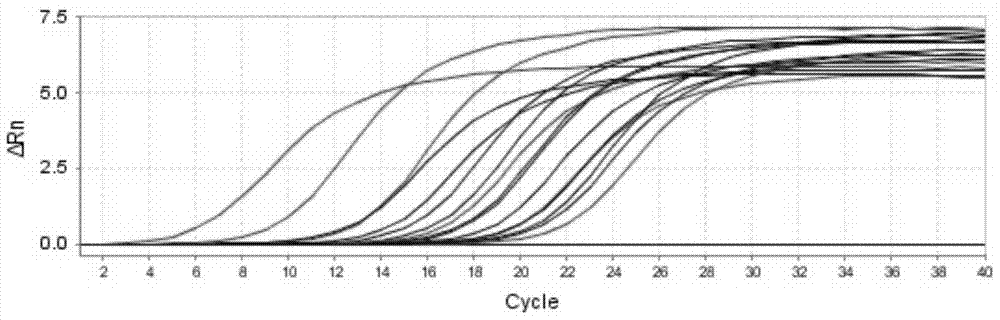
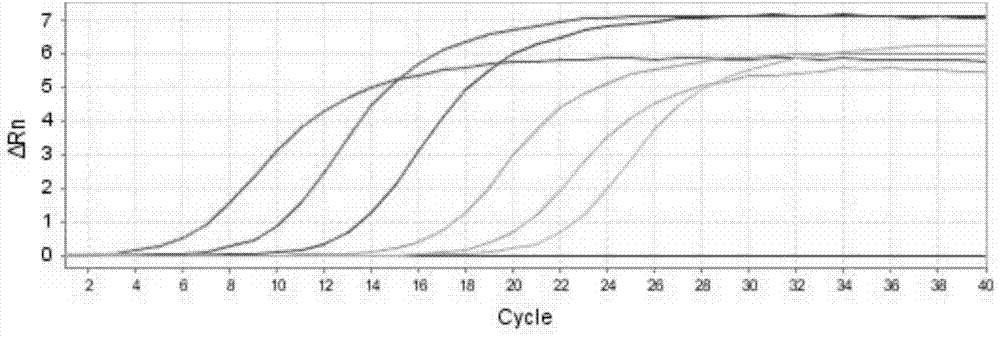
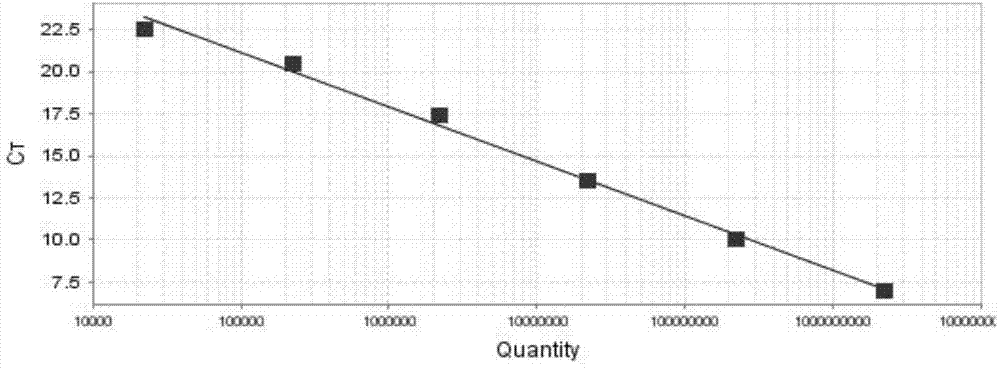
Real-time fluorescent quantitative identification method of Tilletia controversa Kuhn, and kit thereof
A real-time fluorescent quantitative and identification method technology, applied in the field of real-time fluorescent quantitative identification of wheat smut, can solve the problems of small proportion, no signal amplification, low concentration, etc., and achieve the effect of avoiding interference and competition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0036] 1. Experimental main reagents
[0037] Table I List of reagents used
[0038]
[0039] Unless otherwise specified, the reagents used in the present invention are commonly used reagents in the art.
[0040] 2. The main instruments of the experiment
[0041] Table II List of equipment used
[0042] equipment name Instrument model factory Vortex shaker QL-902 Haimen Qilin Bell Instrument Manufacturing Co., Ltd. centrifuge Centrifuge 5415D Eppendorf spectrophotometer NANODROP 2000 Therno scientific Fluorescent quantitative PCR instrument ABI7500 Applied Biosystems
[0043] 3. Experimental material of the present invention:
[0044] Five strains of T. controversa Kühn (TCK) came from the United States; two strains of T. foetida Liro (TFL) came from the Czech Republic, and the other 1 indivual country of originDifferent areas in the country were collected by the wheat disease group of the Institute of Plant Pr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com