Dual cycle construction method suitable for high code rate quasi cyclic-low density parity check (QC-LDPC) code
A construction method and a double-cycle technology, applied in the field of low-density parity-check codes, can solve problems such as increasing column weight, increasing the minimum code distance, limiting the number of rows and maximum column weight, etc., and achieving the effect of improving codeword performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0049] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
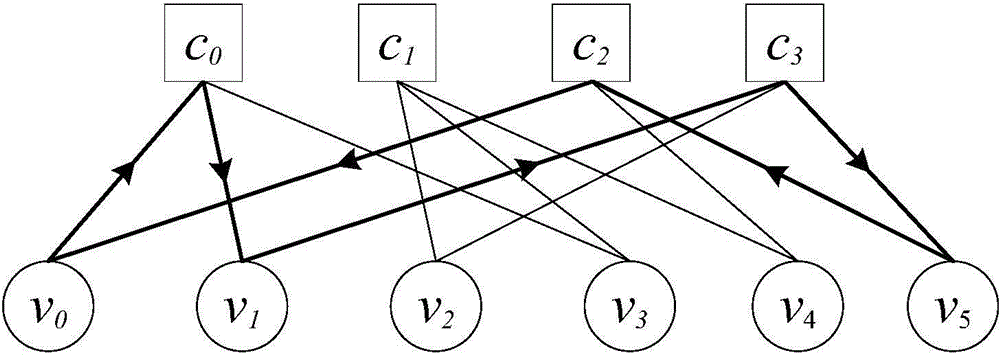
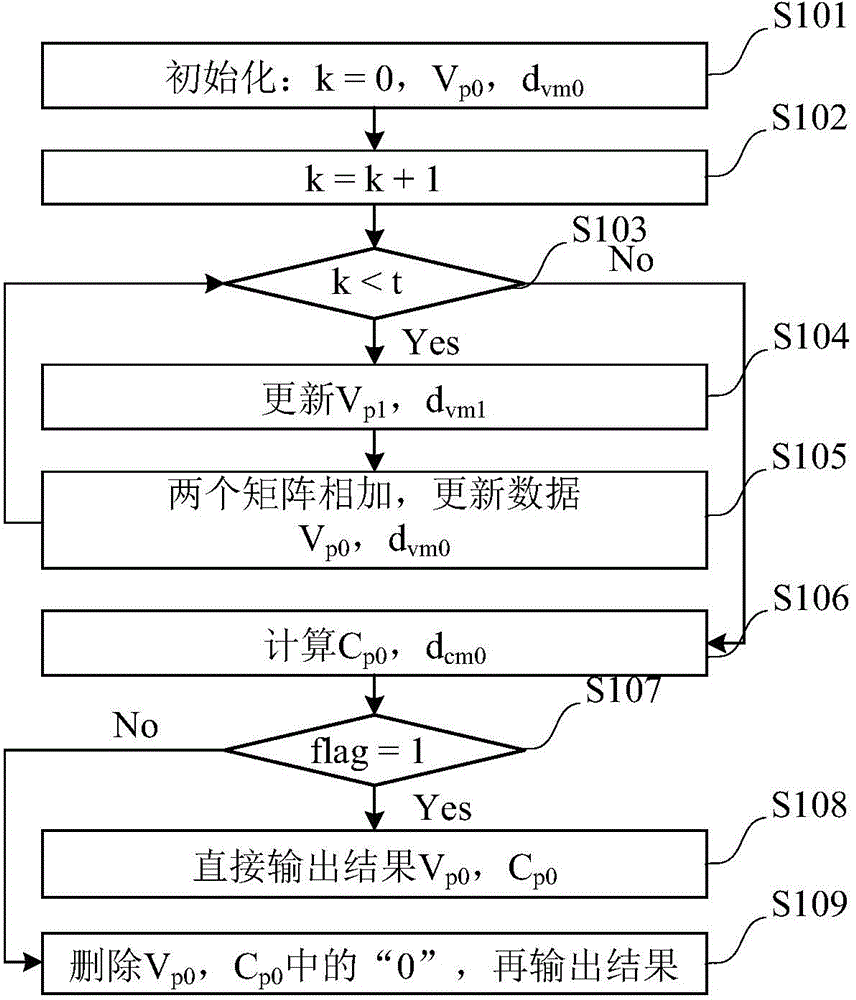
[0050] Known QC-LDPC code base matrix column number N, code rate R, row number M=N(1-R), column weight is λ, row weight is ρ, maximum column weight and maximum row weight are respectively λ m and ρ m express. Use the DE algorithm to traverse and optimize the edge distribution of the basis matrix, and then construct the basis matrix H through the PEG-ACE algorithm M×N . Column weight λ of the current first variable node m0 = M, assuming we still need to increase the column weight of the first variable node to λ m (Mm ≤2M). So for the basis matrix H M×N The processing steps are as follows:
[0051] 1) Construct a size with H M×N The same all-zero matrix H 0 The first column of the matrix (λ m -M) element set "1";
[0052] 2) put H M×N and H 0 These two matrices are simply merged into a single matrix H of size 2(MxN) 2(MxN) , using the construction method of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com