Heat treatment process capable of improving low temperature impact toughness of 9Ni steel
A low-temperature impact toughness and process technology, which is applied in the field of heat treatment process to improve the low-temperature impact toughness of 9Ni steel, can solve the problems of small impact toughness margin and affect the safety of 9Ni steel, achieve uniform distribution, reduce strength, and improve thermal stability. sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
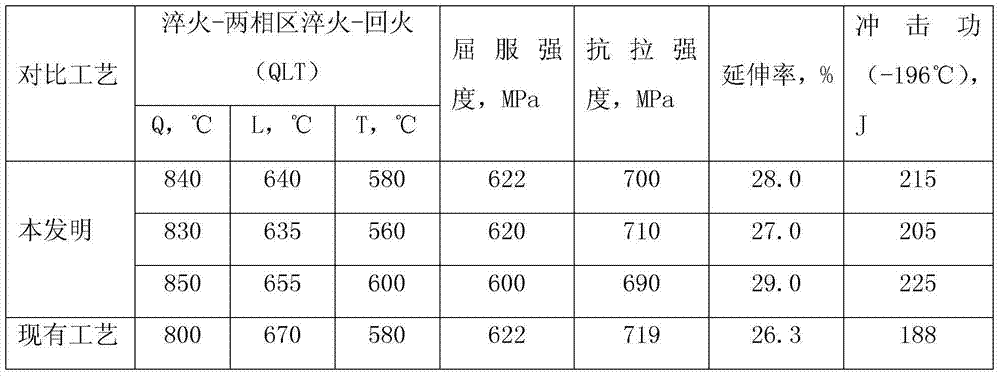
[0019] This embodiment is a manufacturing method of a heat treatment process for improving the low-temperature impact toughness of 9Ni steel. It adopts a quenching-two-phase zone quenching-tempering (QLT) process, quenching at 830-850°C, sub-temperature quenching at 635-655°C, and quenching at 560- Tempering at 600°C; Quenching heating is carried out in the normalizing furnace, completed in the process of water cooling, and tempering heating is carried out in the tempering furnace, completed in the process of air cooling. The yield strength of the 9Ni steel manufactured in this embodiment is 590-630MPa, the tensile strength is 680-720MPa, the elongation is 26.0-30.0%, and the impact energy is 200-230J. The specific process comparison is shown in Table 1:
[0020] Table 1 Mechanical properties after enlarging the QL temperature difference
[0021]
Embodiment 2
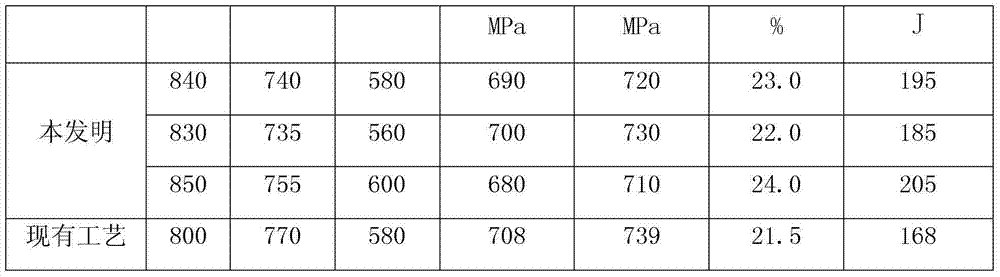
[0023] This embodiment is a manufacturing method of heat treatment process for improving the low temperature impact toughness of 9Ni steel. It adopts the quenching-quenching-tempering (QQT) process, quenching at 830-850°C, secondary quenching at 735-755°C, and tempering at 560-600°C. Fire; quenching heating is carried out in the normalizing furnace, completed in the water cooling process, and tempering heating is carried out in the tempering furnace, completed in the air cooling process. The yield strength of the 9Ni steel manufactured in this embodiment is 670-710MPa, the tensile strength is 700-740MPa, the elongation is 21.0-25.0%, and the impact energy is 180-210J. The specific process comparison is shown in Table 2:
[0024] Table 2 Mechanical properties after enlarging the QQ temperature difference
[0025]
[0026]
Embodiment 3
[0028] This example is a manufacturing method of a heat treatment process for improving the low-temperature impact toughness of 9Ni steel. It adopts the normalizing-normalizing-tempering (NNT) process, normalizing at 830-850°C, secondary normalizing at 735-755°C, and 560°C. Tempering at -600°C; normalizing heating is carried out in the normalizing furnace and completed during the air cooling process, and tempering heating is carried out in the tempering furnace and completed during the air cooling process. The yield strength of the 9Ni steel manufactured in this embodiment is 640-680MPa, the tensile strength is 670-710MPa, the elongation is 20.0-24.0%, and the impact energy is 150-180J. The specific process comparison is shown in Table 3:
[0029] Table 3 Mechanical properties after enlarging the temperature difference of NN
[0030]
[0031] Due to the adoption of the above-mentioned technical scheme, the 9Ni steel manufactured in this specific embodiment, by expanding th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Impact energy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com