Method for firing porous cristobalite at low temperature by adopting diatomite as raw material
A technology of diatomite and cristobalite is applied in the field of low temperature firing of porous cristobalite, which can solve the problems of limited industrial application of products, various kinds of additives, complicated processes, etc., and achieve the effects of abundant reserves, low price and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Weigh 0.8g of sodium metasilicate nonahydrate, dissolve it in 10ml of ultra-pure water, add 5g of diatomaceous earth powder, stir the suspension thoroughly, put it in an oven for 5 hours at 80°C, and dry it. The dried solid is placed in In a muffle furnace, the temperature was raised to 600° C. at a rate of 5° C. / min, and kept at 600° C. for 24 hours to obtain porous cristobalite.
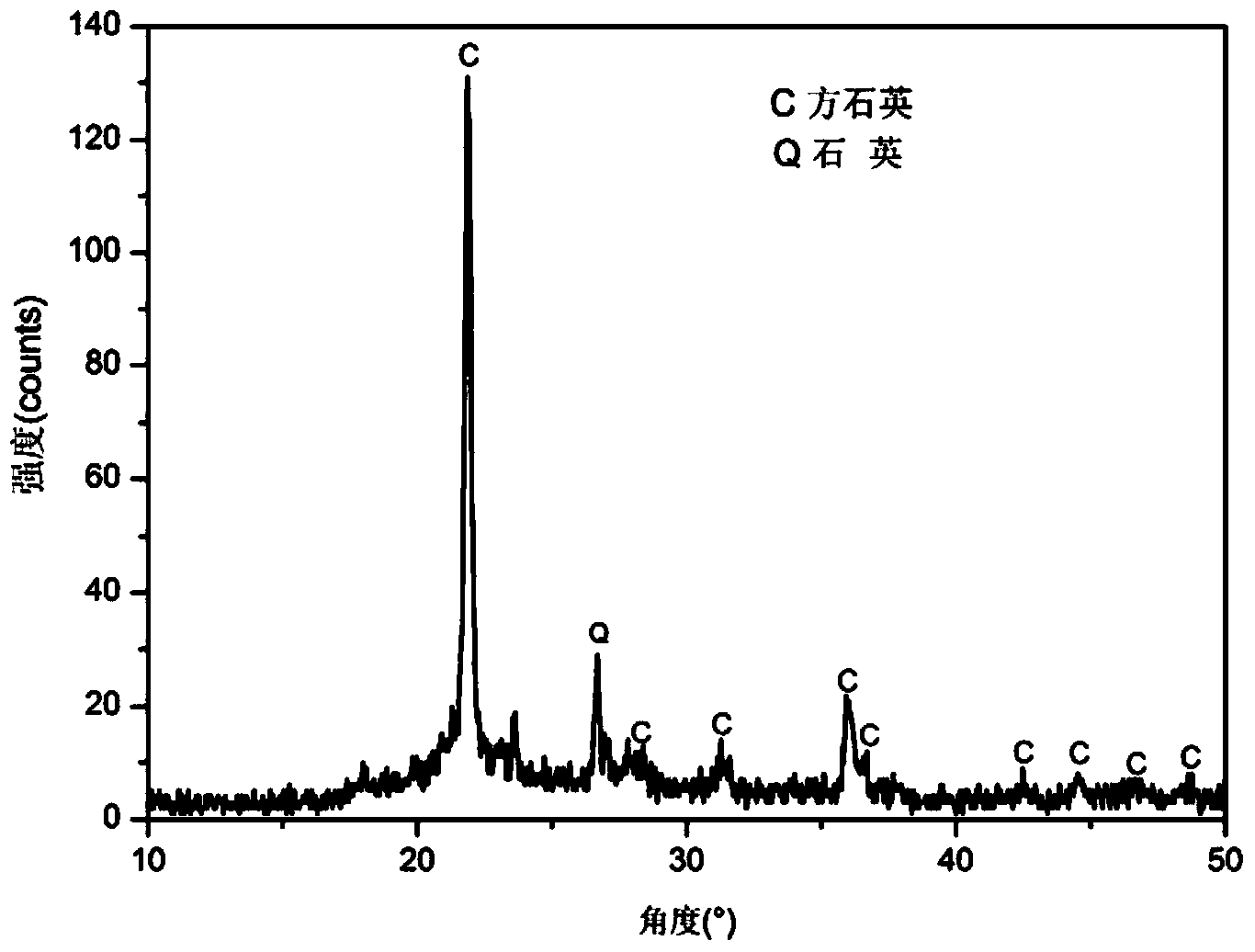
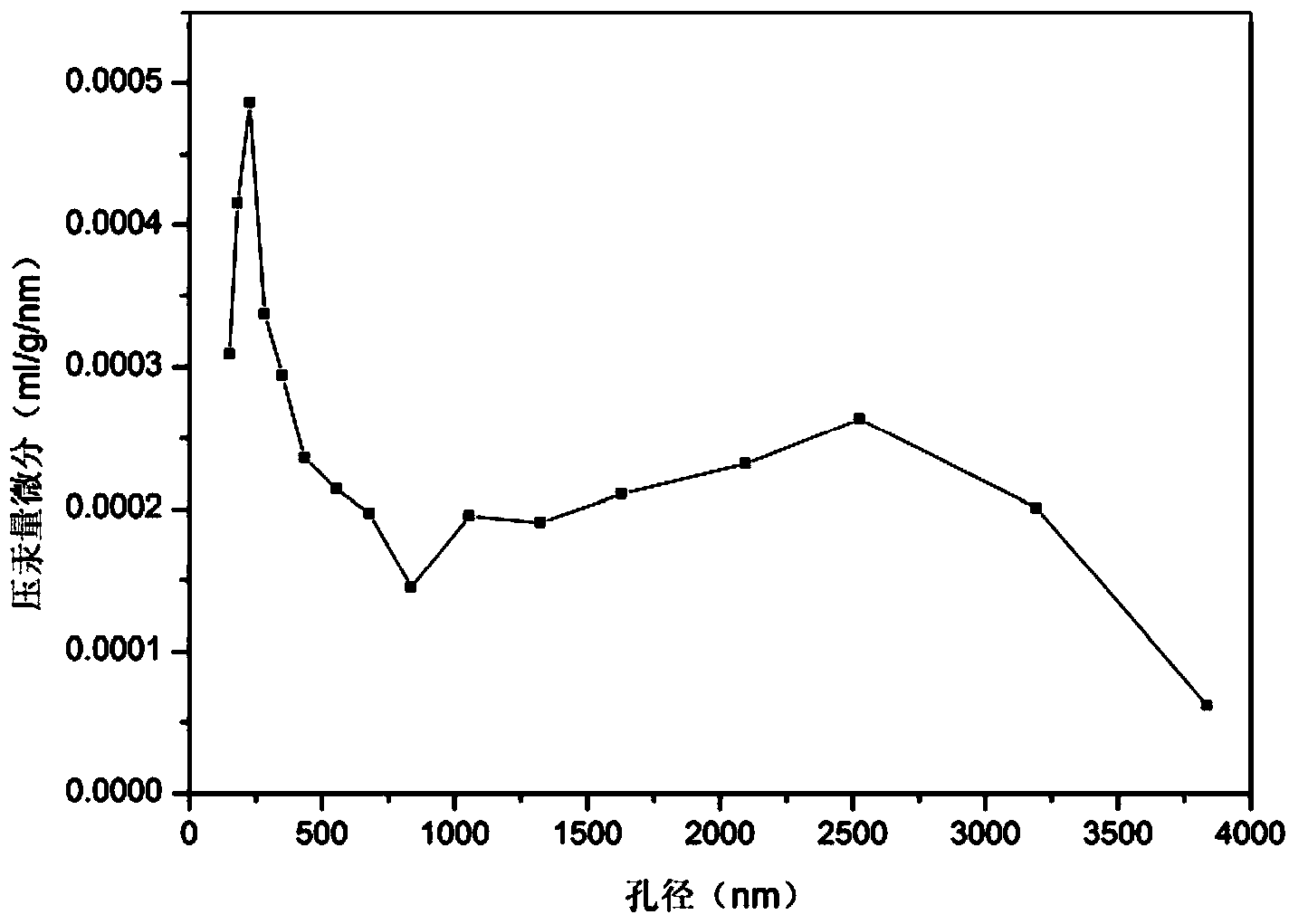
[0028] In this example, the mass fraction of sodium metasilicate in the additive solution is 7.20%, and diatomaceous earth is calcined at 600°C for 24 hours and all of them are converted into cristobalite. For specific diffraction results, refer to figure 1 . The generated cristobalite material has a porous structure with a pore size between 200-500nm, and the microscopic morphology of the material refers to figure 2 . Mercury intrusion experiment measured that the pore diameter of porous cristobalite material is mainly distributed between 250-300nm, belonging to nanoscale pores, and 2.5-...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Weigh 2.1g of sodium metasilicate nonahydrate, dissolve it in 10ml of ultra-pure water, add 2g of diatomaceous earth powder, stir the suspension thoroughly, put it in an oven at 80°C for 2 hours, and dry the dried solid in In a muffle furnace, the temperature was raised to 600° C. at a rate of 5° C. / min, and kept at 600° C. for 24 hours to obtain porous cristobalite.
[0031] In this example, the mass fraction of sodium metasilicate in the additive solution is 17.33%, and diatomaceous earth is calcined at 600°C for 24 hours to form cristobalite. For specific diffraction results, refer to Figure 4 . The thermal conductivity of the material at room temperature is 0.16W / m K, and the thermal diffusivity is 0.23mm 2 / s, good thermal insulation performance.
Embodiment 3
[0033] Weigh 0.8g of sodium metasilicate nonahydrate, dissolve it in 10ml of ultra-pure water, add 5g of diatomaceous earth powder, stir the suspension thoroughly, put it in an oven for 5 hours at 80°C, and dry it. The dried solid is placed in In a muffle furnace, the temperature was raised to 700° C. at a rate of 5° C. / min, and kept at 700° C. for 24 hours to obtain porous cristobalite.
[0034] In this example, the mass fraction of sodium metasilicate in the additive solution is 7.2%, and diatomaceous earth is calcined at 700°C for 24 hours to form cristobalite. For specific diffraction results, refer to Figure 5 . The thermal conductivity of the material at room temperature is 0.078W / m K, and the thermal diffusivity is 0.29mm 2 / s, in line with the requirements of thermal insulation materials, good thermal insulation performance.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com