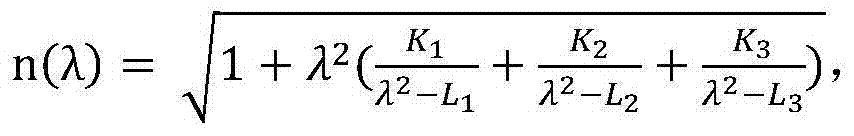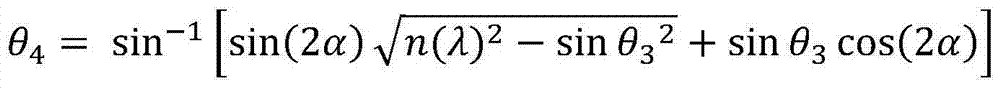Linear frequency domain optical grating and design method thereof
A design method, grating technology, applied in the field of optics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
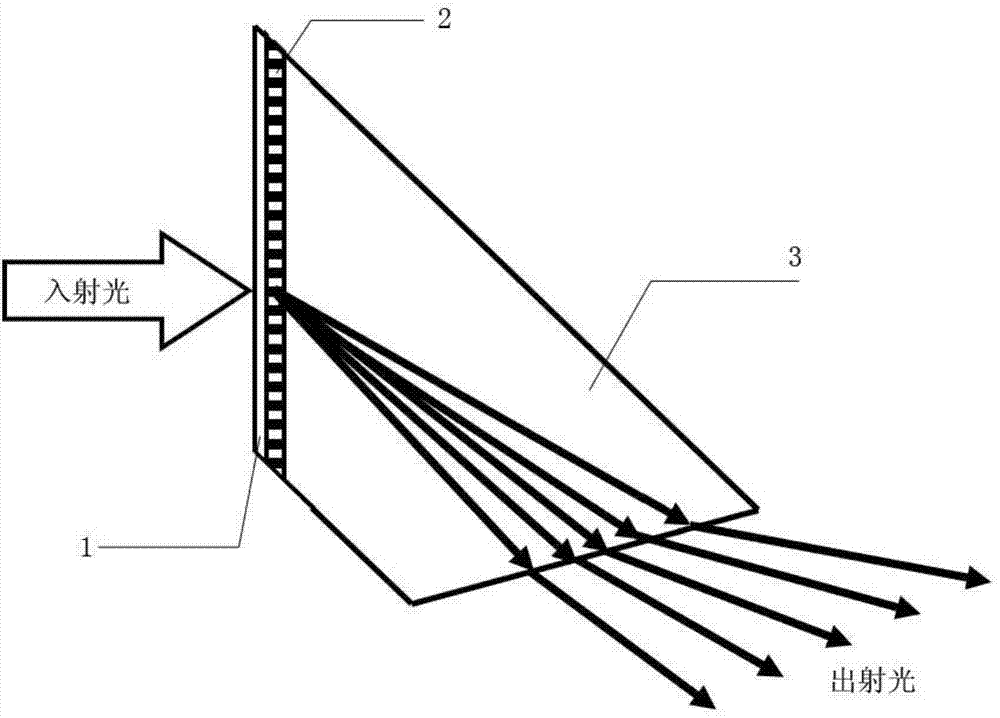
[0034] Such as figure 1 As shown, a design method of a linear frequency domain grating of the present invention includes attaching a diffractive medium to a prism to form a diffractive layer, and then covering with an optical glass protective layer; by
[0035] no 1 sinθ 1 =n 2 sinθ 2
[0036] Obtain the exit angle of the incident light after passing through the optical glass protective layer, where n 1 is the refractive index of the first medium, n 2 is the refractive index of the second medium, where the first medium can be air, and the second medium here is an optical glass protective layer, θ 1 is the incident angle of the incident light incident on the optical glass protective layer, θ 2 is the exit angle of the incident light after passing through the optical glass protective layer, θ 2 is also the incident angle when the incident light enters the diffractive layer; then by the grating equation:
[0037] λ·μ·m=sinθ 2 +sinθ 3
[0038] Obtain the diffraction ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com