Novel electrode structure of silicon solar cell
A solar cell and electrode structure technology, applied in the field of solar cells, can solve problems such as power reduction, broken grids, and burned out components, and achieve the effect of reducing battery costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
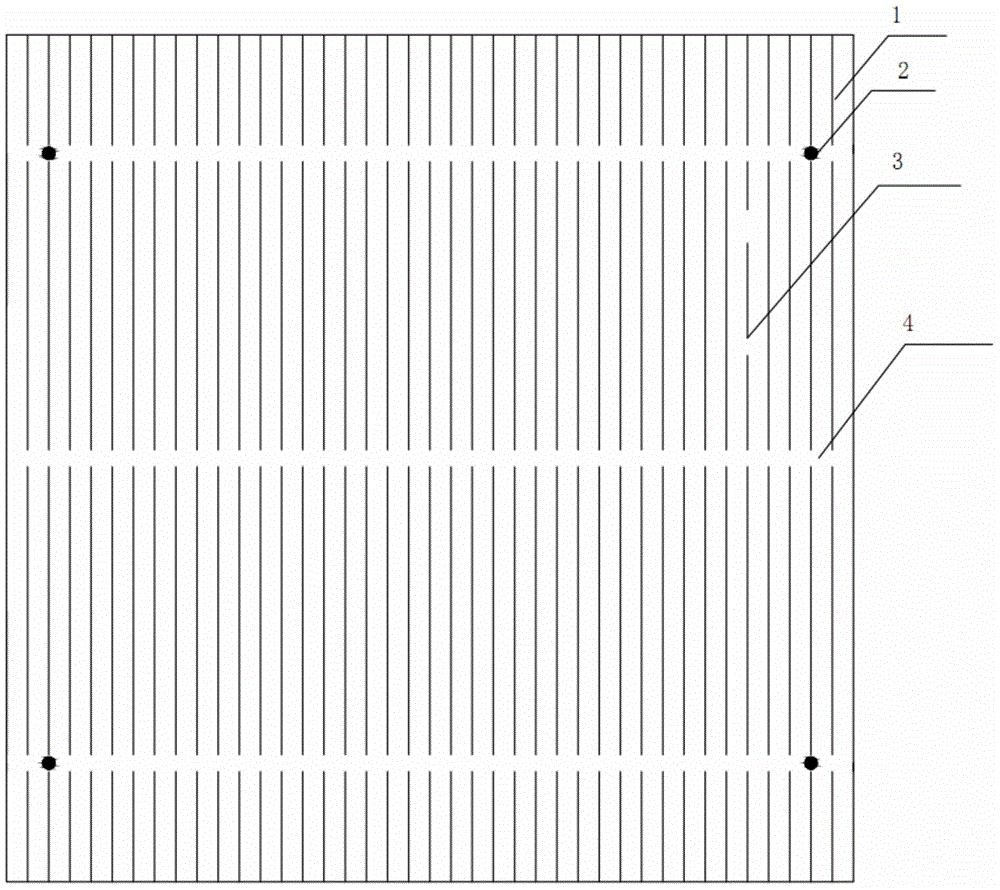
[0021] Such as figure 1 As shown, the front electrode of the crystalline silicon solar cell of the present invention includes three gaps 4 for busbar printing, two parallel sub-grids 5 and more than three vertical sub-grids 1; the gaps 4 for busbar printing are equidistant and Arranged in parallel, the parallel sub-grid lines 5 are parallel to the gap 4 for printing the main grid lines and located in the middle of the two gaps 4, the parallel sub-grid lines 5 connect two adjacent vertical sub-grid lines 1; The width of the grid printing gap 4 is 1.2 mm, the width of the main grid 6 is 1.5 mm, the width of the parallel auxiliary grid lines 5 is 0.05 mm, and the width of the vertical auxiliary grid lines 1 is 0.05 mm.
[0022] After this design, the photocurrent collected by the vertical sub-grid at 3 can be as follows image 3 As shown by the middle arrow, it can flow to the gap 4 for the printing of the main grid line through the adjacent vertical fine grid lines 1 connected ...
Embodiment 2
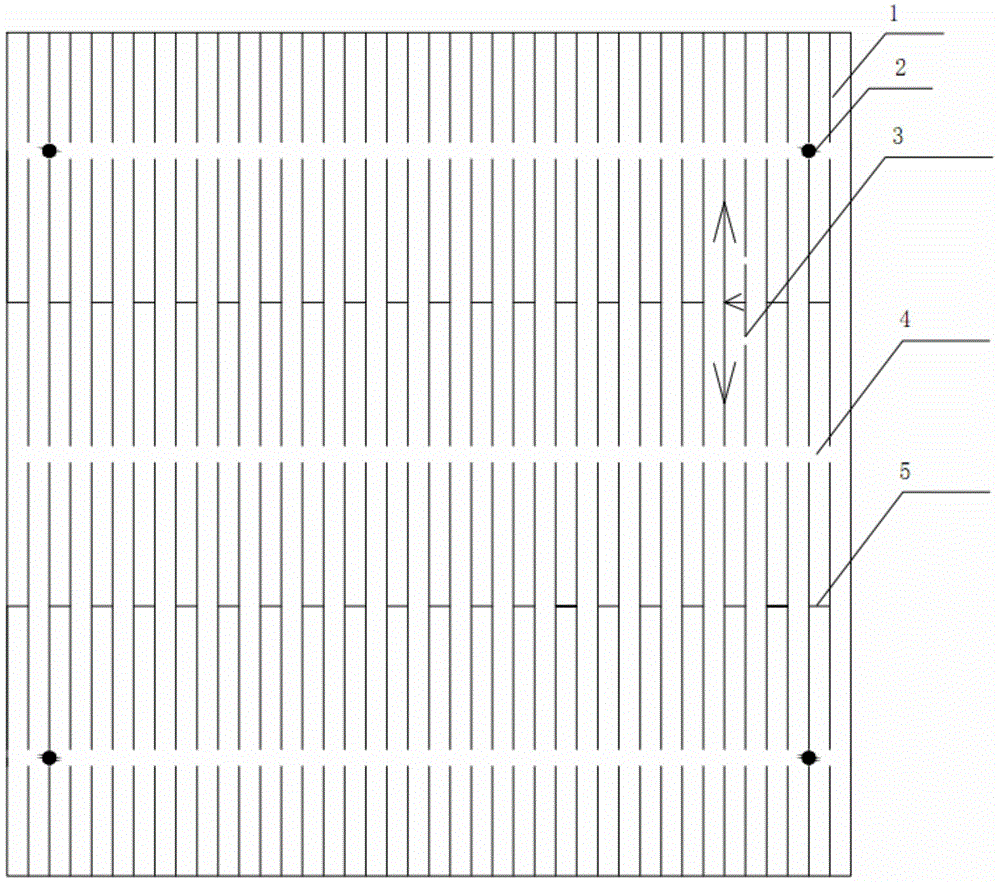
[0024] Through a large number of actual production, it can be seen that most of the broken grid positions in the printing process are concentrated between two adjacent main grids. Therefore, in order to effectively solve this problem, the Figure 4 The program design:
[0025] The front electrode of the crystalline silicon solar cell of the present invention includes three gaps 4 for busbar printing, four parallel sub-grids 5 and more than three vertical sub-grids 1; the gaps 4 for busbar printing are equidistant and parallel Arranged, the parallel sub-grid lines 5 are parallel to the gaps 4 for printing the main grid lines, and two parallel sub-grid lines 5 are equidistantly distributed between the two gaps 4 . The parallel sub-grid lines 5 are connected to two adjacent vertical sub-grid lines 1; the width of the gap 4 for printing the main grid lines is 1.2 mm, the width of the main grid lines 6 is 1.5 mm, and the width of the parallel sub-grid lines 5 is 0.05 mm. The width...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com