Process for intensifying anaerobic degradation and transformation of azo dyes based on breath of microbial electrode
A microbial electrode and microbial electrochemistry technology, which is applied in the field of anaerobic degradation and transformation of azo dyes based on microbial electrode respiration enhancement, can solve the problems of obvious treatment effect of easily degradable organic matter, long start-up period and low decolorization rate, and achieves the distribution of microbial populations. Reasonable, good hydraulic conditions, and enhanced biodegradation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] The artificially prepared nutrient solution is used as the influent, and the composition of 1L influent nutrient solution is:
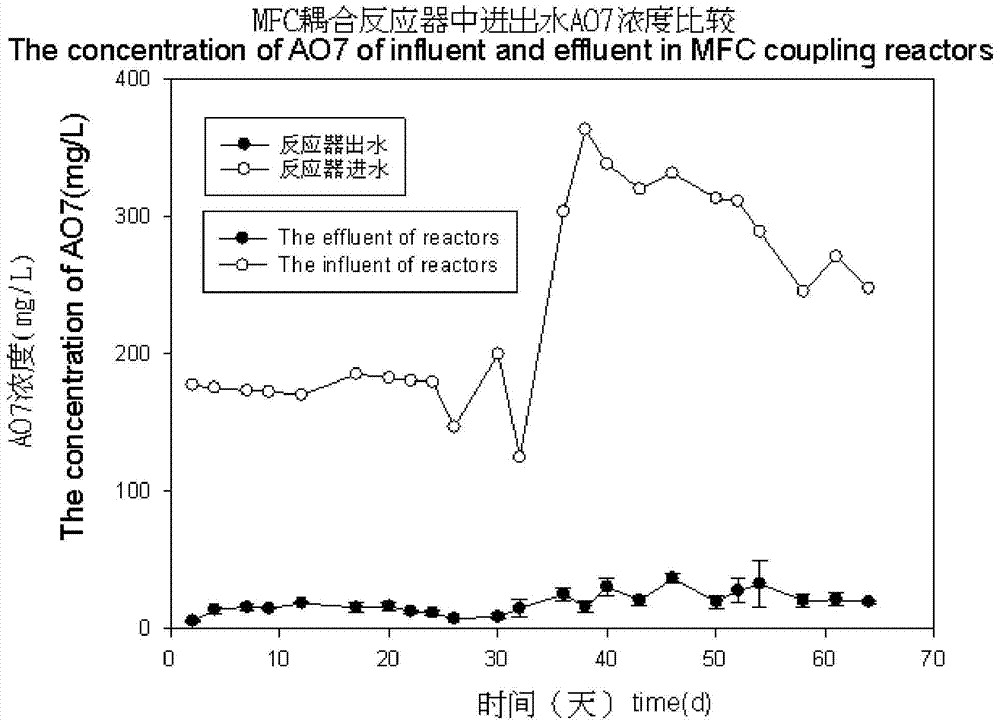
[0032] 0.393g CH3COONa, 0.407g NH4Cl, 0.600g Na2HPO4, 0.300gKH2PO4, 0.500g NaCl, 0.100g MgSO4 7H2O, 0.015g CaCl2 7H2O, the azo dye is Orange II (acid orange 7).
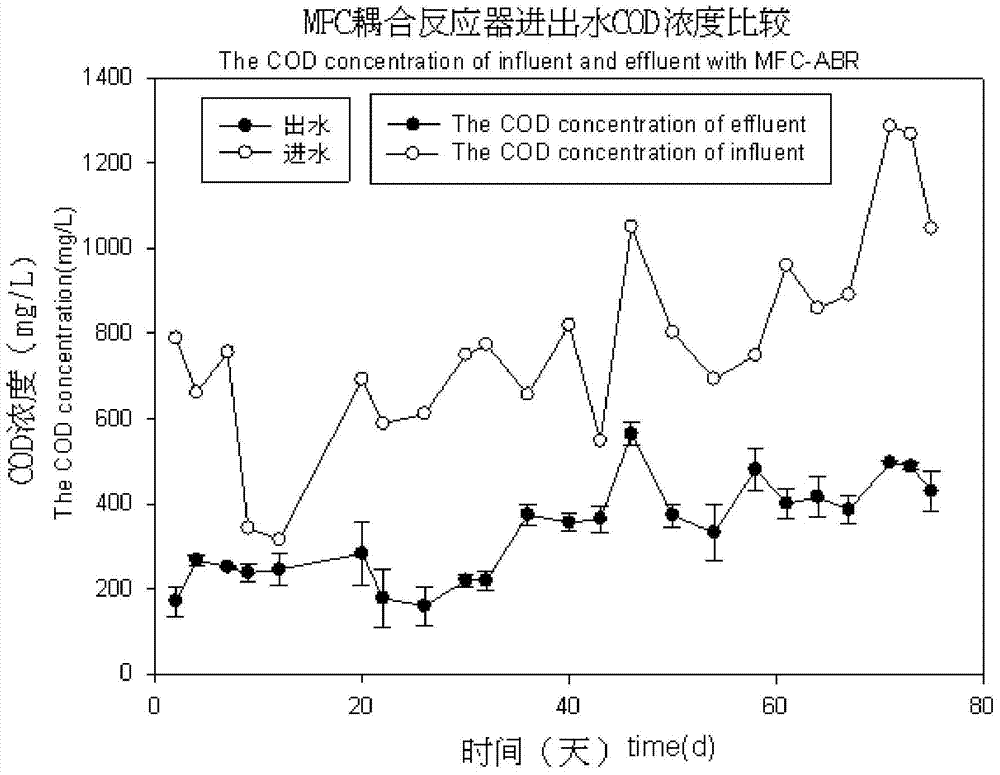
[0033] In the first 27 days, the acid orange 7 concentration in the influent water was 200 mg / L.
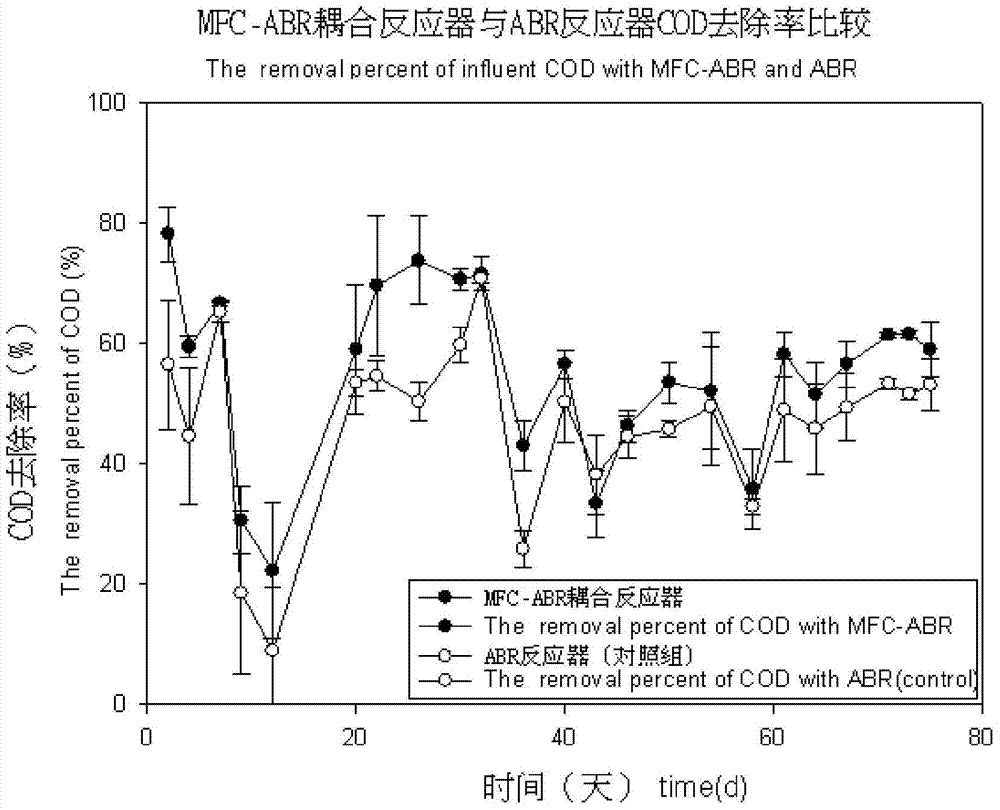
[0034] The microbial electrochemical system is placed in an anaerobic reactor to form a coupled reactor, such as figure 1 shown.
[0035] Then inoculate anaerobic sludge at a room temperature not higher than 35°C, adjust the pH value to 7-8, the hydraulic retention time to 1-3 days, the concentration of influent azo dyes to 200-800mg / L, and the influent COD concentration to 500- After 800 mg / L, the azo dye wastewater is filtered through a sieve with a diameter of 0.15 mm in turn, precipitated in the primary sedimentation adjustment tank, and enters the coupling reactor through the acti...
Embodiment 2
[0039] The nutrient solution is artificially configured as water intake, and the method is the same as in Example 1.
[0040] The acid orange 7 concentration in the influent water was 400mg / L on the 28th-60th day.
[0041] The microbial electrochemical system is placed in an anaerobic reactor to form a coupled reactor, such as figure 1 shown.
[0042]Then inoculate anaerobic sludge at a room temperature not higher than 35°C, adjust the pH value to 7-8, the hydraulic retention time to 1-3 days, the concentration of azo dyes in the influent to 200-800mg / L, and the influent COD concentration to 700- After 1000mg / L, the azo dye wastewater is filtered through a screen with a hole diameter of 1.0mm, precipitated in the primary sedimentation adjustment tank, and enters the coupling reactor through the action of a peristaltic pump. In the coupling reactor, the azo dye wastewater is drained The decolorization is obvious after the initial degradation of the oxygen reactor; at the same...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com