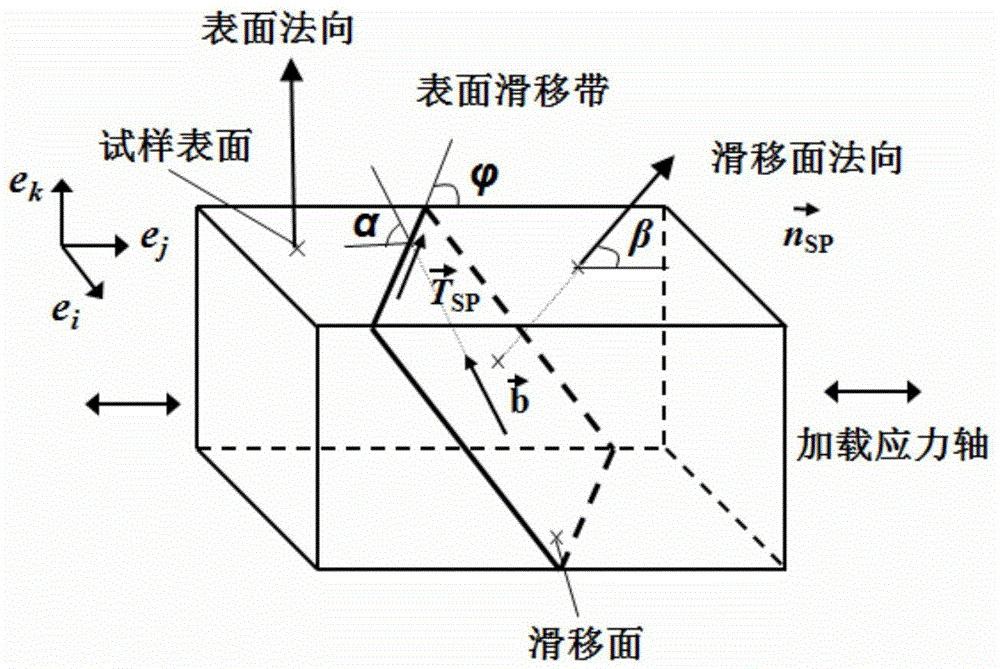
Method for determining polycrystalline metal deformation activation slippage system
A polycrystalline metal and slip technology, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices, instruments, and material analysis through optical means, can solve the inconvenience of orientation information corresponding to the grain position and damage morphology, the inability to determine the slip system, and the inability to realize Analysis of crystal orientation and damage morphology etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
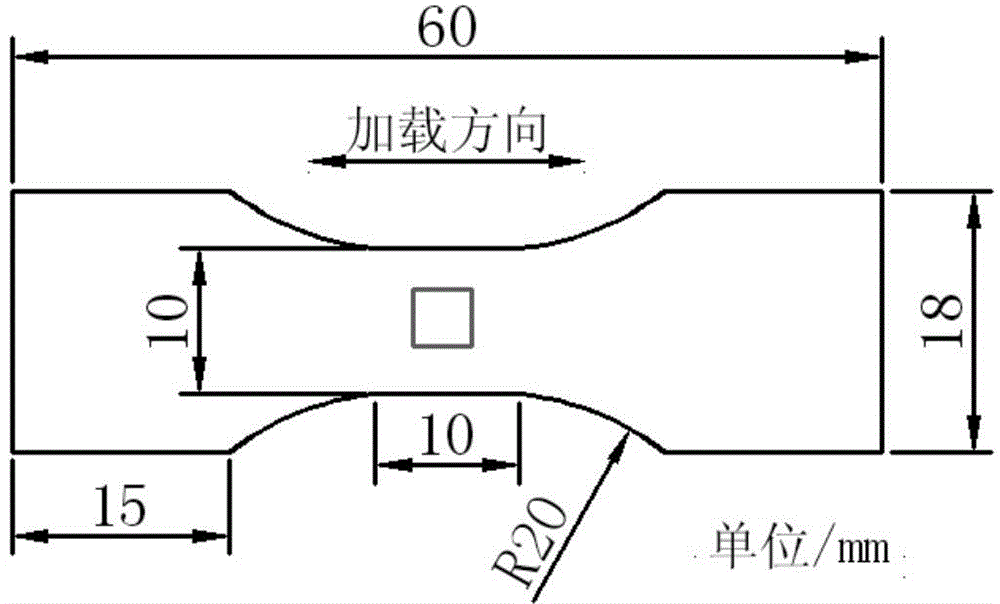
[0020] Step 1. Cut the Z2CND18.12N austenitic stainless steel wire into a thin sheet sample with a thickness of 1.8mm, such as figure 1 shown. Firstly, the surface of the sample was mechanically polished, from 200# sandpaper to 1000# sandpaper, then polished with a diamond abrasive paste with a particle size of 1.5 μm, and finally vibrated on a Buller Vibrome-2 vibration polishing machine for 2 hours to remove the residual stress on the surface. Prepare for subsequent EBSD analysis.
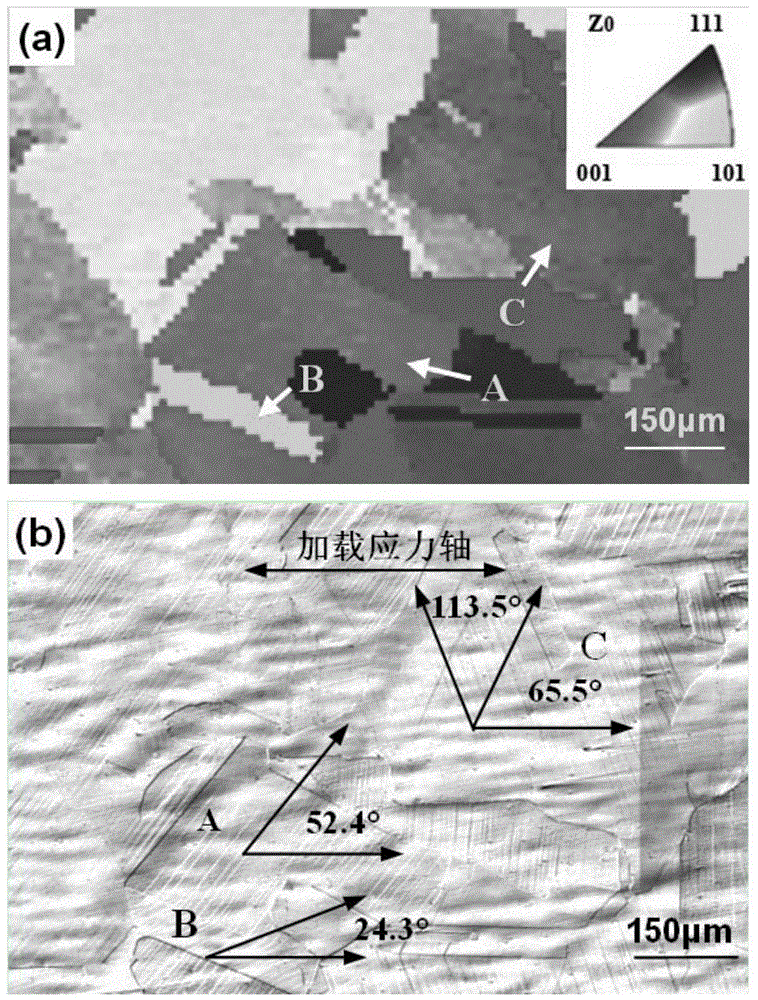
[0021] Step 2. Analyze the crystal orientation of the parallel segment region on a Zeiss Supra 55 field emission scanning electron microscope and an Oxford EBSD analyzer. The test step size is 10 μm, the magnification is 200×, and the crystal orientation distribution of a certain number of grains is obtained, such as figure 2 (a), where the crystal orientation indices of the three grains A, B, and C are [104], [516], and [235], respectively, and the orientation indices in the direction of the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com