An enzyme composite and a method for regulating nuclease sequence selectivity
A nuclease, selective technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, which can solve problems such as heavy workload and lack of versatility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Embodiment 1
[0031] In this embodiment, the target DNA strand sequence is:
[0032] 5'-TAT CTG CAC TAG ATG CAC CTT-3';
[0033] The unrelated DNA strand sequence is:
[0034] 5'-CGGAAGACAGATGCUAAGTGCTTGACCTTCCG-3';
[0035] The sequence of the all-thio DNA template strand (S-DNA) of the synthetic target DNA sequence is:
[0036] 5'-AAAAAAAAAAAGGTGCATCTAGTGCAGATA-3';
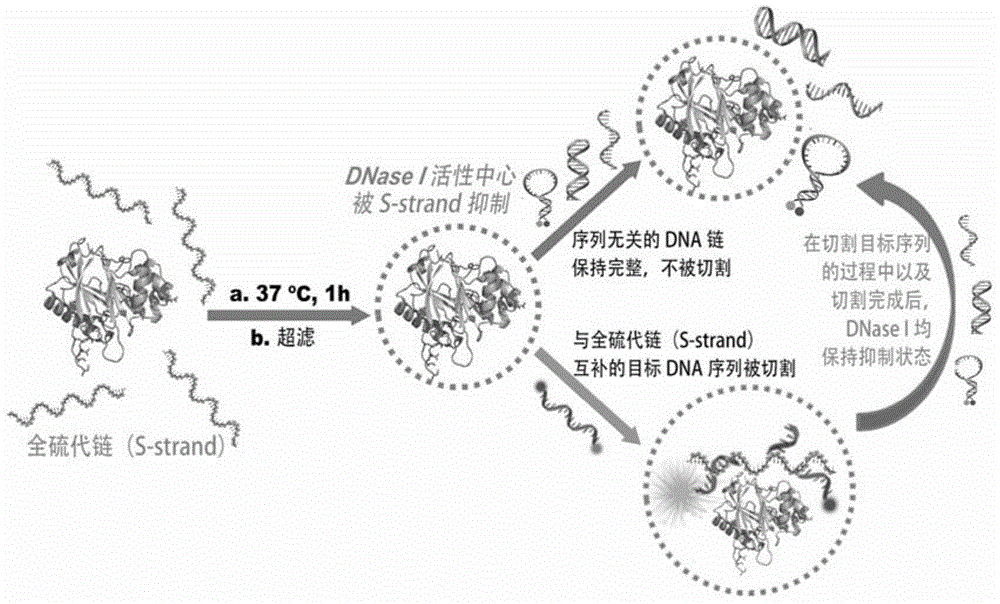
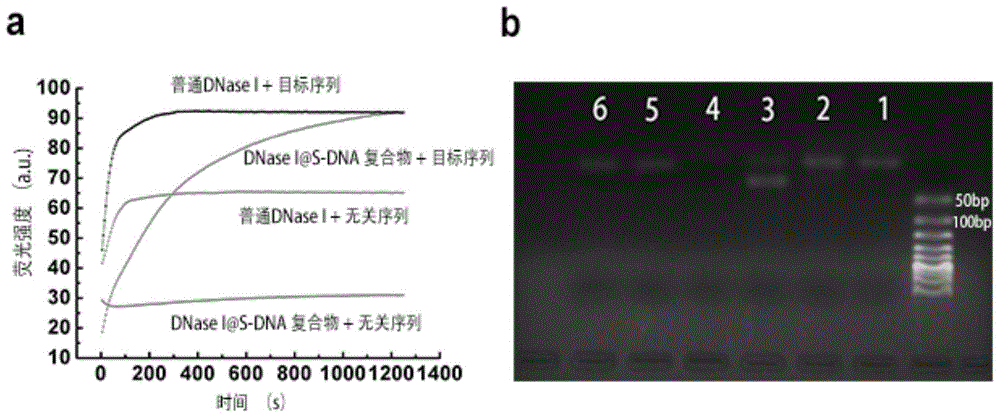
[0037] For the principle of the combination of the above S-DNA and DNase I to form DNase IS-DNA and sequence selectivity, see figure 1 .
[0038] In the present invention, in order to effectively indicate the cleavage of DNase I / RNase A to the target DNA / RNA sequence and other irrelevant sequences to be cleaved, the applicant has used two methods:
[0039] 1) Fluorescent probe indication method. Such as figure 1 As shown in , both the intended cleavage target sequence and the unrelated sequence are labeled with a fluorescent group and a quencher group, and high-efficiency FRET can occur between t...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Embodiment 2
[0062] In this example,
[0063] The target RNA strand sequence is: 5'-UAUCUGCACUAGAUGCACCUU-3';
[0064] The unrelated RNA strand sequence is: 5'-UUGUACUACACAAAAGUACUG-3';
[0065] The synthetic all-thio-RNA sequence is:
[0066] 5'-AUACAGCUAAGGUGCAUCUAGUGCAGAUA-3'.
[0067] The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0068] 1) Mix 1 μL of 2 mg / mL RNase A and 1.60 nmol of all-thio-RNA strands in 50 μL of buffer, which consists of: 50 mM sodium phosphate, 150 mM sodium chloride, pH 7.2. Warm the solution at 37 ° C Incubate for 1 hour.
[0069] 2) The solution obtained in 1) was ultrafiltered using an ultrafiltration tube with a cut-off molecular weight of 30 kD and a treatment volume of 500 μL. The buffer used for ultrafiltration is the same as that used in 1). The rotating speed used for the first ultrafiltration is 5000g, and the ultrafiltration time is 15min. The second ultrafiltration rotating speed is 3000g, and the time is 15min.
...
Embodiment 3
[0089] The applicant has used the SPDP method to carry out covalent coupling reaction after DNase I is combined with S-DNA, and the reaction steps are as follows:
[0090]1. Use 0.05M sodium phosphate buffer (containing 0.15M sodium chloride, pH 7.2) to prepare a DNase I solution with a concentration of 10mg / mL. To 1 mL of the DNase I solution, 25 μL of 6.2 mg / mL SPDP solution dissolved in DMSO was added, and left overnight at room temperature.
[0091] 2. Ultrafiltration to remove excess SPDP, the buffer solution used for ultrafiltration consists of: 0.05M sodium phosphate, 0.15M sodium chloride, 0.01M EDTA, pH 7.2.
[0092] 3. Mix the S-DNA labeled with -SH at the end and the DNase I solution obtained in step 2 at a molar ratio of 1:1, and leave it overnight at room temperature.
[0093] 6. Ultrafiltration to remove free DNase I and S-DNA.
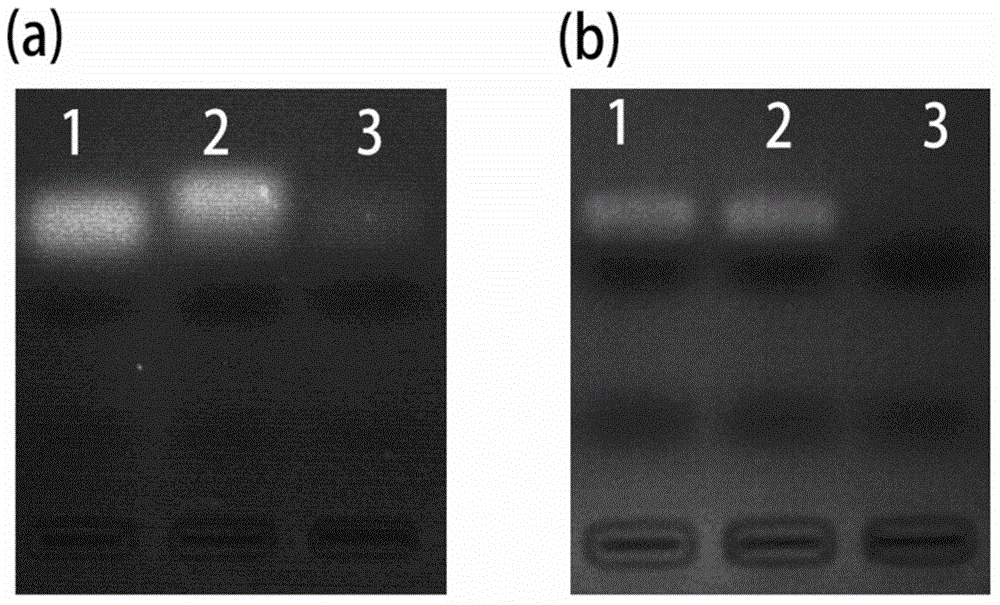
[0094] The DNase IS-DNA covalent complex prepared by the above steps also exhibits specific cleavage of the S-DNA complementary stran...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com