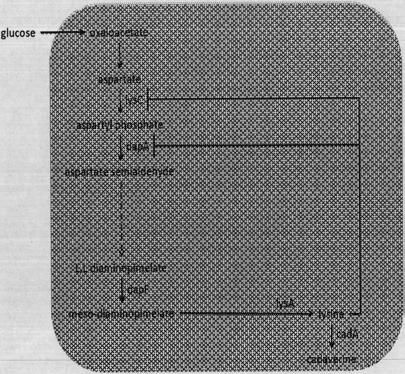
A method for producing fermented products using two or more microbial strains
A technology for microbial strains and fermented products is applied in the field of producing fermented products by using two or more microbial strains, and can solve the problems of complex steps, long metabolic steps, and low conversion rate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] The Escherichia coli strain with the preservation number CCTCC M2013100 was cultured in shake flasks. The shake flask was selected to be 500ml, the liquid volume was 30ml, the shaker speed was 180rpm, the fermentation temperature was 35°C, and the fermentation medium formula was as follows. The initial pH of the fermentation was 7.0. After inoculation, culture was carried out for 50 hours, and the strain Hafnia alvei which was capable of producing lysine decarboxylase produced by Kaiser Company was inserted, and the culture was continued at 30° C. for 30 hours.
[0019] Component
[0020] CuSO4
[0021] After the fermentation was finished, the content of 1,5-pentanediamine in the fermentation broth was determined to be 5.3 g / L.
Embodiment 2
[0023] The Escherichia coli MG1655 K12 purchased by Cathay Biological Company was genetically modified to weaken the enzyme activity of diaminopimelate decarboxylase, and then it was cultured in a shaker flask. The shaker flask was 500ml, the liquid volume was 30m1, the shaker speed was 180rpm, and the fermentation temperature was 35°C. The medium formulation is as follows. After inoculation, it was cultivated for 50 hours, and the strain Hafnia alvei, which can produce lysine decarboxylase from Cathay Company, was inserted, and the culture was continued for 30 hours at 30°C.
[0024] Component
[0025] After the fermentation ended, the content of 1,5-pentanediamine in the fermentation broth was 9.5g / L.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com