Mutation relaxation buffer layer for InGaAs probe with high In component
A buffer layer and detector technology, applied in semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as unfavorable epitaxial growth of high-quality materials, and achieve the effects of increasing diversity, reducing constraints, and good versatility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Suitable for In on GaAs substrate 0.8 Ga 0.2 Abrupt Relaxation Backgrading Buffers for As Detectors
[0022] (1) GaAs single crystal material with [100] crystal orientation is used as the substrate, and InAs with a thickness of about 0.5 μm is first grown on the substrate as a sudden relaxation layer by conventional molecular beam epitaxy method to obtain a relatively flat surface;
[0023] (2) Re-grow a gradient buffer layer with reverse graded In composition, respectively: In with a thickness of 0.4 μm 0.9 al 0.1 As layer, In with a thickness of 0.4 μm 0.85 al 0.15 As layer, In with a thickness of 0.4 μm 0.8 al 0.2 As layer, which is the required suitable In 0.8 Ga 0.2 Abrupt-relaxation reverse-graded buffer layer structure for As detectors.
Embodiment 2
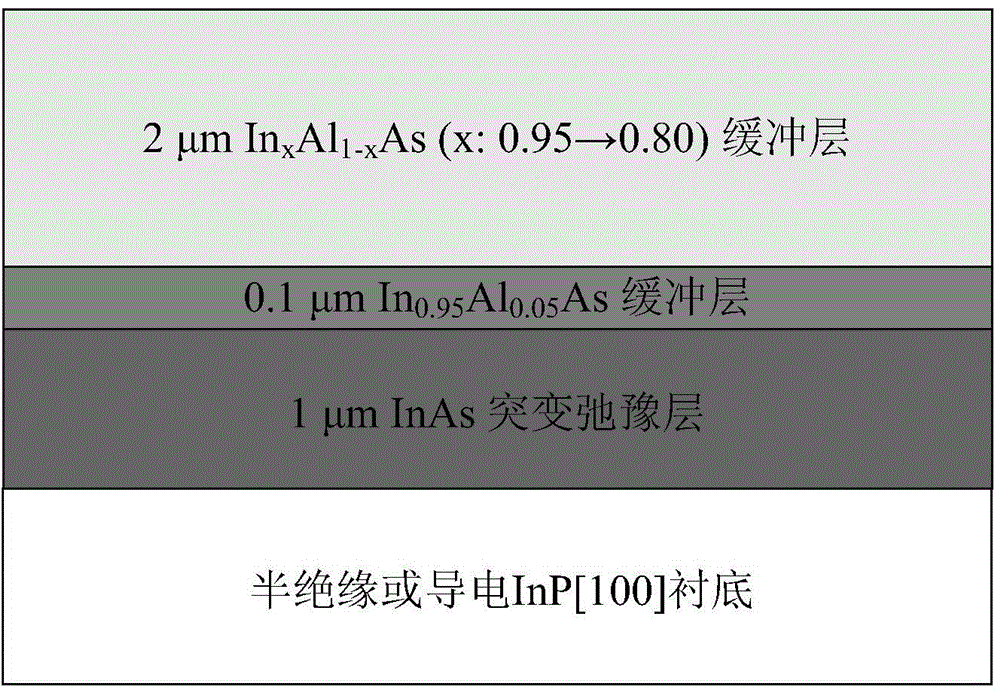
[0025] InP substrate suitable for In 0.8 Ga 0.2 Abrupt Relaxation Backgrading Buffers for As Detectors
[0026] (1) Using the InP single crystal material with [100] crystal orientation as the substrate, and using the conventional molecular beam epitaxy method to first grow InAs with a thickness of about 1 μm on the substrate as a sudden relaxation layer to obtain a relatively flat surface;
[0027] (2) Then grow In with a thickness of 0.1 μm 0.95 al 0.05 AS layer;
[0028] (3) Re-grow In with a thickness of 2 μm and reverse continuous gradient of In composition x al 1-x As buffer layer, where x is reversely graded from 0.95 to 0.8, and its mismatch rate is about 0.67% / μm, this structure is suitable for InP substrate 0.8 Ga 0.2 Abrupt-relaxation reverse-graded buffer layer structure for As detectors.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com