Method and device for removing metal impurities in polycrystalline silicon by electron beam overheat smelting
A metal impurity, polysilicon technology, applied in the metallurgical field, can solve the problems of wasting electricity and long production time, and achieve the effect of reducing the purification process, the number of times, and the production cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
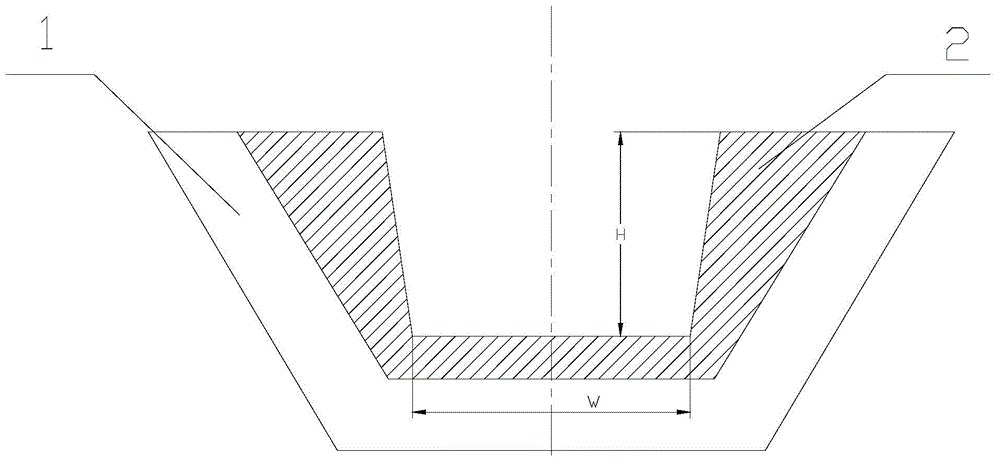
[0025] like figure 1 As shown, an electron beam melting polysilicon device includes a water-cooled melting crucible, the angle between the inner wall of the water-cooled copper crucible and the bottom of the water-cooled copper crucible is 105°, the water-cooled copper crucible is provided with a graphite bushing, and the graphite The outer surface of the liner is attached to the inner surface of the water-cooled copper crucible, the bottom of the graphite liner is horizontal to the bottom of the water-cooled copper crucible, and the angle between the side wall of the inner surface of the graphite liner and the bottom of the graphite liner is 95°.
[0026] The bottom thickness of the graphite bushing is 20mm.
[0027] The thickness of the thinnest part of the side wall of the graphite substrate is equal to 20mm.
[0028] The ratio between the inner height H of the graphite liner and the width W of the bottom is 1:1.
[0029] A method for removing metal impurities in polysili...
Embodiment 2
[0037] like figure 1 As shown, an electron beam melting polysilicon device includes a water-cooled melting crucible, the angle between the inner wall of the water-cooled copper crucible and the bottom of the water-cooled copper crucible is 110°, the water-cooled copper crucible is provided with a graphite bushing, and the graphite The outer surface of the liner is attached to the inner surface of the water-cooled copper crucible, the bottom of the graphite liner is horizontal to the bottom of the water-cooled copper crucible, and the angle between the side wall of the inner surface of the graphite liner and the bottom of the graphite liner is 97°.
[0038] The bottom thickness of the graphite bushing is 30mm.
[0039] The thickness of the thinnest part of the side wall of the graphite substrate is equal to 20mm.
[0040] The ratio between the inner height H of the graphite liner and the width W of the bottom is 1.5:1.
[0041] A method for removing metal impurities in polysi...
Embodiment 3
[0049] like figure 1 As shown, an electron beam melting polysilicon device includes a water-cooled melting crucible, the angle between the inner wall of the water-cooled copper crucible and the bottom of the water-cooled copper crucible is 120°, the water-cooled copper crucible is provided with a graphite bushing, and the graphite The outer surface of the liner is attached to the inner surface of the water-cooled copper crucible, the bottom of the graphite liner is horizontal to the bottom of the water-cooled copper crucible, and the included angle between the side wall of the inner surface of the graphite liner and the bottom of the graphite liner is 100°.
[0050] The bottom thickness of the graphite bushing is 40mm.
[0051] The thickness of the thinnest part of the side wall of the graphite substrate is equal to 20mm.
[0052] The ratio between the inner height H of the graphite liner and the width W of the bottom is 2:1.
[0053] A method for removing metal impurities i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com