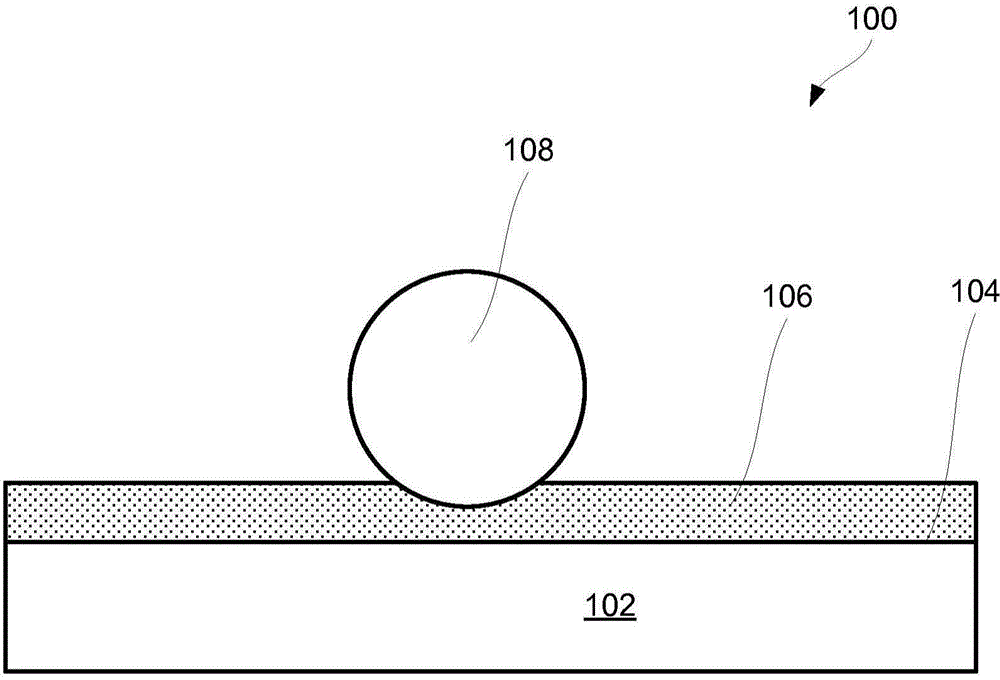
Thermally conductive flexible adhesive material for aerospace applications
An adhesive, thermal conductivity technology, applied in the direction of adhesive, application, adhesive type, etc., can solve problems such as high thermal conductivity values
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
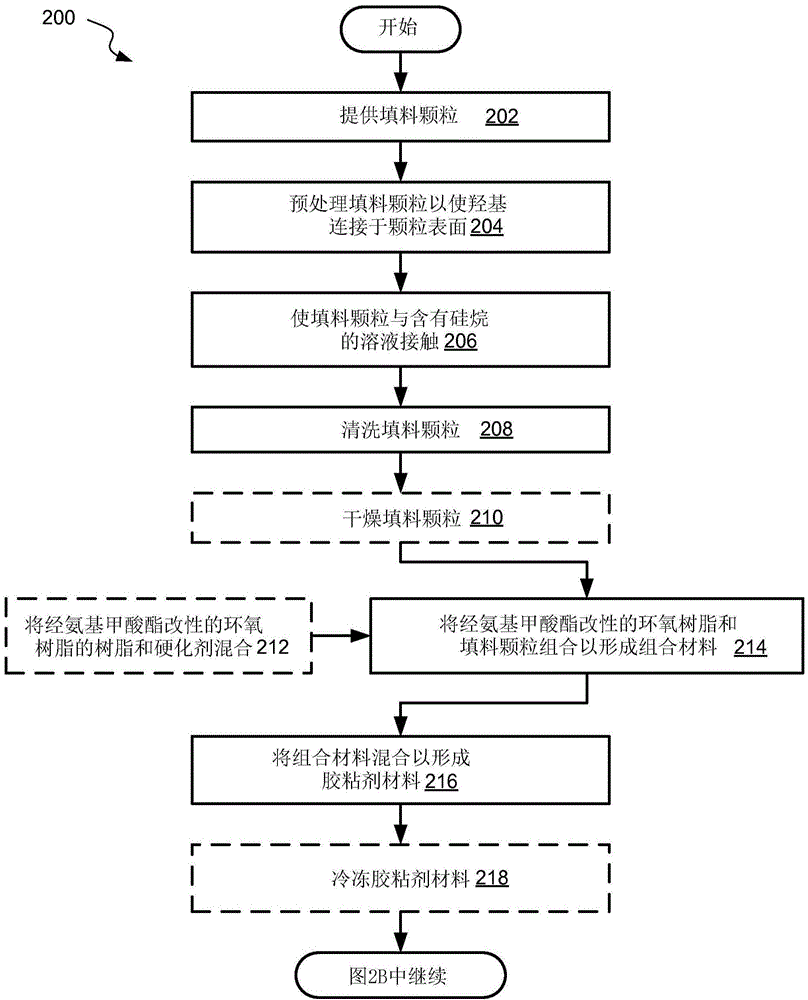
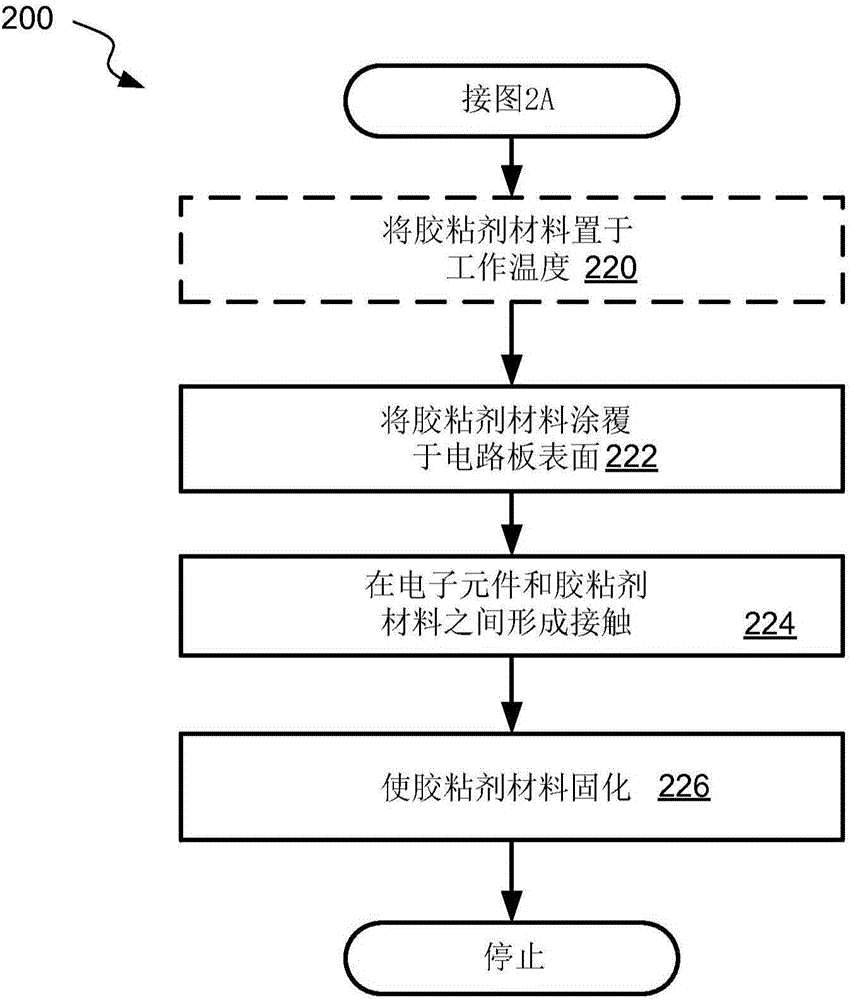
[0067] Figure 2A and 2B A process flow diagram corresponding to a method 200 of forming a thermally conductive flexible bond for circuit boards for unmanned spacecraft and other aerospace applications is shown in accordance with some aspects. The thermally conductive flexible bond is formed using a thermally conductive flexible adhesive material, often referred to herein as the adhesive material. In some aspects, a method of preparing a thermally conductive flexible adhesive material and / or components thereof is also part of method 200 . Alternatively, pre-prepared adhesive material may be used in method 200 without upstream operations. For example, a frozen premix can be provided, and method 200 can begin at process 220, where the frozen premix can be brought to an operating temperature.
[0068] Furthermore, it is possible to perform a method of making a thermally conductive flexible adhesive without subsequently using this adhesive by the same entity. For example, trea...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tap density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com