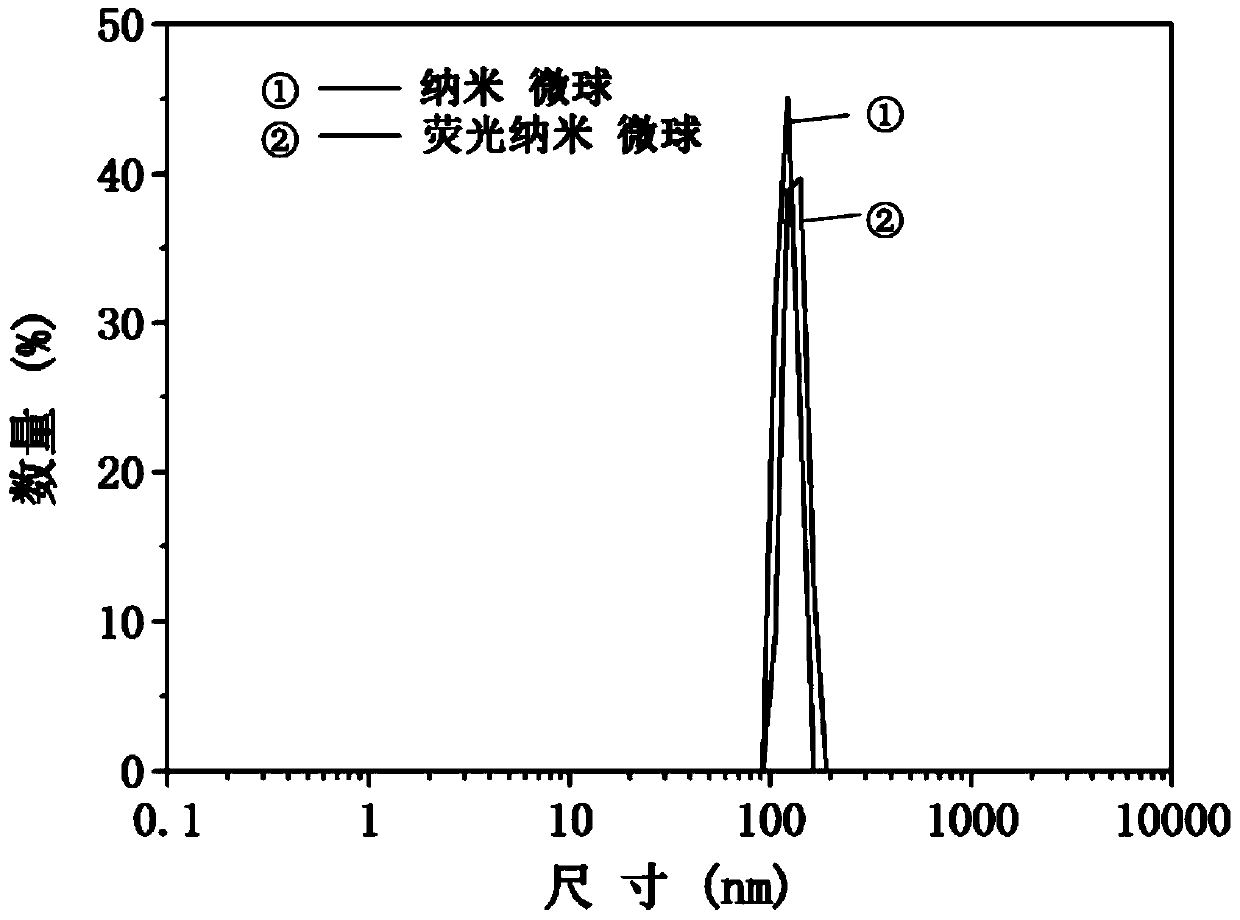
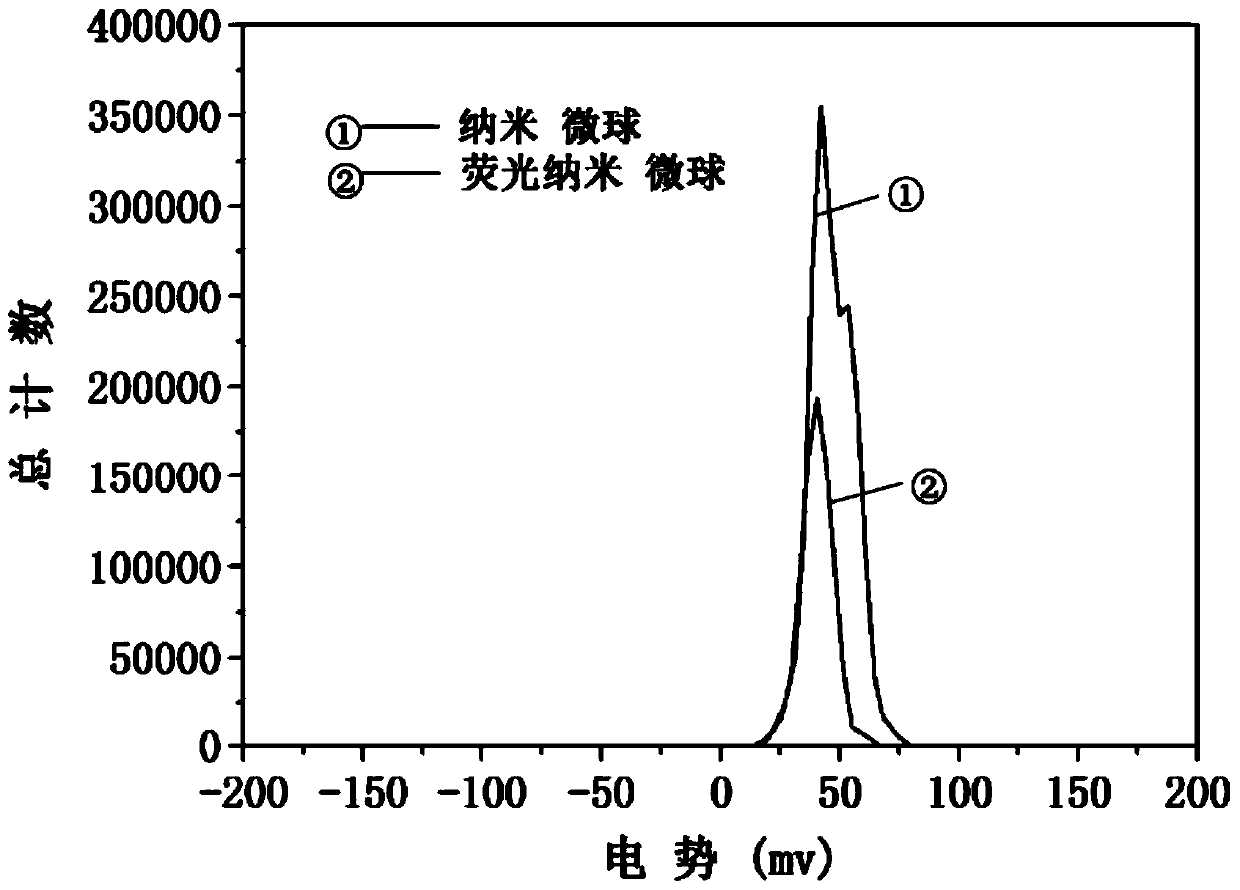
Fluorescent Nanospheres with Positively Charged Surface and Aggregation-Induced Fluorescence Enhanced Properties and Their Biological Applications
An aggregation-induced fluorescence, positively charged technology, used in fluorescence/phosphorescence, nanotechnology, material excitation analysis, etc., can solve the problems of short cycle time, ineffective entry into cells, poor biocompatibility, etc., and achieve excellent AIE properties, Low toxicity, low cytotoxic effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] (1) Take 5mL styrene (analytically pure, the polymerization inhibitor is removed by distillation under reduced pressure) and 0.06g N,N,N-trimethylvinylbenzyl ammonium chloride (VBTAC) and add it to a tank containing 185mL deionized water In a 500mL three-necked flask, stir mechanically (400rpm) at room temperature and under nitrogen protection for 30 minutes to remove oxygen in the reaction system, then heat up to 70°C, add 10mL containing 0.37mmol azobisisobutylamidine hydrochloride (V 50 ) The aqueous solution of the initiator initiates the polymerization, and the polymerization is carried out for 10 h under nitrogen protection and a stirring speed of 400 rpm. The nano-microspheres obtained by polymerization were centrifuged 3 times at a speed of 18500rpm, washed 3 times with deionized water to remove unreacted monomers, oligomers, initiators, etc., and redispersed into 100mL deionized water to obtain The mass concentration is 2.92% of the positively charged nanometer...
Embodiment 2
[0038] (1) Take 5mL styrene (analytically pure, the polymerization inhibitor is removed by distillation under reduced pressure) and 0.5g N,N,N-trimethylvinylbenzyl ammonium chloride (VBTAC) and add it to a tank containing 185mL deionized water In a 500mL three-necked flask, stir mechanically (400rpm) at room temperature and under nitrogen protection for 30 minutes to remove oxygen in the reaction system, then heat up to 70°C, add 10mL containing 0.37mmol azobisisobutylamidine hydrochloride (V 50 ) The aqueous solution of the initiator initiates the polymerization, and the polymerization is carried out for 10 h under nitrogen protection and a stirring speed of 400 rpm. The polymerized nanospheres were centrifuged 3 times at a speed of 18500rpm, washed 3 times with deionized water to remove unreacted, oligomers, initiators, etc., and redispersed into 100mL deionized water to obtain the mass concentration It is a 2.92% solution of nano-microspheres with positive charges on the su...
Embodiment 3
[0042] (1) Take 5mL styrene (analytically pure, the polymerization inhibitor is removed by distillation under reduced pressure) and 0.05g N,N,N-trimethylvinylbenzyl ammonium chloride (VBTAC) and add it to a tank containing 185mL deionized water In a 500mL three-necked flask, stir mechanically (400rpm) at room temperature and under nitrogen protection for 30 minutes to remove oxygen in the reaction system, then heat up to 70°C, add 10mL containing 0.37mmol azobisisobutylamidine hydrochloride (V 50 ) The aqueous solution of the initiator initiates the polymerization, and the polymerization is carried out for 10 h under nitrogen protection and a stirring speed of 400 rpm. The polymerized nanospheres were centrifuged 3 times at a speed of 18500rpm, washed 3 times with deionized water to remove unreacted, oligomers, initiators, etc., and redispersed into 100mL deionized water to obtain the mass concentration It is a 2.92% solution of nano-microspheres with positive charges on the s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com