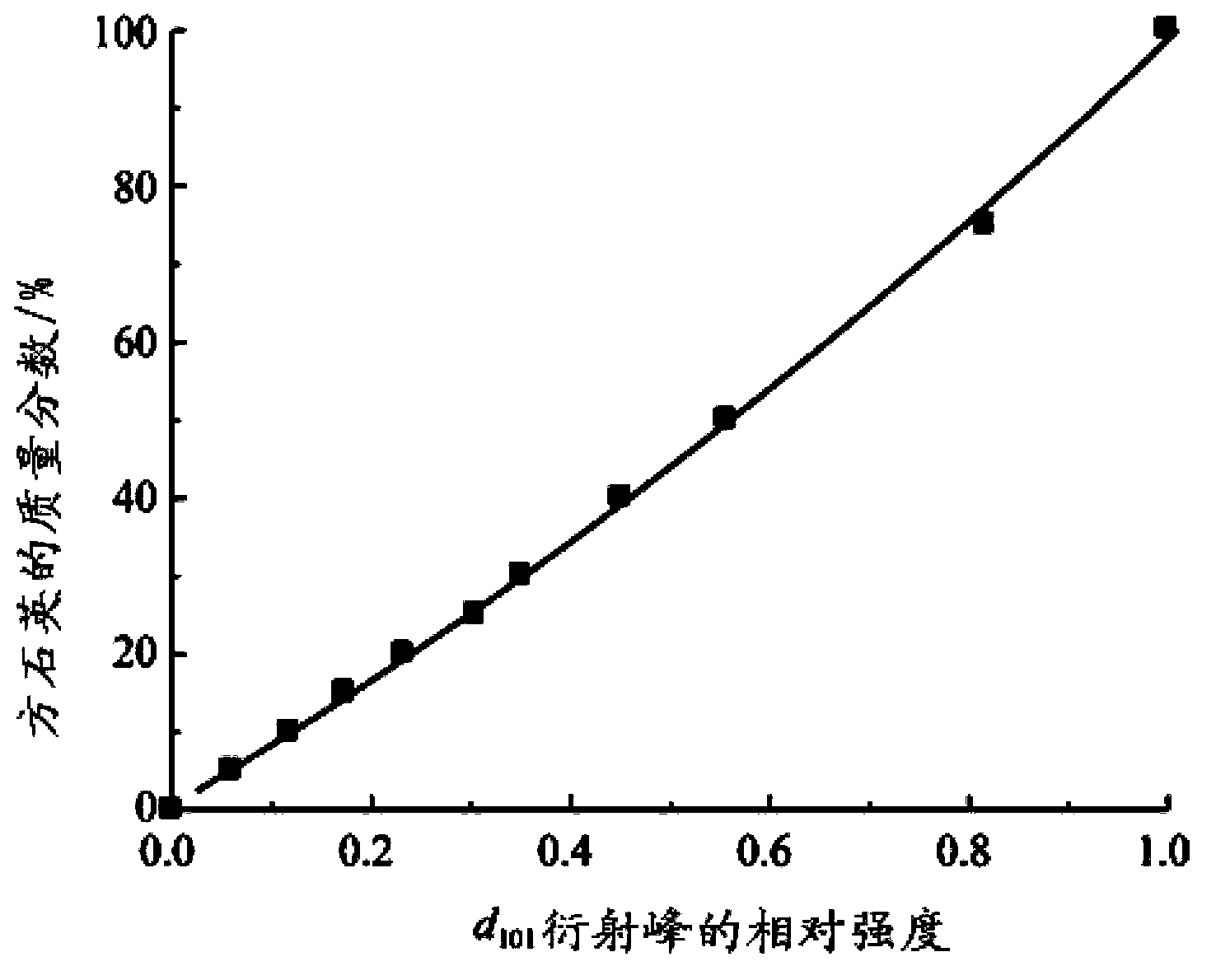
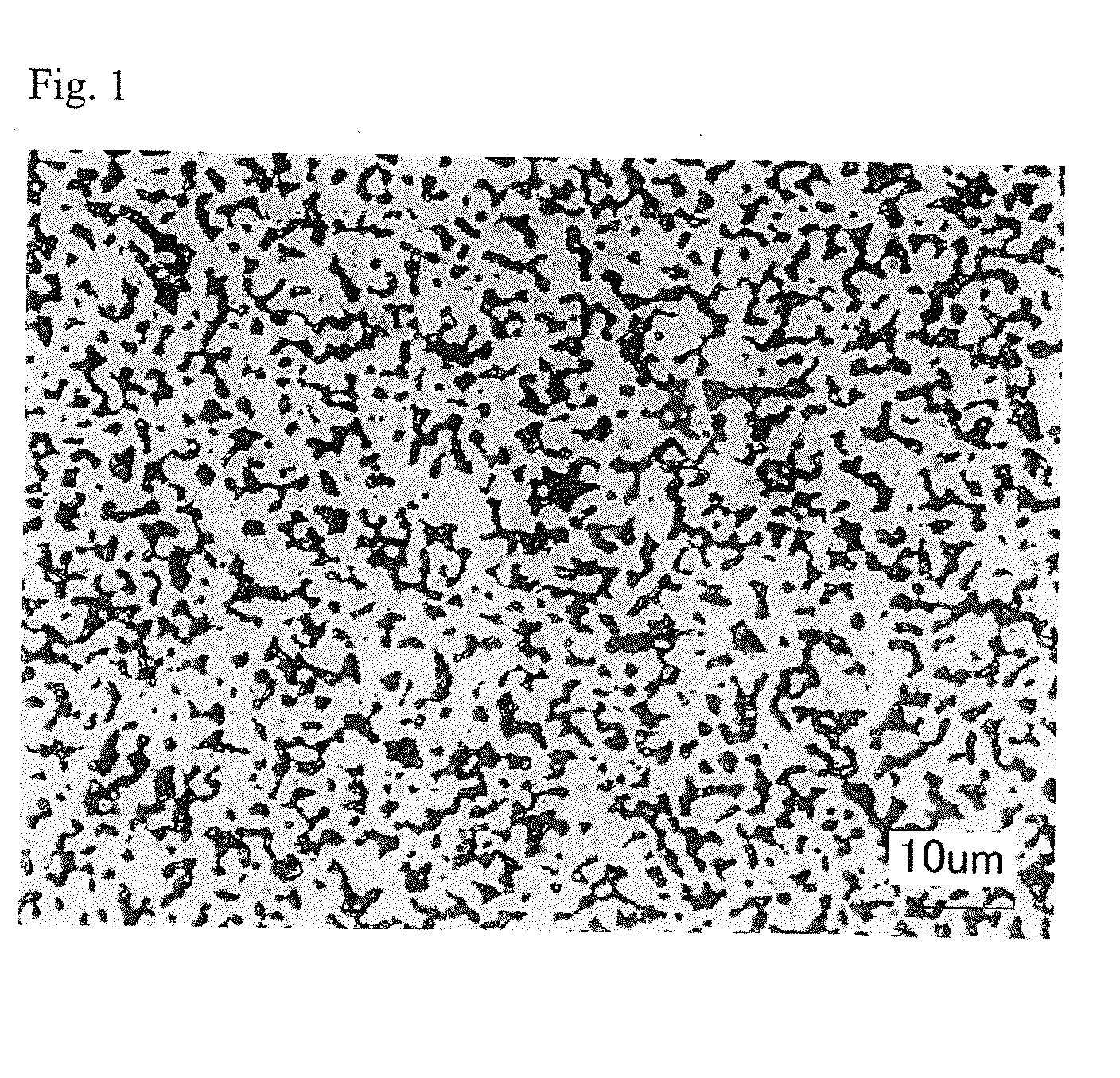
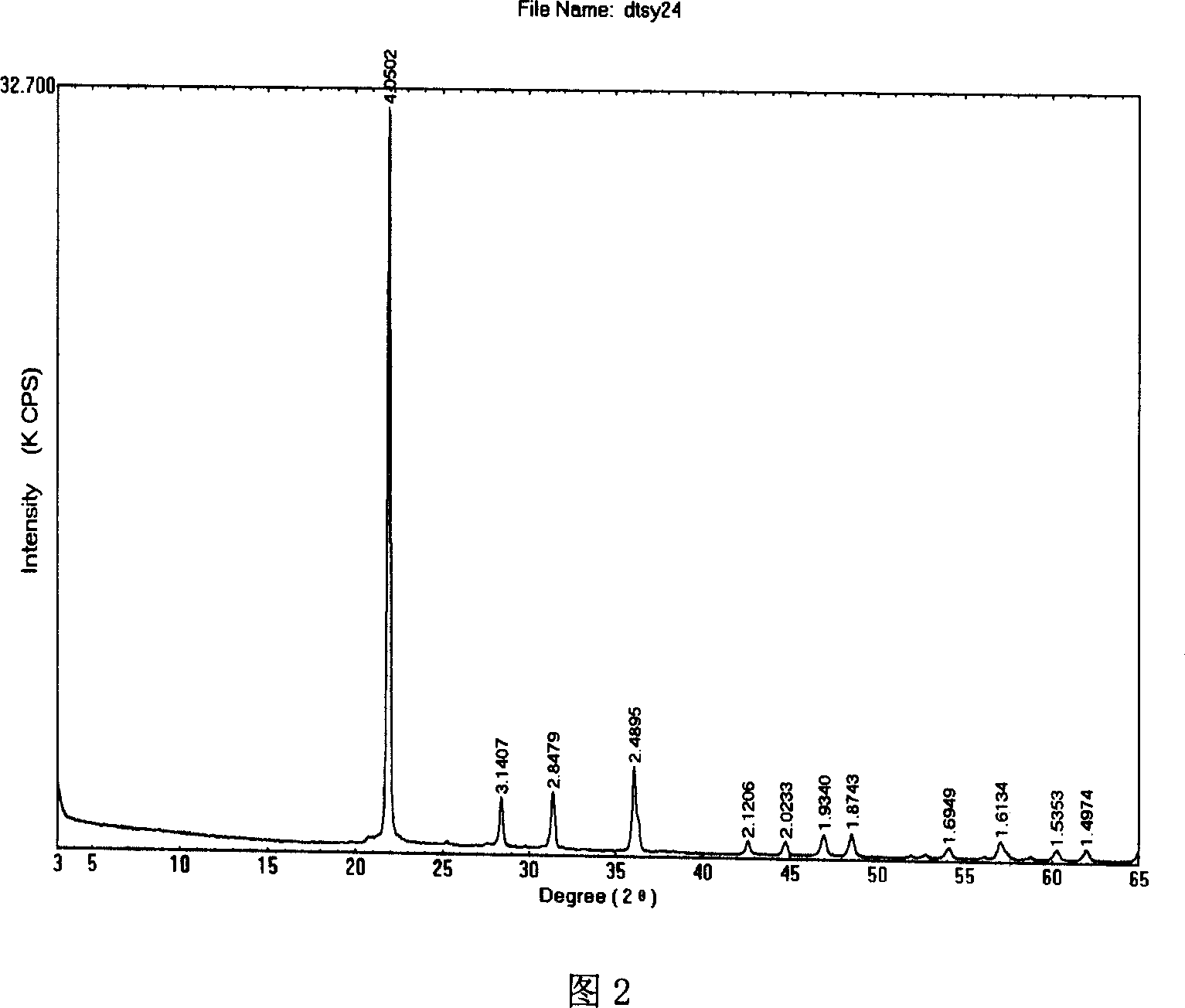
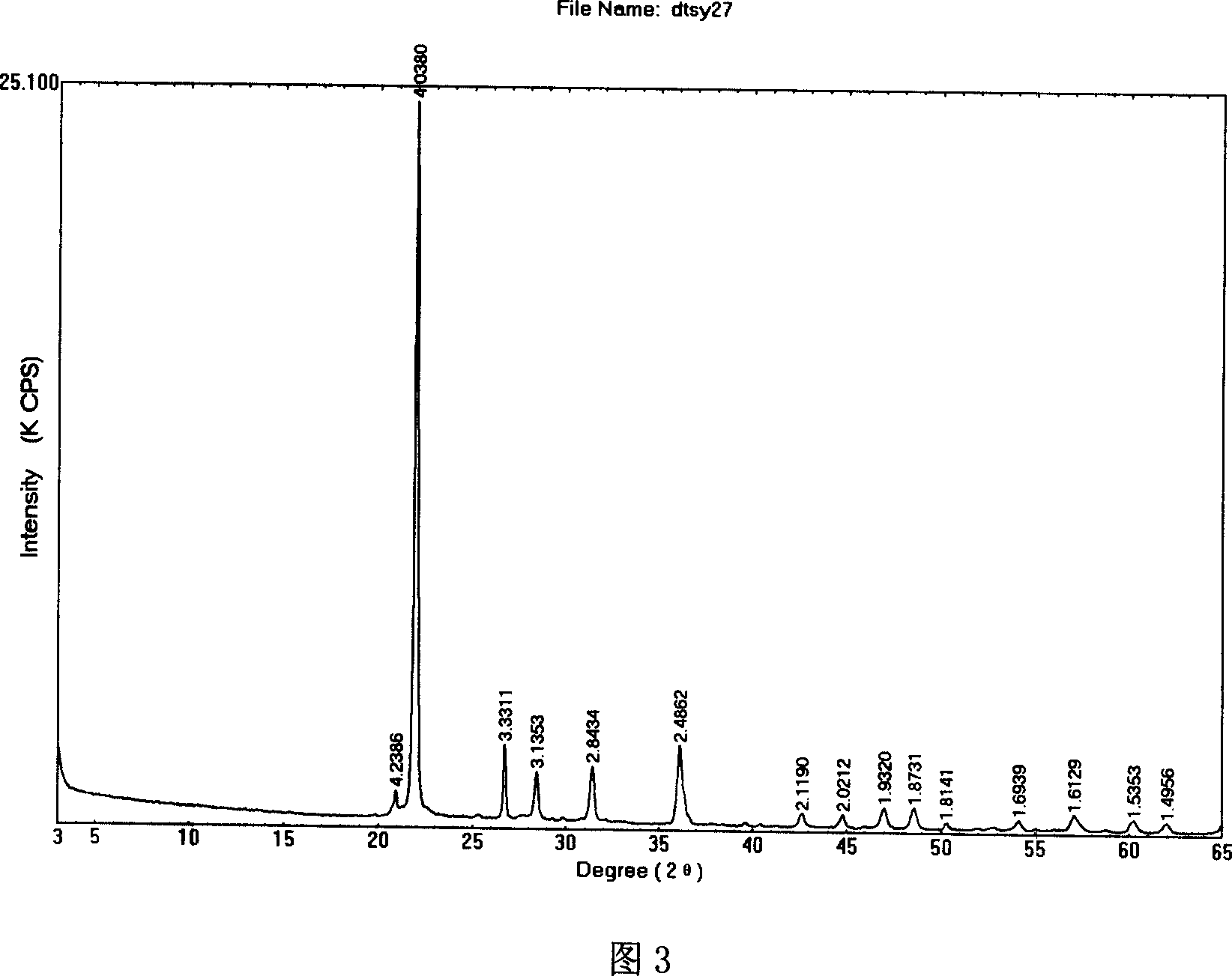
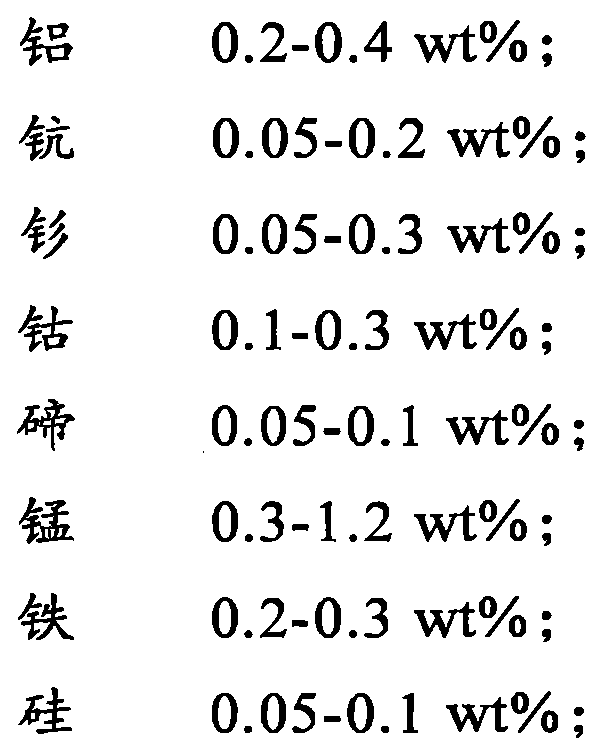
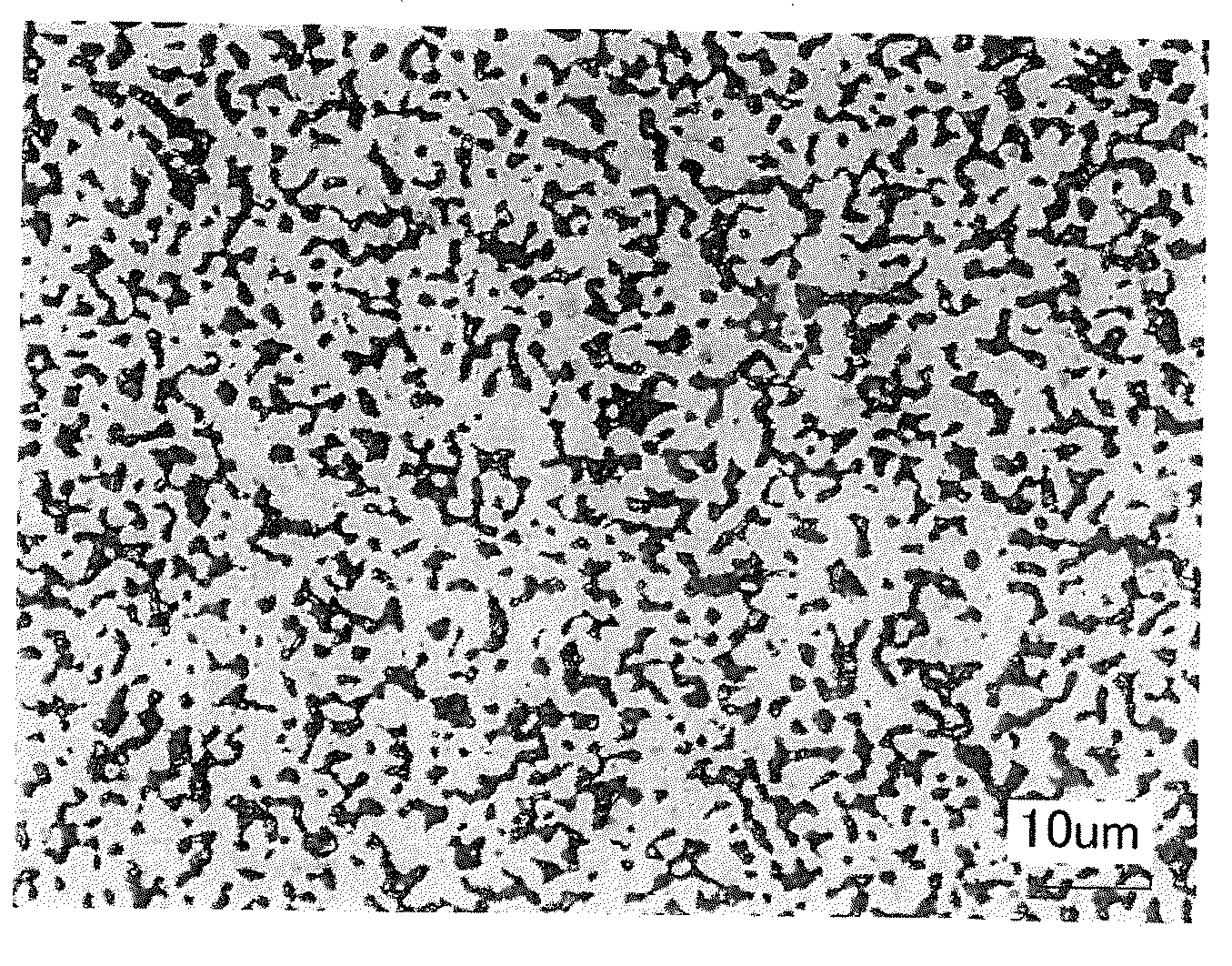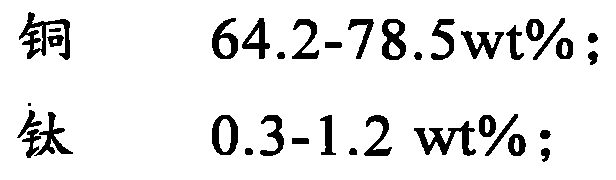Patents
Literature
211 results about "Cristobalite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
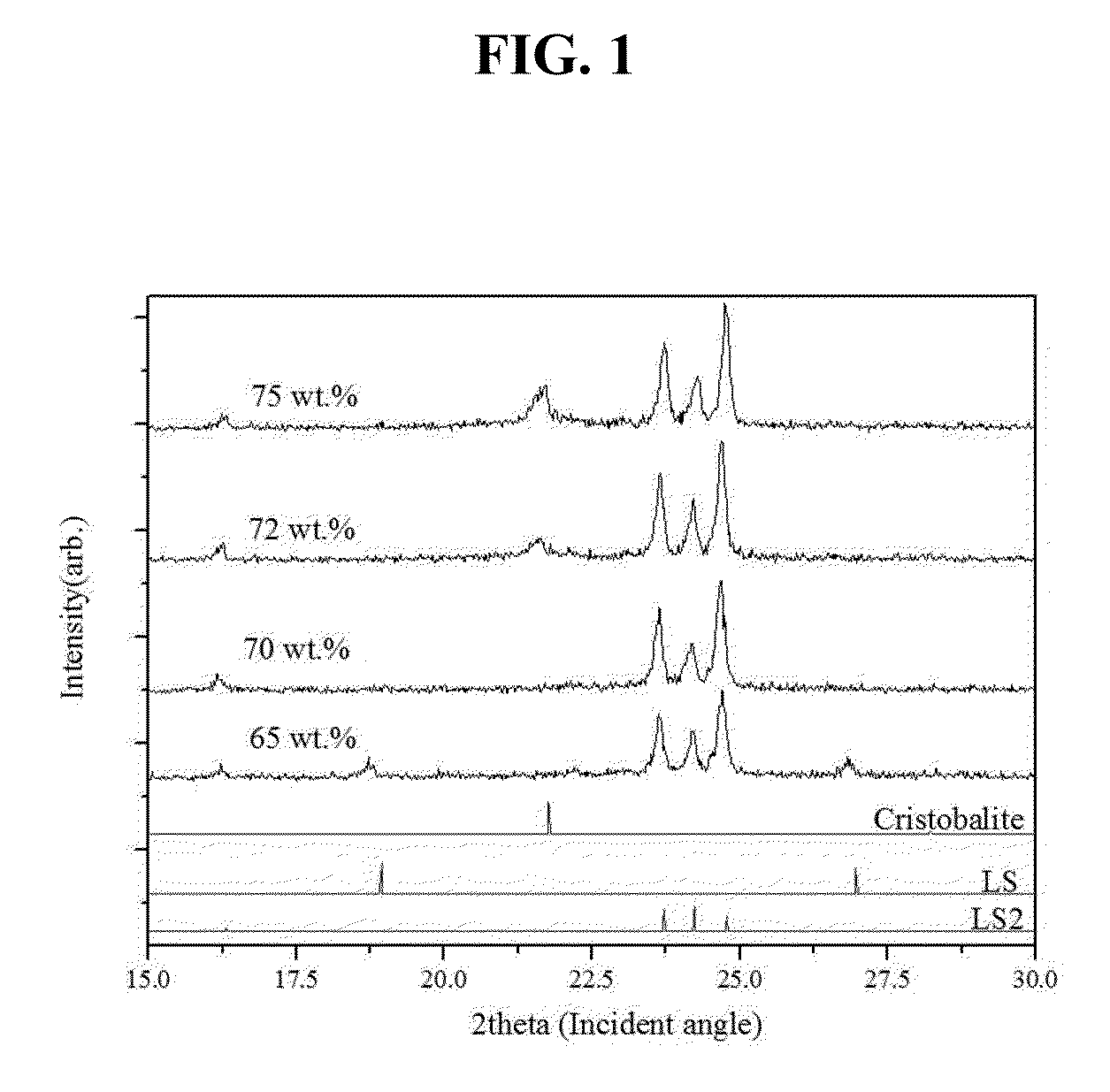
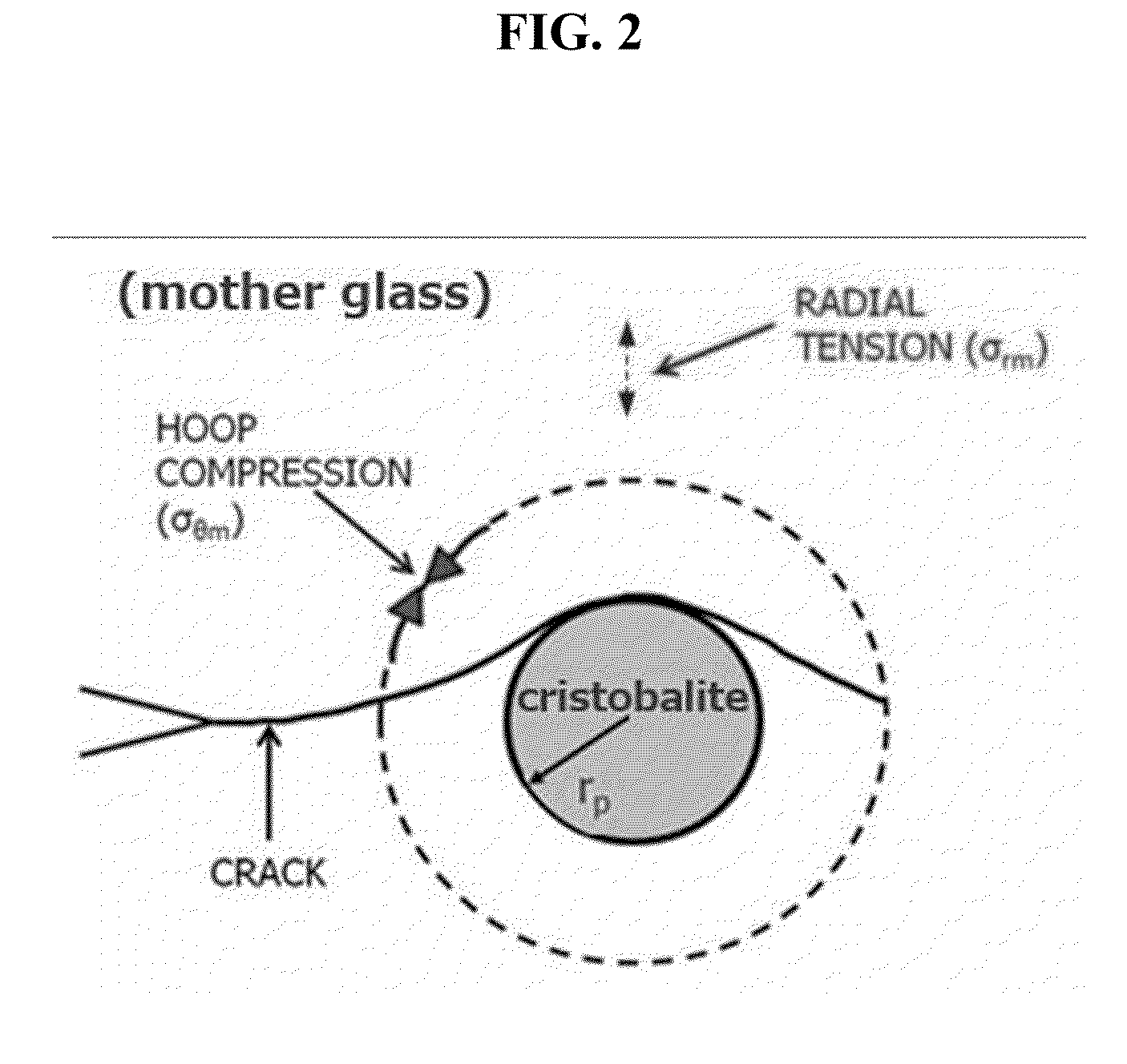
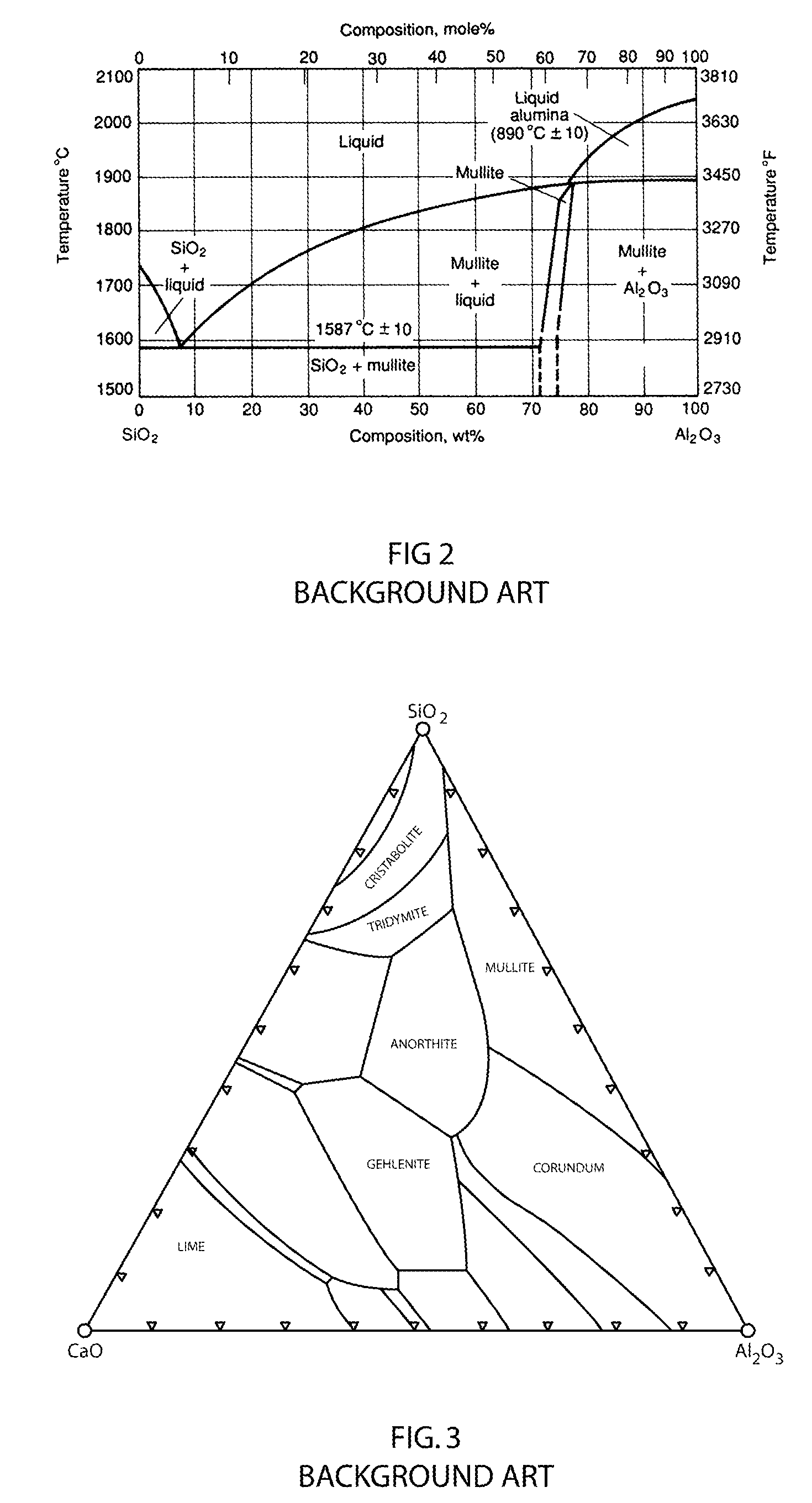
Cristobalite is a mineral polymorph of silica that is formed at very high-temperatures. It is used in dentistry as a component of alginate impression materials as well as for making models of teeth It has the same chemical formula as quartz, SiO₂, but a distinct crystal structure. Both quartz and cristobalite are polymorphs with all the members of the quartz group, which also include coesite, tridymite and stishovite.
High-strength lithium disilicate glass ceramic and preparation method thereof
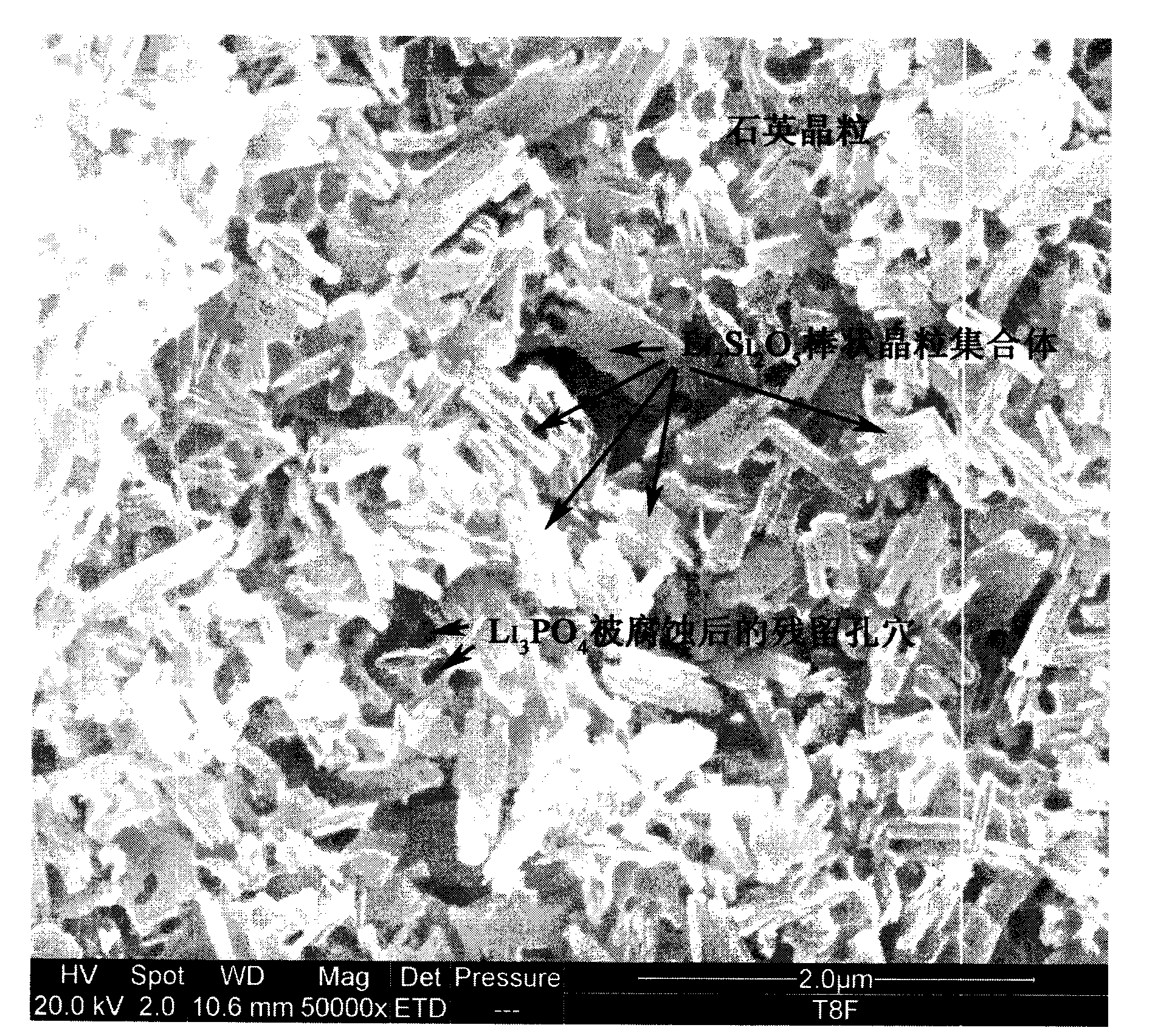
The invention discloses high-strength lithium disilicate glass ceramic and a preparation method thereof. The glass ceramic comprises the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 59-80% of SiO2, 10-18% of Li2O, 0.1-14% of MgO, 0-15% of Al2O3, 1-8% of P2O5, 0-5% of Na2O, 0-7% of CaO, 0-9% of K2O, 0.5-8% of stabilizer and 0-10% of colorant, wherein the stabilizer is selected from one or more of ZrO2, SrO, BaO and Y2O3, and the colorant is selected from one or more of Eu2O3, CeO<+>, Tb4O7, La2O3, Ta2O5, MnO2 and Fe2O3. The lithium disilicate glass ceramic is a material which contains a residual glass phase, a Li2Si2O5 principal crystalline phase and a small quantity of Li3PO1, quartz, cristobalite, zirconium oxide or magnesium-aluminum silicate phase and is prepared by controlling nucleation and crystallization processes after carrying out heat treatment on lithium disilicate matrix glass. The lithium disilicate glass ceramic is very high in bending strength and fracture toughness and favorable in translucence and chemical stability and can serve as a full-ceramic dental material applied to the field of dental restoration.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
Fruit fresh-keeping paperboard and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101806016AControl metabolic rateImprove securityNon-fibrous pulp additionCoated paper substrateSlagPaperboard
The invention provides a fruit fresh-keeping paperboard and a preparation method thereof. The fruit fresh-keeping paperboard consists of paperboard base paper and fresh-keeping coat which is spread on the surface of the paperboard base paper. The paperboard base paper is mainly made from the waste paper, and the base weight is 90 to 100 g / m2. The fresh-keeping coat mainly comprises the following components in part by weight: 1 part of cristobalite, 0.25 to 1.5 parts of kaolin, 0.005 to 0.01 part of sodium polyacrylate, 0.0003 to 0.0005 part of nisin, 0.0001 to 0.0003 part of natamycin, 0.2 to 0.5 part of oxidized starch and 1.0 to 2.0 parts of water, and the base weight is 5 to 30 g / m2. The waste paper is made into the paperboard base paper through, disintegration, high-consistency slag removal, defibering, low-consistency slag emoval and screening, the cristobalite, kaolin, the sodium polyacrylate, the nisin, the natamycin and water are added into a high-speed dispersion machine to be made into pigment dispersion liquid after being adequately dispersed and filtered, and the oxidized starch and the water are heated to be dissolved to obtain the oxidized starch liquid. The pigment dispersion liquid is mixed with the oxidized starch liquid to obtain the fresh-keeping paint liquid, after being filtered by 180 to 200-mesh sieve, the fresh-keeping paint liquid is spread onto the surface of the paperboard base paper through a spreading machine, and the paperboard base paper with the surface being coated with the fresh-keeping paint is secondarily dried, press finished and decorated to obtain the finished product. The fruit fresh-keeping paperboard has the advantages that the fresh-keeping effect is good, the environment compatibility is good, the fresh-keeping package and the storage and transportation package are integrated, and the continuous mass production can be realized on the papermaking machine.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY +1
Fiber-Based Ceramic Substrate and Method of Fabricating the Same
InactiveUS20090035511A1Low costReduce coefficient of thermal expansionLayered productsGlass shaping apparatusFiberChemical reaction
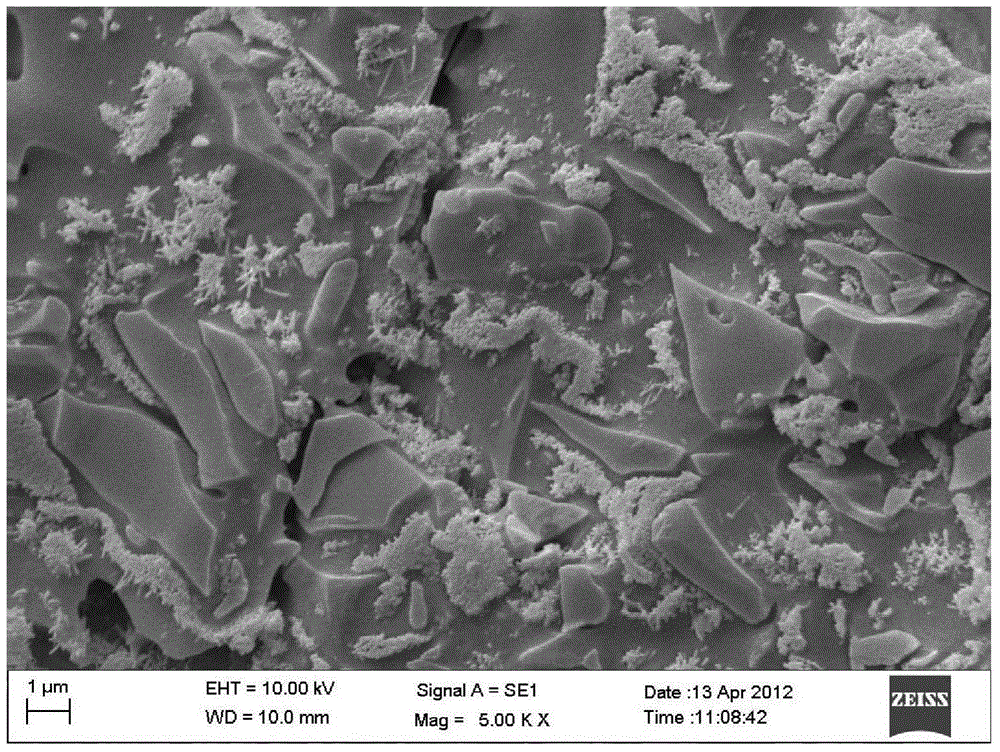
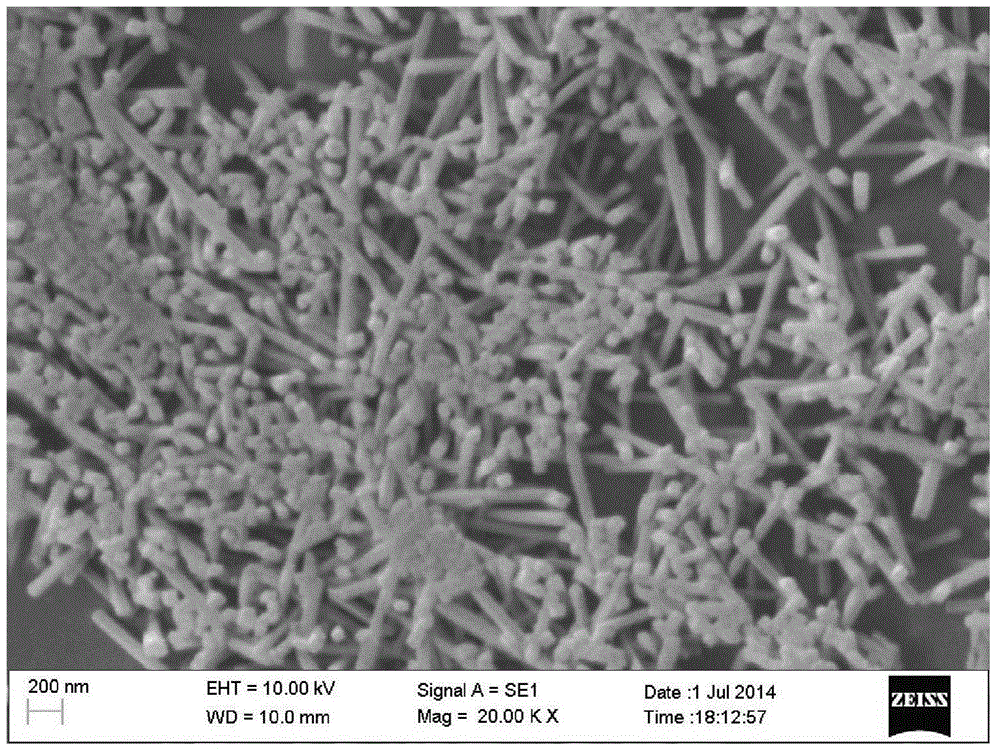
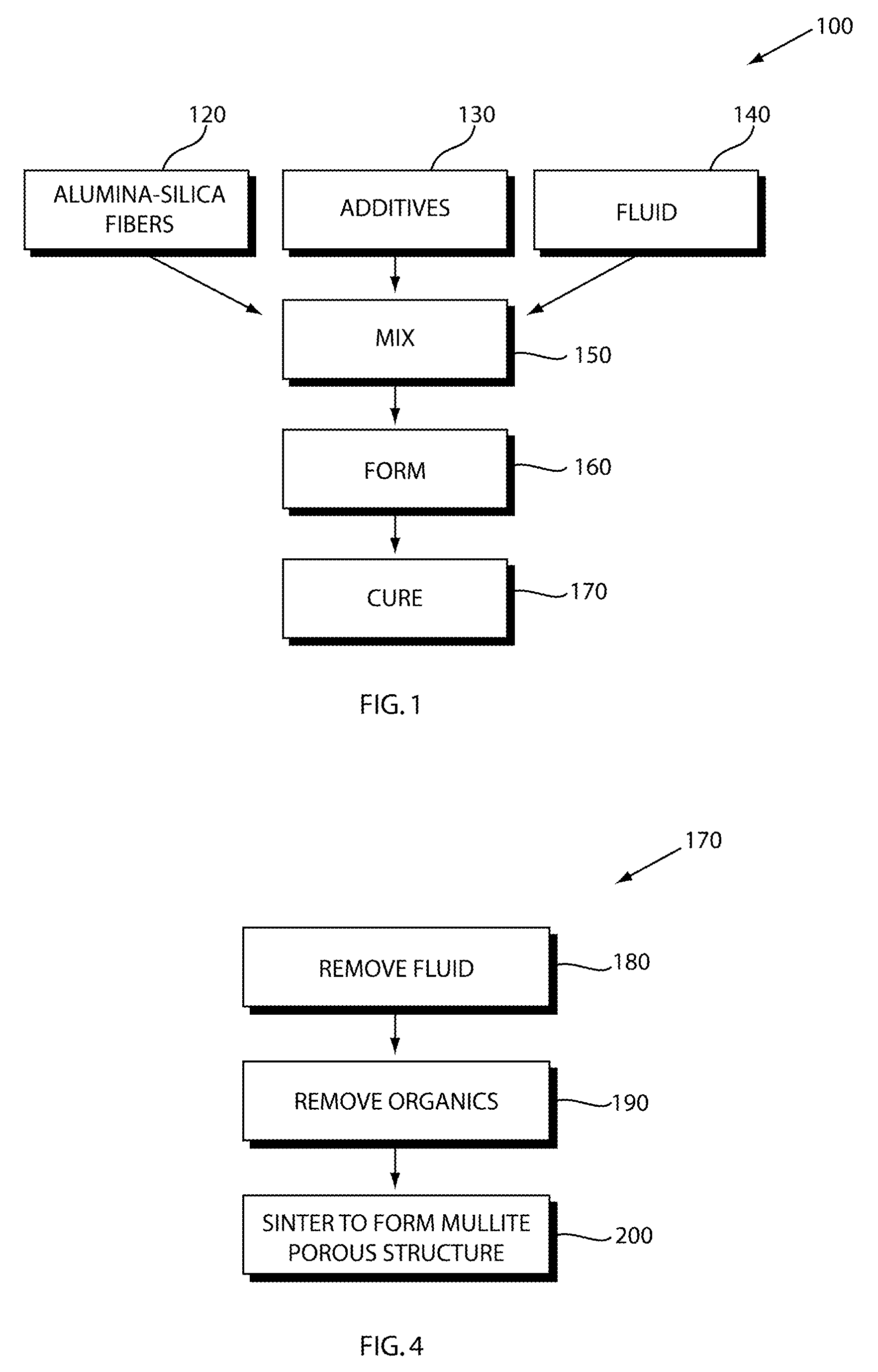
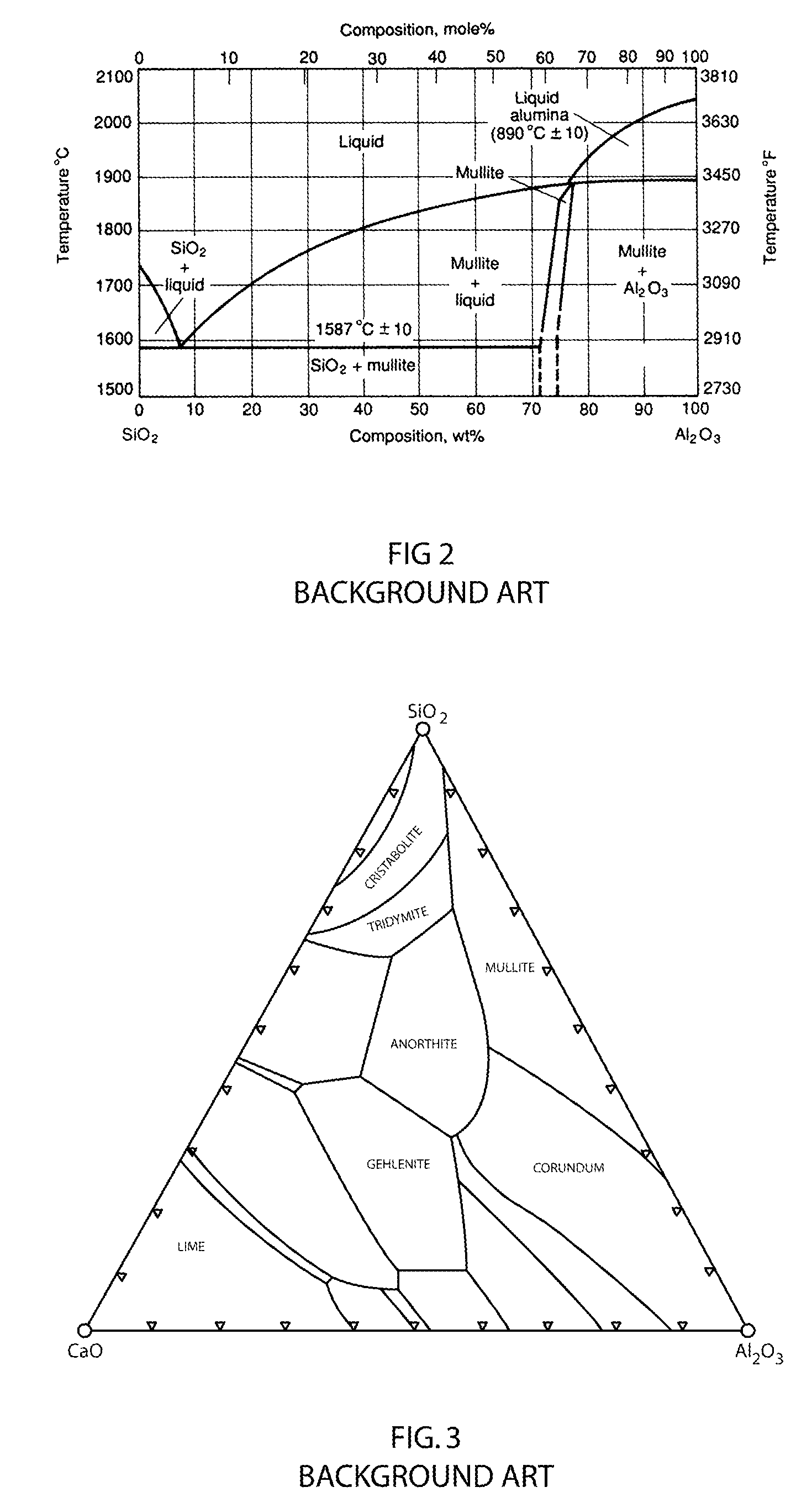
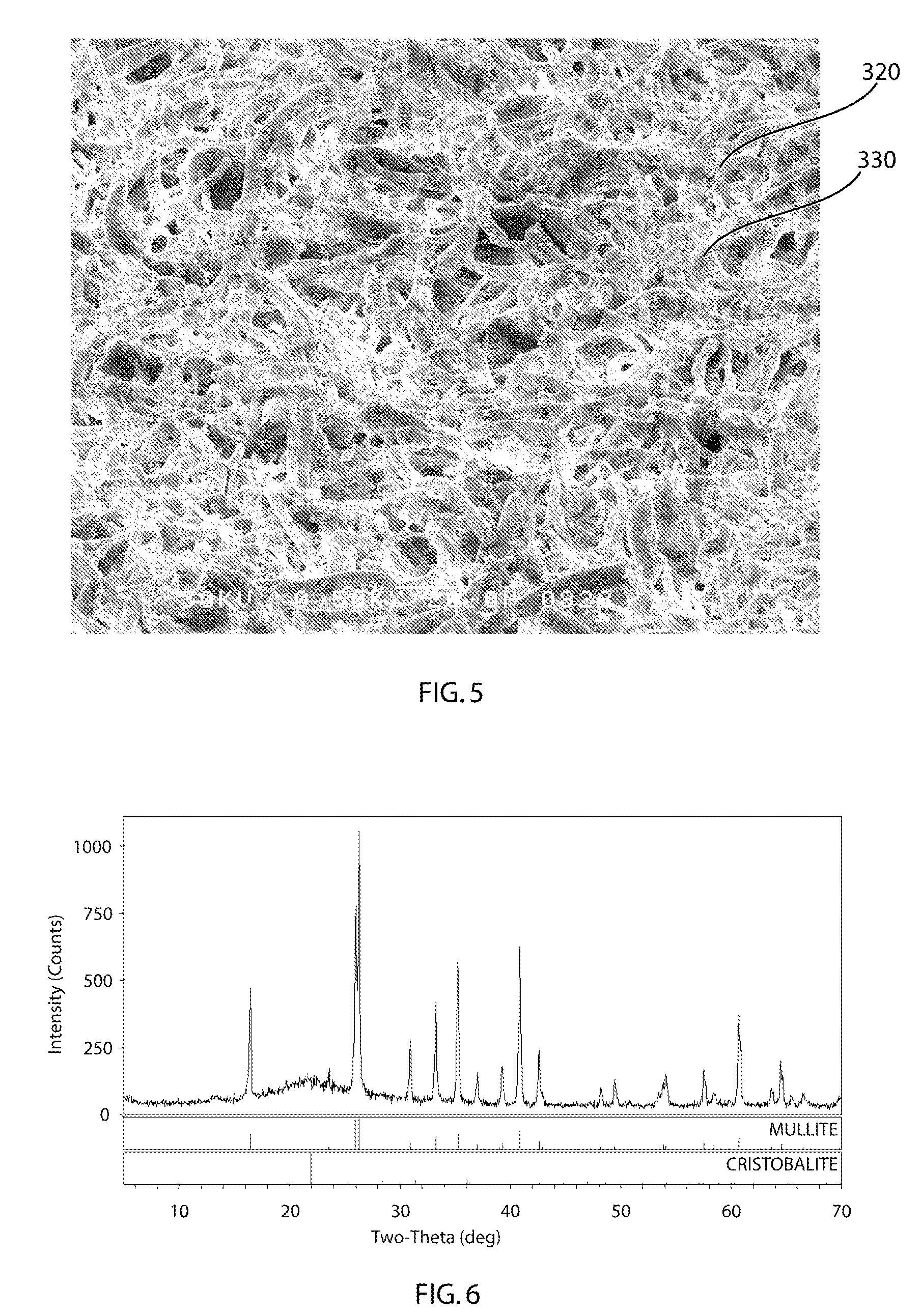
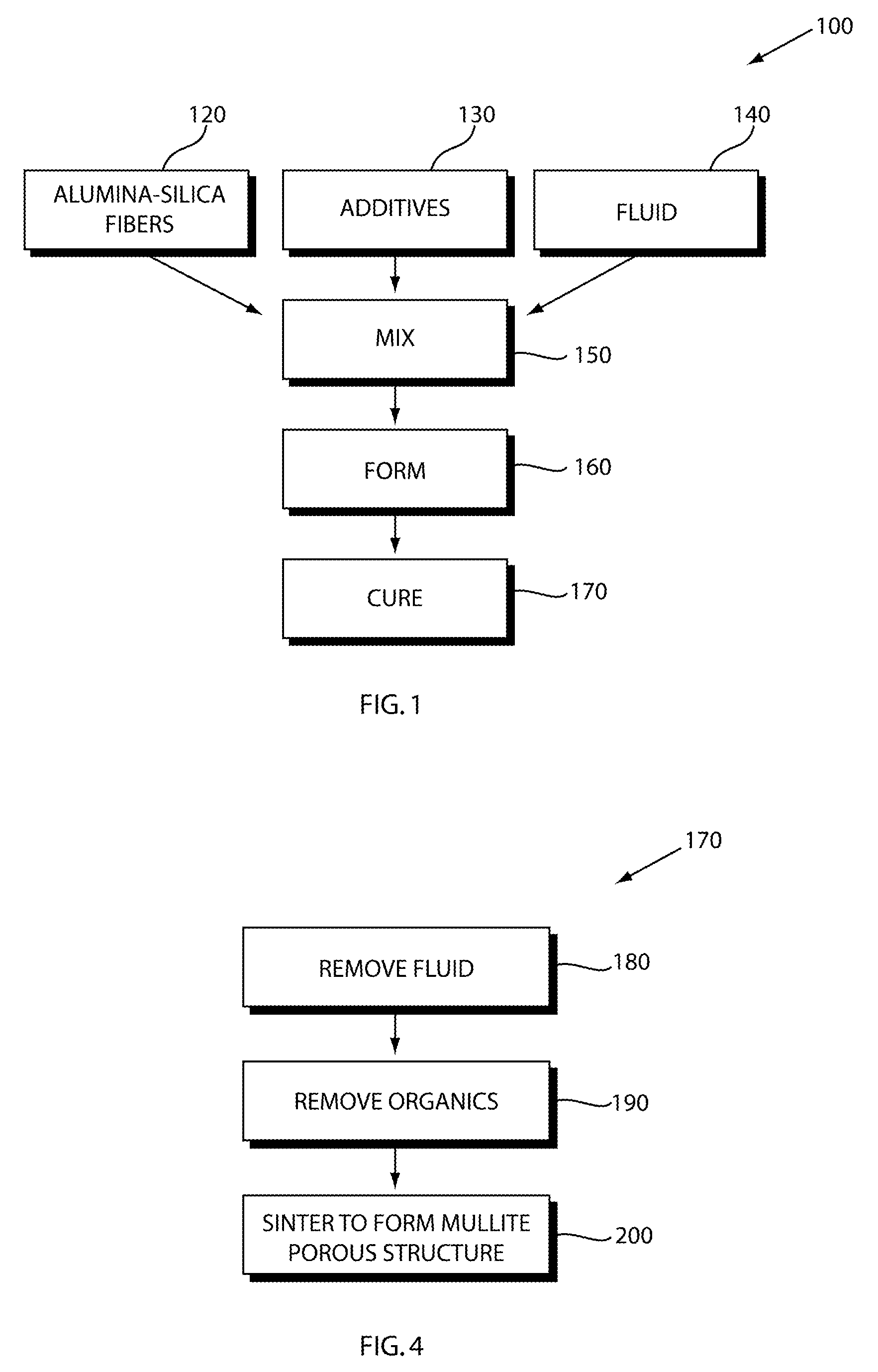
Low cost aluminosilicate fibers are used to form a ceramic substrate material using inorganic binders that promote the formation of stable compounds that inhibit the formation of crystal silica, or cristobalite, when the substrate is used or exposed to high operating temperatures. The aluminosilicate fibers are mixed with additives including organic and inorganic binders and a fluid to form a plastic mixture. The plastic mixture is formed into a green substrate, and subsequently cured into the ceramic substrate. The fiber-based constituents permit the formation of rigid porous structures for filtration, insulation, and high temperature processes and chemical reactions.
Owner:GE02 TECH INC
Chemically stabilized beta-cristobalite and ceramic bodies comprising same
A method for rigidifying a fiber-based paper substrate for use in the exhaust system of a combustion device. In the method, a green ceramic fiber-based paper substrate is impregnated with an impregnating dispersion. The impregnated substrate is then dried, calcined and fired to form a rigidified substrate that is suitable for use in the exhaust system of a combustion device. This rigidification process is performed at least once and, preferably, two or more times. The green paper substrate comprises two or more sheets of green ceramic fiber-based paper, with at least one creased sheet and another sheet being a laminated together to form a plurality of tubular channels. The rigidified substrate comprises refractory ceramic fibers in the form of a ceramic fiber-based paper and agglomerates of ceramic particles. The ceramic particle agglomerates are bonded to and disposed so as to thereby bond together the refractory ceramic fibers at spaced locations along and at intersections of the refractory ceramic fibers so that the refractory ceramic fibers retain much of their original flexibility while in the paper.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
High strength and aesthetic lithium disilicate crystalline glass-ceramics containing cristobalite crystal and preparation method thereof
ActiveUS20160060159A1High strengthEnhances strength and aesthetic light transmittanceImpression capsTooth crownsGlass-ceramicDental restoration
Provided is lithium disilicate crystalline glass containing cristobalite crystal phase for high strength and aesthetic traits and its manufacturing process thereof. Exemplary embodiments of the present invention provide the high strength and aesthetic lithium disilicate crystalline glass, one kind of dental restoration materials, and its manufacturing method which induces the growth of the different crystal phase, cristobalite, from glass with lithium disilicate crystal.
Owner:HAAS & CO GMBH
Formula for firing light ceramic once and production method of light ceramic
ActiveCN104230309ARealize one firingLow reaction temperatureClaywaresCalcium silicateReaction temperature
The invention belongs to the field of ceramics, and particularly relates to a formula for firing light ceramic once and a production method of the light ceramic. By means of the formula of the light ceramic, wollastonite and magnesite soil are introduced to replace part of dolomite and limestone, the wollastonite does not contain volatile matters and cannot perform thermal fractionation to release gas, so that the wollastonite is introduced into a blank to form an aluminum calcium silicate system, high-temperature products are anorthite and cristobalite, the reaction temperature is lower, the firing temperature can be reduced, and accordingly, one-time firing of the light ceramic is feasible through the formula; and with adoption of the production method of the light ceramic, energy crisis can be relieved effectively, the production cost can be reduced, the water absorption of a light ceramic product is reduced on the basis of a twice fired product, the mechanical strength is improved, the application range can be enlarged, energy consumption can be reduced by 40% with the production method, the production cost can be reduced by 20%, and remarkable economic and social benefits are achieved.
Owner:FUJIAN DEHUA HUANYU CERAMICS
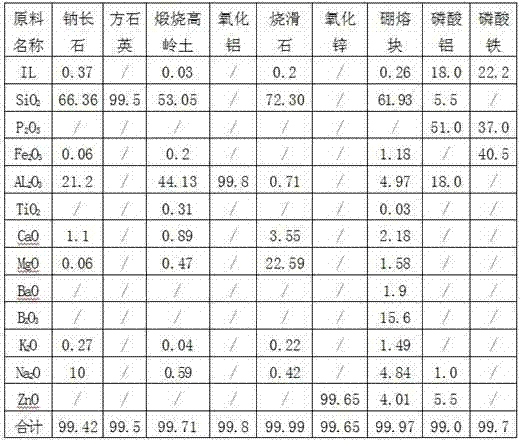
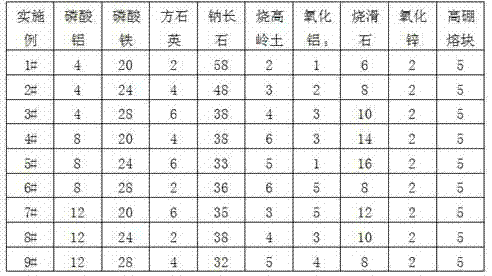
Purple bronze glaze with metallic luster and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103833419ALittle acid and alkali resistanceLittle high temperature fluidityTalcMaterials science
The invention discloses a purple bronze glaze with metallic luster and a preparation method thereof. The purple bronze glaze with metallic luster is prepared from the following raw materials by weight through sintering: 4 to 12% of a ceramic catalyst, 20 to 28% of a crystallization agent, 2 to 6% of cristobalite, 32 to 58% of albite, 2 to 6% of calcined kaolin, 1 to 5% of alumina, 6 to 16% of calcined talcum, 2% of zinc oxide and 5% of high-boron frit, wherein the ceramic catalyst is a P-Al catalyst, and the crystallization agent is a P-Fe crystallization agent. According to the invention, chemical composition of a formula is reasonably adjusted, the leadless P-Al catalyst and the P-Fe crystallization agent are employed, a stable spinel crystal structure is obtained through recrystallization of the glaze, metal coloring ions (Fe<2+> and Zn<2+>) and the like are enriched on the surface of a glaze layer, so the whole surface of the glaze presents metal-like luster. The glaze shows a purple bronze metal effect, and the hardness of the glaze is almost equal to the glaze of common sanitary china; acid resistance and alkaline resistance of the glaze reach national standards in China; and defects like pin holes and small holes of the glaze are substantially improved, and the glaze is applicable to production under conventional production kiln condition.
Owner:HUIDA SANITARY WARE
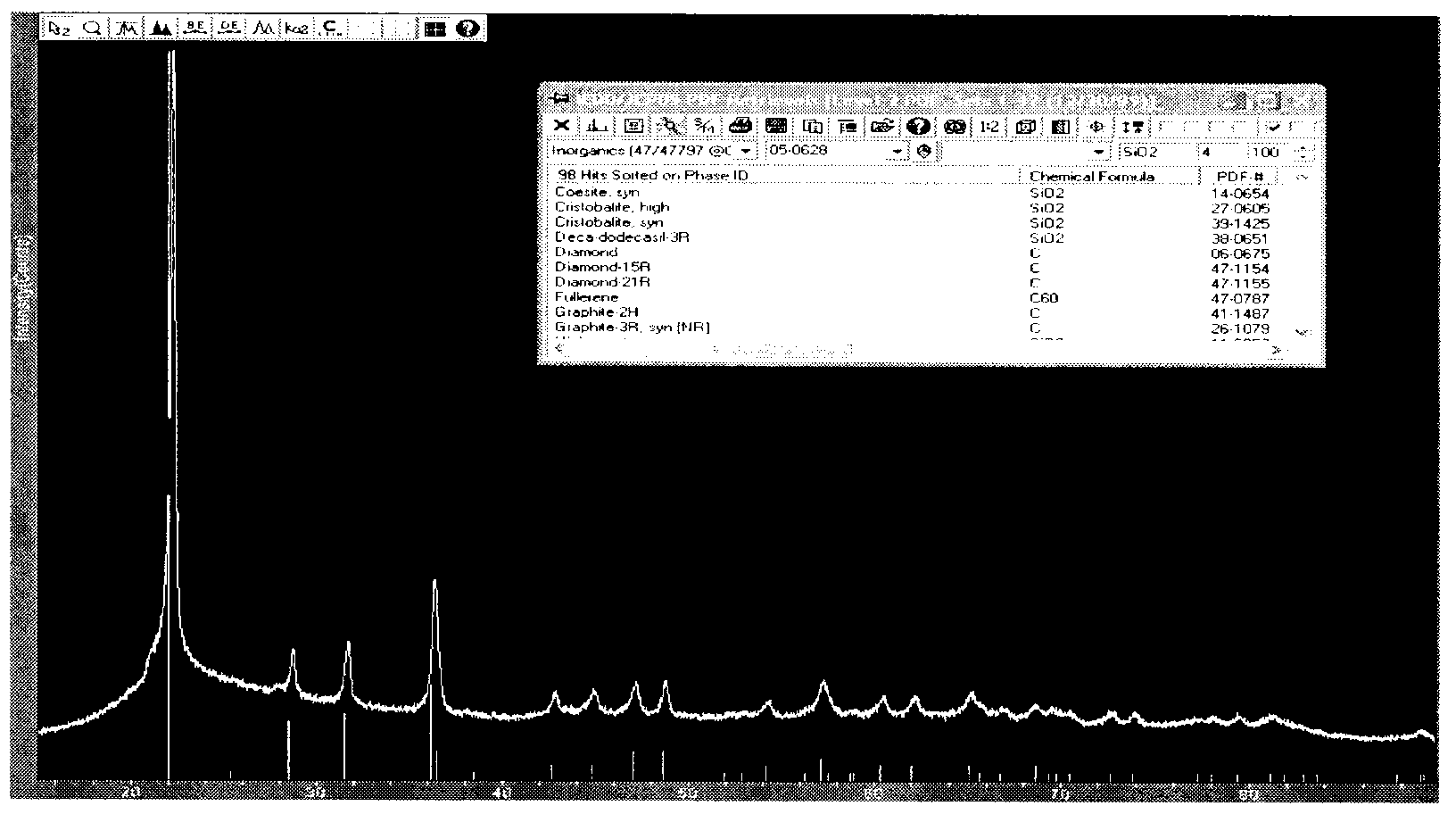
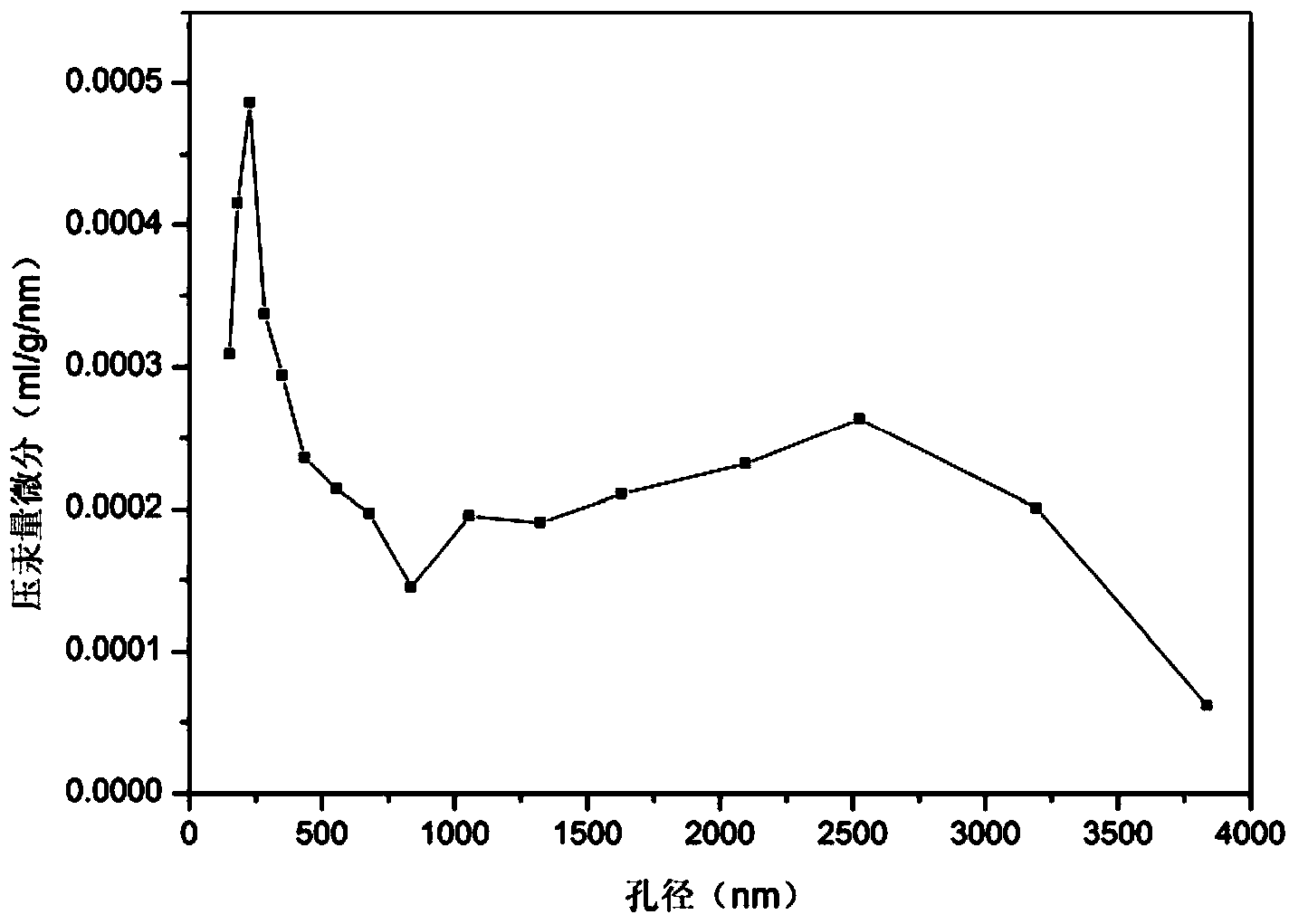
Cristobalite as well as preparation method and application thereof
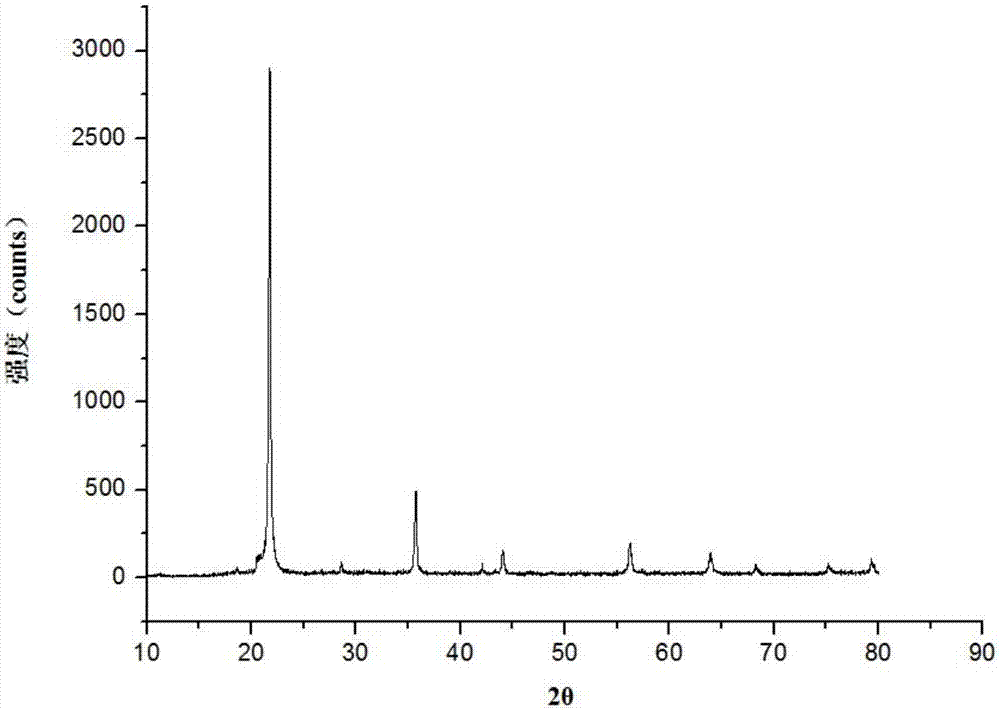
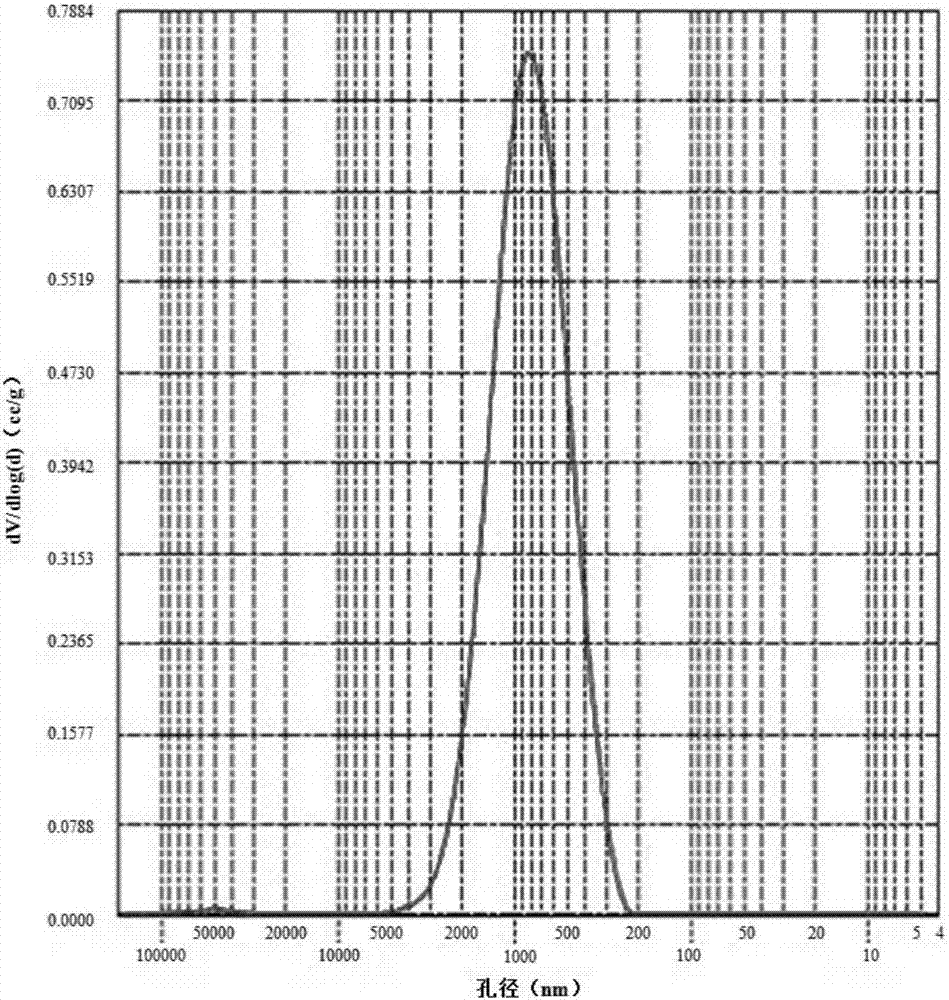
ActiveCN107282035AUniform pore size distributionHas industrial application valueCatalyst carriersSilicaSilicon dioxideTungsten
The invention discloses cristobalite, a preparation method of the cristobalite and application of the cristobalite serving as a carrier of a catalyst. The cristobalite has a porous structure; the specific pore volume of the cristobalite is 0.5 to 0.7ml / g, the average pore size is 400 to 900nm, most probable pore size is 400 to 850nm, and the cristobalite contains 70 to 99.9 weight percent of silicon dioxide and 0.1 to 30 weight percent of tungsten component counted by oxide. The cristobalite serving as the carrier of the catalyst has a stable property at high temperature; the cristobalite disclosed by the invention has intrinsic properties of cristobalite prepared by other methods, the porous structure and potential industrial application value, and is expected to develop a new industrial application field of the cristobalite. The method for preparing the cristobalite, disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simplicity, low requirement on equipment and low energy consumption; in addition, the silicon dioxide raw material is easily obtained and abundant in reserves, so that the production cost is low.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
CASTING MOLD, METHOD OF MANUFACTURING SAME, TiAl ALLOY CAST PRODUCT, AND METHOD OF CASTING SAME
ActiveUS20170008073A1Reduce casting mold strengthSuppressing fracture and crackBlade accessoriesFoundry mouldsRefractoryCasting mold
A casting mold to cast a TiAl alloy includes a casting mold body formed into a bottomed shape and provided with a cavity. The casting mold body includes a reaction-resistant layer provided on the cavity side, formed from a refractory material containing at least one of cerium oxide, yttrium oxide, and zirconium oxide and a back-up layer formed on the reaction-resistant layer. The back-up layer includes a weakening layer formed from a refractory material including a silica material in a range from 80% by mass to 100% by mass inclusive, the silica material containing cristobalite in a range from 26% by mass to 34% by mass inclusive and the rest being fused silica, the weakening layer being designed to reduce casting mold strength and a shape-retention layer formed from a refractory material.
Owner:IHI CORP
Improved silicon oxide ceramic core and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103880406ALow firing shrinkageReduce high temperature deflectionFoundry mouldsFoundry coresParaffin waxPlasticizer
The invention discloses an improved silicon oxide ceramic core and a preparation method thereof and relates to a ceramic core and a preparation method thereof. The improved silicon oxide ceramic core disclosed by the invention is used for solving the problem that the conventional ceramic core is high in shrinkage rate and bad in high-temperature resistance. The product is prepared from ceramic slurry and a plasticizer, wherein the ceramic slurry is formed by mixing quartz glass powder, zircon power, analytically pure yttrium oxide and cristobalite; the plasticizer is prepared by mixing paraffin, beewax and polyethylene. The method comprises the following steps: 1, preparing the plasticizer; 2, preparing the ceramic slurry; 3, preparing a precast material; 4, preparing the improved silicon oxide ceramic core. The sintered shrinkage rate of the improved silicon oxide ceramic core is 0.041 percent and is far lower than the shrinkage rate of an existing silicon oxide ceramic core, the shrinkage rate is reduced by 0.193 percent, the high temperature deformation is 1.51mm and is lower than high temperature deformation of the existing ceramic core, and the high temperature deformation is reduced by 2.66mm. The method is simple in operation, and the experimental time is shortened.
Owner:佛山市非特新材料有限公司
Method for preparing monodisperse crystal silicon dioxide spherical particles by coating carbon
The invention relates to a method for preparing monodisperse crystal silicon dioxide spherical particles by coating carbon, which mainly solves the problems of particle agglomeration, nonuniform size, irregular shape and high cost in the existing silicon dioxide crystal particle preparation process. The method comprises the following steps: (1) coating a carbon layer with uniform thickness on the monodisperse amorphous silicon dioxide spherical particle surface by an aerosol method or hydrothermal method to obtain core-shell structure silicon dioxide / carbon particles; (2) carrying out high-temperature treatment on the core-shell structure particles to crystallize amorphous silicon dioxide into quartz or cristobalite; and (3) removing the carbon layer by oxidation at low temperature to obtain the monodisperse spherical silicon dioxide crystal particles. The technical scheme provided by the invention solves the problems. The spherical monodisperse nano / sub-micro / micro silicon dioxide crystal particles can be used in catalysis, membrane separation, very large-scale integrated circuit packaging material and semiconductor industry, precision valves, hard disks, surface polishing treatment of magnetic heads and the like.
Owner:CHANGZHOU YINGZHONG NANO TECH
Mullite-shrunk glass complex phase material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a mullite-silica-rich glass material (Mullica) and a preparation method thereof. The adopted technical proposal is as follows: firstly, 60 to 100 weight percent of fused corundum dusting powder and 0 to 40 weight percent of fine SiO2 powder are mixed, stirred, and then molded; and then the mixture is heated to between 1,300 and 1,600 DEG C at a temperature increase rate of between 2 and 5 DEG C / min in a reaction furnace under air atmosphere, the thermal insulation is performed for 2 to 8 hours, and then the mixture is naturally cooled. A raw material used by the mullite-silica-rich glass material is the fused corundum dusting powder, alumina and silica in the fused corundum dusting powder are utilized as compositions of synthetic mullite, and impurities such as potassium oxide can form a glass phase. The method uses waste as the raw material to synthesize the mullite-silica-rich glass material (Mullica), which can change wastes into valuables, reduce environmental pollution and production cost. At the same time, the mullite-silica-rich glass material (Mullica) does not contain cristobalite and corundum, and has the characteristics of high refractability, low expansion coefficient, wear resistance, and good thermal shock resistance.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
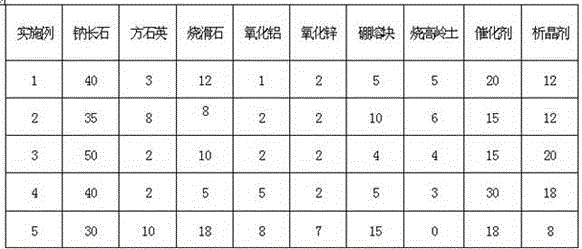
Aventurine metallic luster glaze and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to aventurine metallic luster glaze and a preparation method thereof.The aventurine glaze is prepared from, by weight, the raw materials of 30-50 parts of albite, 2-10 parts of cristobalite, 5-18 parts of calcined talc, 2-8 parts of aluminium oxide, 2-7 parts of zinc oxide, 4-15 parts of boron frit, 0-6 parts of calcined kaolin, 15-30 parts of catalyst, and 8-20 parts of crystallization agent.The preparation method of the aventurine metallic luster glaze comprises the steps that the raw materials are evenly mixed in proportion to obtain the total dry material, water is added in a certain proportion to be mixed, glaze slip with the concentration of 325-335g / 200ml is obtained, and the glaze slip with the granularity smaller than or equal to 10 microns is controlled to range from 50% to 55%.By means of reasonable adjustment of the firing process system and optimization of chemical composition of the formula, during later condensation after high-temperature firing, many micro ferric oxide crystalline granules are separated out from the glaze of the aventurine glaze produced in the invention, and many isolated flake-shaped single crystals sparkling like small gold foils are formed, so that an aventurine metallic glaze effect is shown.
Owner:HUIDA SANITARY WARE
Copper clad laminate with low dielectric constant and manufacturing method of copper clad laminate
ActiveCN105131527ALow dielectric constantLow dielectric lossSynthetic resin layered productsMetal layered productsCopperMaterials science
The invention relates to a copper clad laminate with a low dielectric constant and a manufacturing method of the copper clad laminate, and belongs to the technical field of the copper clad laminate. A method for acquiring cristobalite with alkali resistance and the low dielectric constant is provided, composition of a resin mixture of the copper clad laminate is improved, and the copper clad laminate with the low dielectric constant is obtained. The problem of a method for acquiring the low dielectric constant by the aid of modified resin or resin with the low dielectric constant all the time is solved, inorganic filler with the low dielectric constant is added more economically and more conveniently, and specifically, the method for reducing the dielectric constant of the copper clad laminate by adopting cristobalite powder prepared from vein quartz ore as inorganic filler composition is provided.
Owner:SUZHOU GINET NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Sputtering Target for Magnetic Recording Film and Method for Producing Same
InactiveUS20130206591A1Good effectShorten aging timeCellsVacuum evaporation coatingOptoelectronicsBoron
Provided is a sputtering target for a magnetic recording film containing SiO2, wherein the sputtering target for a magnetic recording film contains B (boron) in an amount of 10 to 1000 wtppm. An object of this invention is to obtain a sputtering target for a magnetic recording film capable of inhibiting the formation of cristobalites in the target which cause the generation of particles during sputtering, shortening the burn-in time, and realizing a stable discharge with a magnetron sputtering device.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
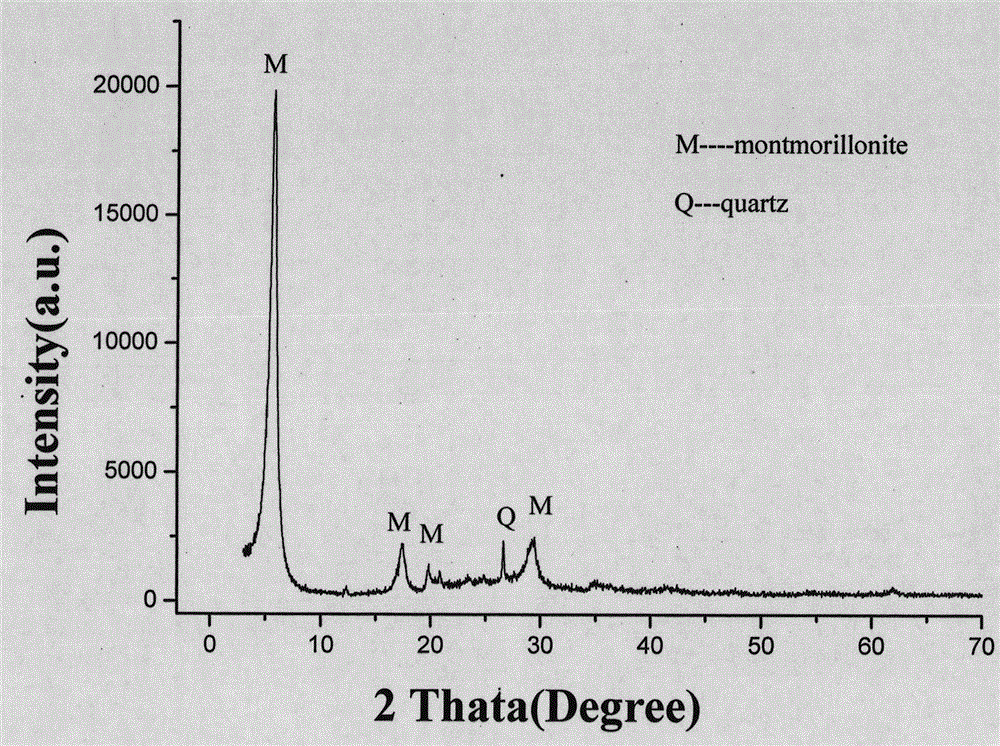
Method of separating and purifying montmorillonite from calcium bentonite
ActiveCN103848430AChemical structure unchangedMild chemical propertiesSilicon compoundsChemical structureSodium Bentonite
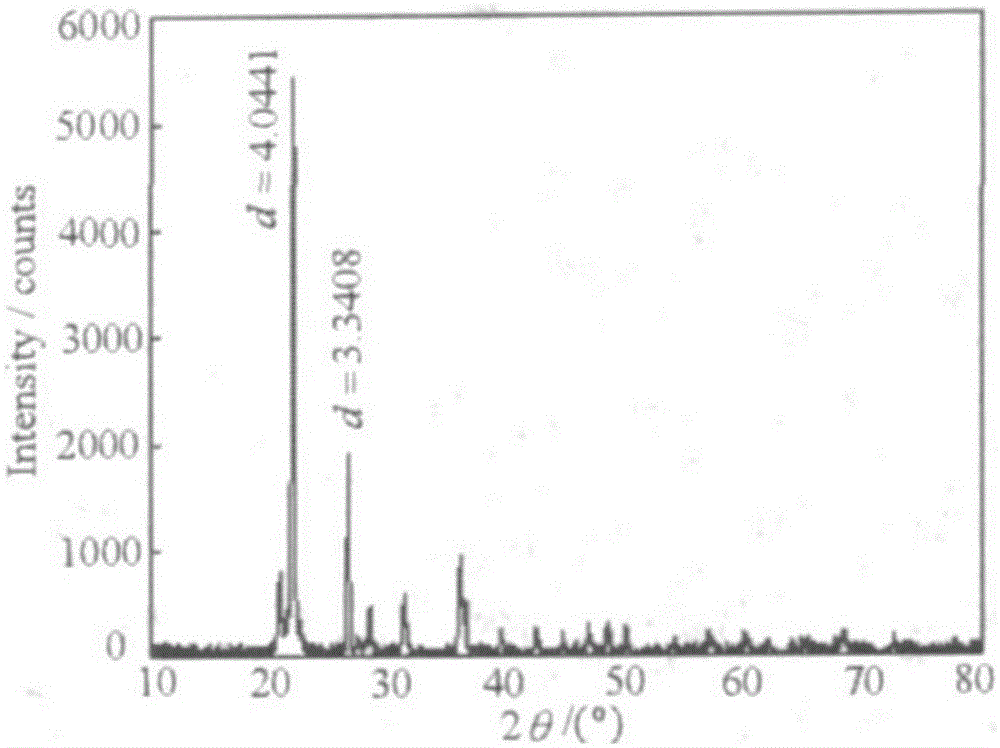
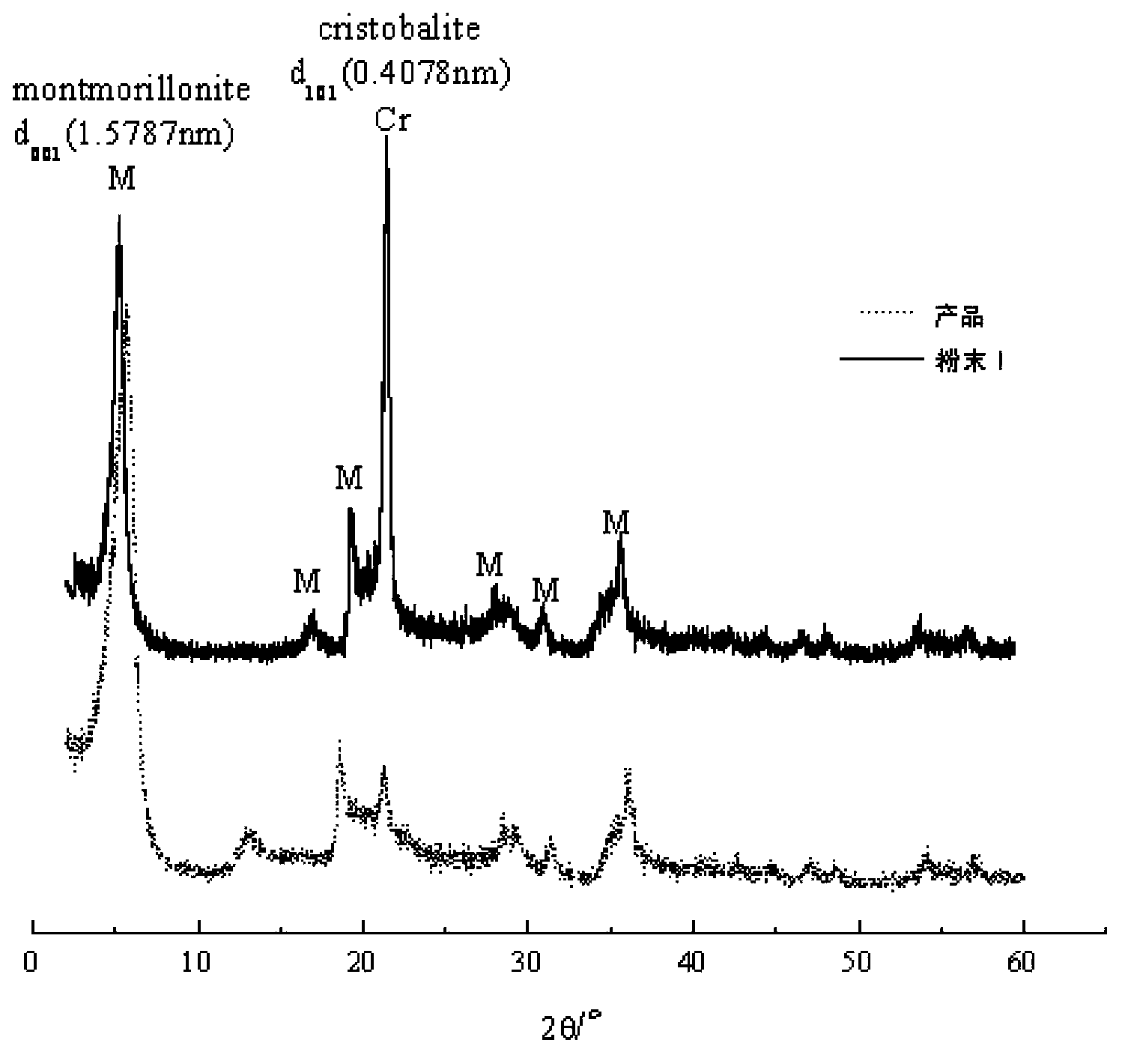
The invention discloses a method of separating and purifying montmorillonite from calcium bentonite. The method includes: adding dispersants such as sodium carbonate into a bentonite suspension, adjusting the pH value of the suspension, separating to obtain primarily-purified montmorillonite, adjusting the pH value of a suspension of the primarily-purified montmorillonite to a certain value, performing ultrasonic wave processing, and separating to obtain the high-purity montmorillonite. The chemical structure of the montmorillonite is unchanged. A superfine cristobalite impurity concomitant with the montmorillonite in the calcium bentonite is effectively removed. By ultrafine particle dispersion, the superfine cristobalite particles and the montmorillonite are depolymerized, thus enhancing dispersion and suspension capability of the superfine cristobalite particles and the montmorillonite. The cristobalite is removed by utilization of fractional centrifugation so as to obtain the high-purity montmorillonite, thus solving the technical problem that the cristobalite is hard to remove in the montmorillonite purification. The method has characteristics of simple process, mild conditions, cheap and easily available raw materials, low equipment requirements, high added value of products, and the like.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
Fe-Pt-Based Sputtering Target Having Nonmagnetic Substance Dispersed Therein
InactiveUS20150107991A1Reduce Particle GenerationImprove production yieldCellsElectric discharge tubesSputteringAlloy
A sintered compact sputtering target configured from an alloy having a composition comprising Pt at a molecular ratio of 35 to 55% and remainder being Fe, and a nonmagnetic substance dispersed in the alloy, wherein the nonmagnetic substance contains at least SiO2, SiO2 is amorphous, and a residual oxygen amount, which is obtained by subtracting an amount of oxygen contained as a constituent of the nonmagnetic substance from a total amount of oxygen contained in the target, is 0.07 wt % or less. An object of this invention is to provide a sintered compact sputtering target having a structure in which a nonmagnetic substance containing SiO2 is dispersed in an Fe—Pt-based alloy and capable of suppressing the crystallization of SiO2 into cristobalite, and reducing the amount of particles that is generated during sputtering.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
Fe-Pt-based sputtering target having non-magnetic substance dispersed therein
ActiveCN104411862AReduce generationImprove yieldElectric discharge tubesVacuum evaporation coatingSputteringChemical composition
A sintered body sputtering target which comprises an alloy having a chemical composition comprising Pt at a molecular population ratio of 35 to 55% and a remainder made up by Fe and a non-magnetic substance dispersed in the alloy, said sintered body sputtering target being characterized in that at least SiO2 is contained as the non-magnetic substance, the SiO2 is amorphous, and the residual oxygen amount, which is determined by subtracting the amount of oxygen contained as a component of the non-magnetic substance from the total amount of oxygen contained in the target, is 0.07 wt% or less. The present invention addresses the problem of providing a sintered body sputtering target which has such a structure that a non-magnetic substance comprising SiO2 is dispersed in a Fe-Pt-based alloy, and in which the crystallization of SiO2 into cristobalite can be avoided and particles are produced in a reduced amount during sputtering.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CORP
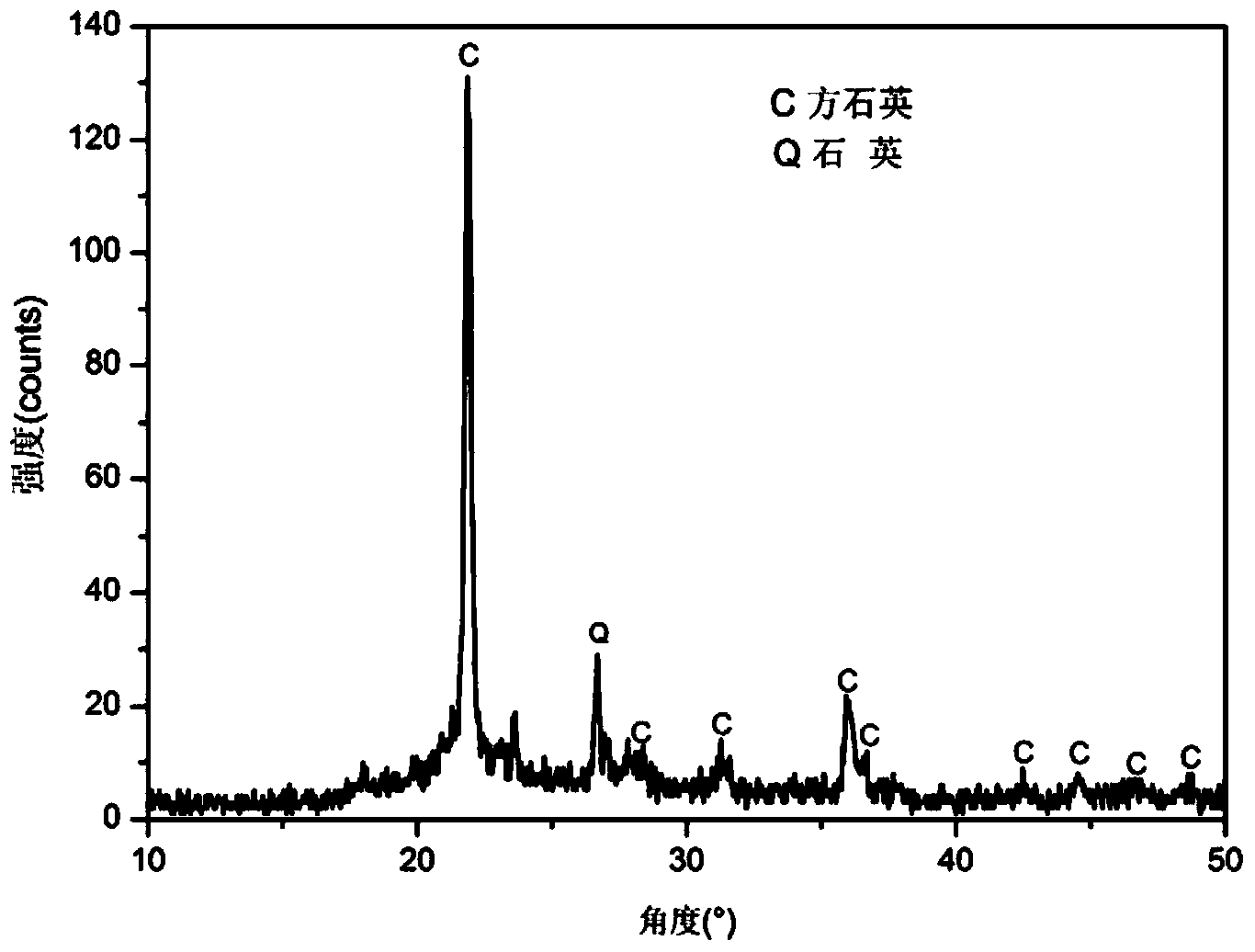
Method for preparing cristobalite material by taking quartz crucible as raw material
InactiveCN101531368AHigh puritySimple production processSilicaGlass shaping apparatusMetallurgyImpurity
The invention discloses a method for preparing a cristobalite material by taking a quartz crucible as a raw material, which adopts the quartz crucible subjected to high temperature treatment of 1,400 to 1,600 DEG C is subjected to surface impurity removal, crushing and grinding processes to obtain a high-purity cristobalite material of which the SiO2 content is more than 99 percent by weight. The method has the advantages of simple production process, low production cost, good product quality, energy conservation, environmental protection and the like.
Owner:伍萍
Method for preparing mullite from gangue
This invention relates to a method for preparing mullite by calcining coal gangue. The method comprises: (1) mixing coal gangue powder and additive uniformly; (2) heating the mixed raw materials at a rate of 2-10 deg.C / min to 1300 deg.C, and keeping the temperature for 3h to obtain the product. The additive is composite catalyst of NaF and La2O3. The addition amounts of NaF and La2O3 are 1-2 wt. % and 0.1-0.5 wt. % of coal gangue powder, respectively. The method has such advantages as low energy consumption and low cost. The mullite product does not contain quartz phase that is harmful to mullite properties.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Method for preparing cristobalite by calcining quartz
InactiveCN101041548AReduce energy consumptionReduce manufacturing costGlass shaping apparatusPhase changeCristobalite
The invention disclose a preparing method of cristobalite through calcining quartz, which comprises the following steps: 1) mixing quartz power and phase-change activator; getting batches; compositing Y2O3,Na2CO and BaF2 as phase-change activator; making the adding quantity of Y2O3, Na2CO3 and BaF2 separately at 1 per mill -5 per mill , 5 per mill -10 per mill and 1 per mill -5 per mill against the weight of quartz power; 2) heating the batches up to 1300 deg.c with speed of 2-10 deg.c per minuet; keeping temperature at 1300 deg.c at 6 h; getting product with quartz phase bigger-than 94%.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Investment casting technology for copper alloy casting
ActiveCN105057593AHigh strengthImprove toughnessFoundry mouldsFoundry coresMicrocrystalline waxDecomposition
The invention provides an investment casting technology for a copper alloy casting. Chlorcosane, Fischer-tropsch wax, stearic acid, glycerol ester of rosin, microcrystalline wax, polypropylene wax, polyisobutene, polyurethane elastomers and aldehyde resin serve as mold materials; and the polyisobutene, the polyurethane elastomers and the aldehyde resin are inserted into the chlorcosane, the Fischer-tropsch wax, the microcrystalline wax, the polypropylene wax and the stearic acid in a penetrating manner, and a formed structure has the good strength and the good heat stability. As for coatings adopted in the investment casting technology, cristobalite has the complete chemical inertness, and splitting decomposition can not occur at a quite high temperature; fused alumina has the beneficial effects of being high in melting point, compact in structure, good in heat conductivity and the like, the thermal expansion coefficient is small, and thermal expansion is even; and boron nitride is quiet low in friction coefficient, quite good in high-temperature stability and heat shock resistance, quite high in strength and heat conduction coefficient and lower in expansion coefficient. In this way, the copper alloy casting obtained with the investment casting technology for the copper alloy casting is high in strength and good in tenacity, no crack is generated on the surface, and the product quality is reliable.
Owner:NINGBO TIANYE PRECISION CASTING
Fiber-based ceramic substrate and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS7781372B2Low costReduce coefficient of thermal expansionLayered productsGlass shaping apparatusFiberChemical reaction
Low cost aluminosilicate fibers are used to form a ceramic substrate material using inorganic binders that promote the formation of stable compounds that inhibit the formation of crystal silica, or cristobalite, when the substrate is used or exposed to high operating temperatures. The aluminosilicate fibers are mixed with additives including organic and inorganic binders and a fluid to form a plastic mixture. The plastic mixture is formed into a green substrate, and subsequently cured into the ceramic substrate. The fiber-based constituents permit the formation of rigid porous structures for filtration, insulation, and high temperature processes and chemical reactions.
Owner:GE02 TECH INC
Gypsum cast material for melt mould casting
The invention discloses a gypsum mould material for casting a precision fusible pattern, characterized in that the gypsum mould material is prepared by respectively mixing 30 to 50% by weight of 10 mum cristobalite, 35 to 60% by weight of 30 mum cristobalite, 15 to 25% by weight of alpha gypsum, 1 to 5% by weight of time regulator and a coating intensifier. By using noble metals such as gold, silver and platinum, the invention can be used for preparation of the precision casting. The mould procedure can be carried out even at high temperature when injecting the molten metal, no crack will be generated and excellent dispersivity is obtained.
Owner:SANYU CO LTD
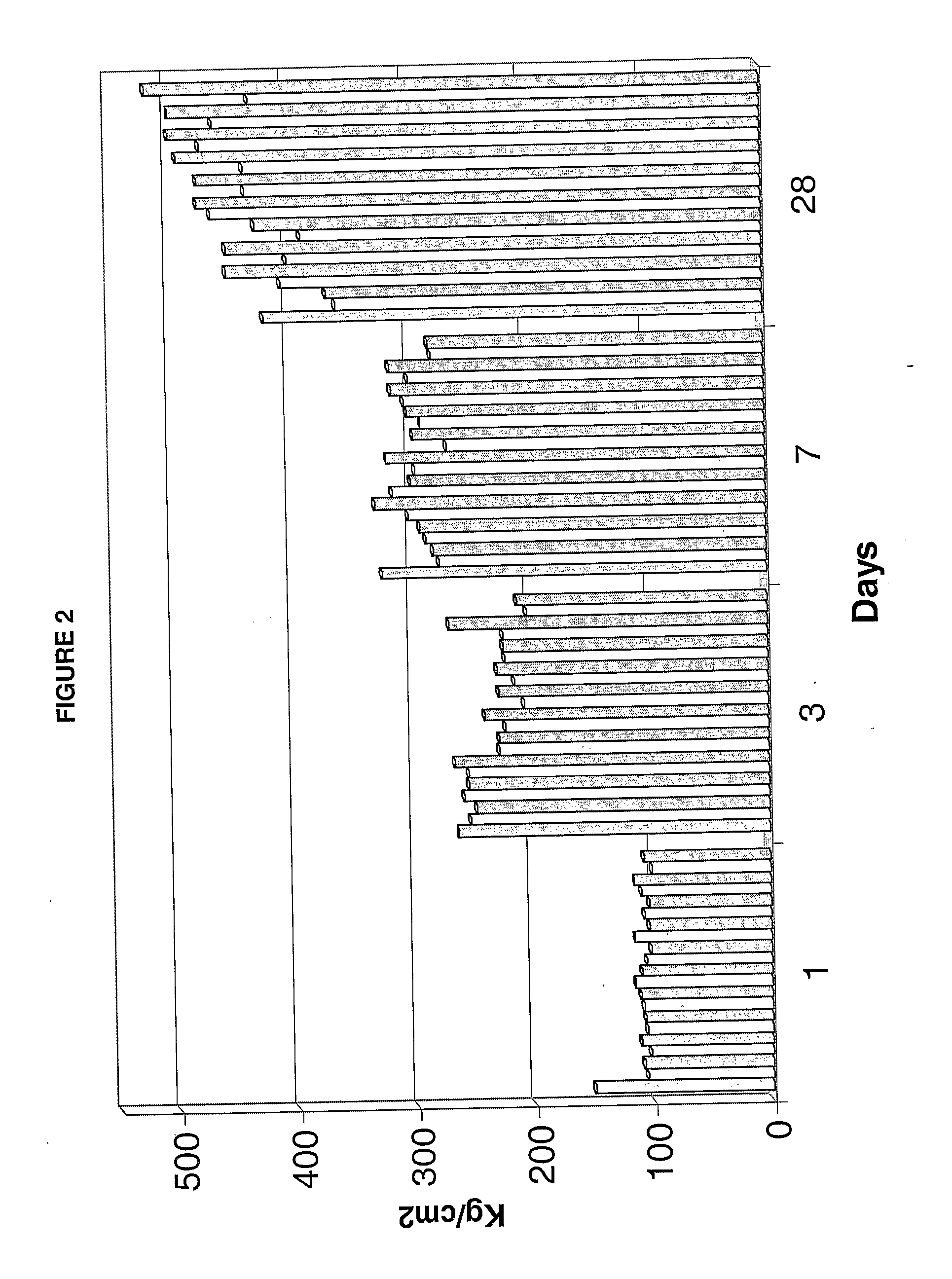
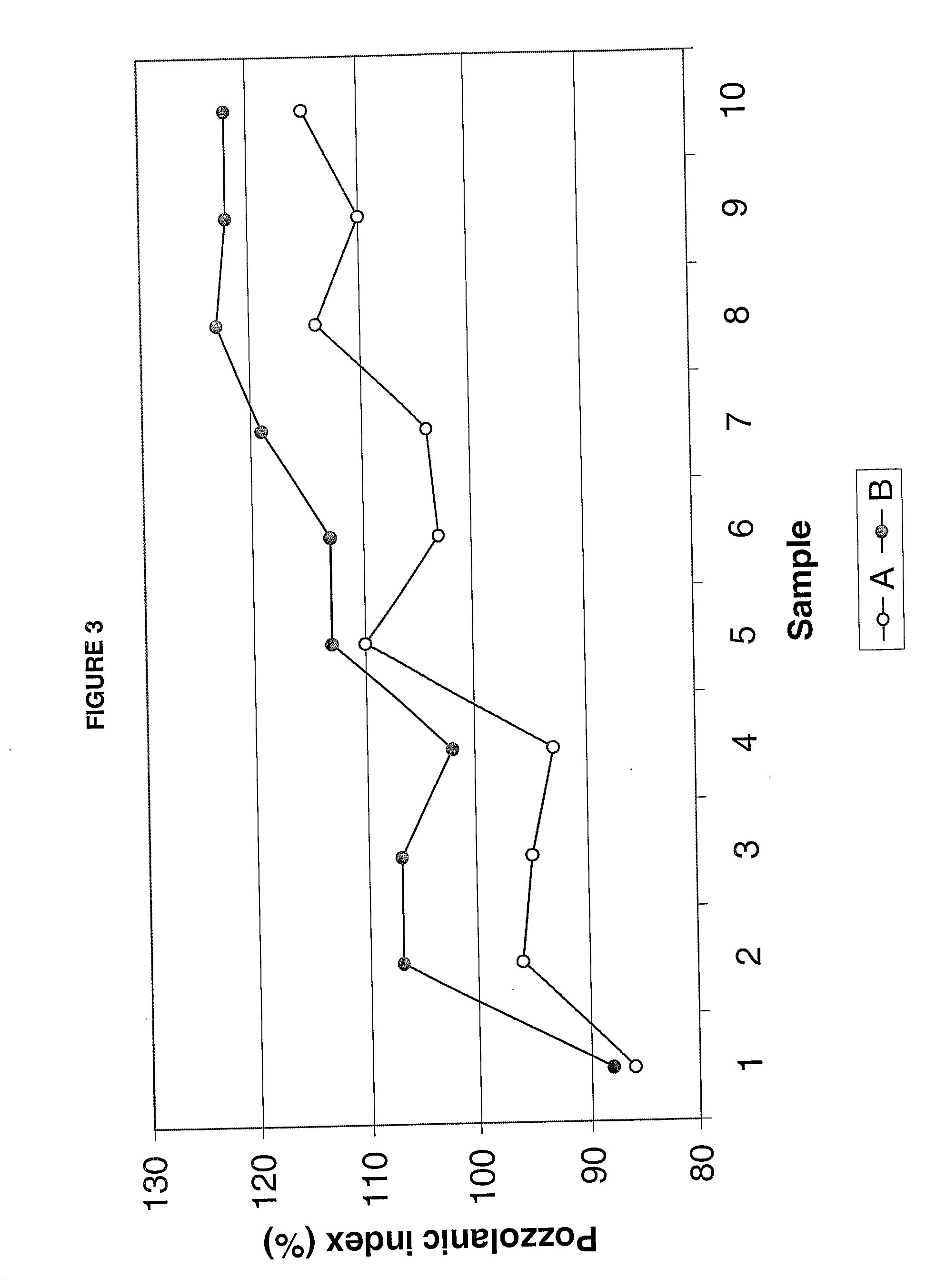
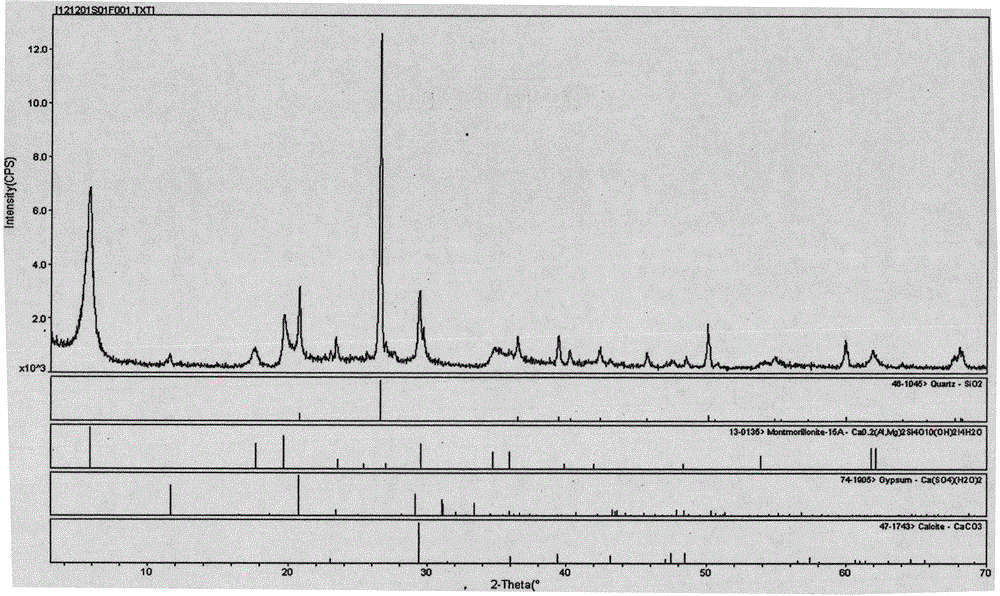
Improved microsilica, its application like pozzolanic material and methods for its obtaining
A new pozzolanic material basically conformed of microsilica with a minimum of silica of 85% in its composition is described, where the silica of the material is conformed mainly of cristobalite and tridimite. Unlike microsilica conformed basically of quartz, the microsilica of the invention exhibits greater pozzolanic indexes and provides improved characteristics of durability to concrete cements and in smaller proportions. Also simple and low consumption energy methods for obtaining the pozzolanic material of the invention are described.
Owner:GCC TECH & PROCESSES
Sputtering Target for Magnetic Recording Film and Process for Production Thereof
ActiveUS20130248362A1Shorten aging timeLow costCellsVacuum evaporation coatingX-rayRecording density
A sputtering target for a magnetic recording film containing SiO2, wherein a peak strength ratio of a (011) plane of quartz relative to a background strength (i.e. quartz peak strength / background strength) in an X-ray diffraction is 1.40 or more. An object of this invention is to obtain a sputtering target for a magnetic recording film capable of inhibiting the formation of cristobalites in the target which cause the generation of particles during sputtering, shortening the burn-in time, magnetically and finely separating the single-domain particles after deposition, and improving the recording density.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
Novel technique for preparing high-purity montmorillonite by deeply purifying bentonite
InactiveCN104944430AChange the assignment statusReduce clumpingSilicon compoundsSodium BentoniteMontmorillonite
The invention discloses a novel technique for preparing high-purity montmorillonite by deeply purifying bentonite which does not contain cristobalite. According to the novel technique, impurity phases, particularly superfine quartz concomitant with montmorillonite in calcium bentonite can be effectively removed, and furthermore, the components and the structure of prepared high-purity montmorillonite are unchanged. According to the technological idea, firstly montmorillonite and impurity quartz particles are depolymerized by virtue of a certain mechanical force, so that the occurring states of montmorillonite and quartz are changed, and the binding force between montmorillonite and quartz is weakened; secondly, the dispersing difference between montmorillonite and quartz is expanded by virtue of a small amount of dispersing agent, so that the separation is relatively easy; finally, high-yield and high-purity montmorillonite is obtained by virtue of the dispersing difference between montmorillonite and quartz through centrifugal separation. The novel technique has the characteristics of simple process, mild conditions, low equipment requirement, high product additional value and the like.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
Method for manufacturing high-tenacity ceramics through tricalcium phosphate
The invention belongs to the field of ceramic industry, and discloses a method for manufacturing high-tenacity ceramics through tricalcium phosphate. The method comprises the following steps that, by weight, 5%-15% of the tricalcium phosphate and 85-95% of ceramic blanks are evenly smashed, mixed, milled in the mode of wet ball milling, dried and ground into powder, green ceramic bodies are manufactured through dry pressing molding and the green ceramic bodies are sintered in a kiln to form the high-tenacity ceramics. According to the high-tenacity ceramic samples manufactured through the method, needle-shaped mullite and anorthite serve as the main crystalline phase, cristobalite serves as the auxiliary crystalline phase, and a Si-O system and P-O system composite glass phase serves as the binding phase. Through the structure, thermal expansion coefficients between the crystalline phases and between the crystalline phases and the glass phase are better matched, micro-cracks can be effectively reduced in the ceramic sintering process, and the tenacity of ceramic products is greatly improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Preparation technology of silicon carbide foam ceramic
The invention discloses a preparation technology of silicon carbide foam ceramic. The preparation technology comprises the steps of raw material preparation, mixed solution preparation, ball milling, modifying firing and the like. The silicon carbide foam ceramic is prepared by an organic foam impregnation technology, MgO-Al2O3-SiO2 is introduced as a sintering aid system, and the main crystal phases of the silicon carbide foam include mullite, cordierite, cristobalite and alpha-silicon carbide. The silicon carbide foam ceramic prepared by the system has the strength up to 1.23MPa as well as excellent high-temperature resistance and is applicable to molten iron filtration.
Owner:任海涛
Method for firing porous cristobalite at low temperature by adopting diatomite as raw material
ActiveCN103771426ALower phase transition temperatureReduce energy consumptionSilicaSodium metasilicateHigh potential
The invention discloses a method for firing porous cristobalite at low temperature by adopting diatomite as a raw material. The method comprises the following steps of: adding diatomite powder into an additive solution, wherein the addition amount of diatomite is 1g / 2-5ml according to the ratio of the mass of the diatomite / the volume of the additive solution; fully stirring, and then drying, wherein the additive solution is sodium metasilicate or alkali-metal silicate solution with the mass fraction being 7.20-17.33%; heating the dried solids to 600-800 DEG C, and calcining for 12-24 hours to obtain the porous cristobalite. The method disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that since the calcining temperature is low, the cristobalite product retains the morphology of the cristobalite and has abundant pore-channel structures so as to achieve unique and good heat retaining property. The prepared cristobalite has the intrinsic property of other synthesized cristobalites, also retains the morphology of the cristobalite and has abundant pore-channel structures so as to achieve good heat retaining property. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of low energy consumption, simple process and low cost and the product has high potential industrial value.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF GEOCHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com