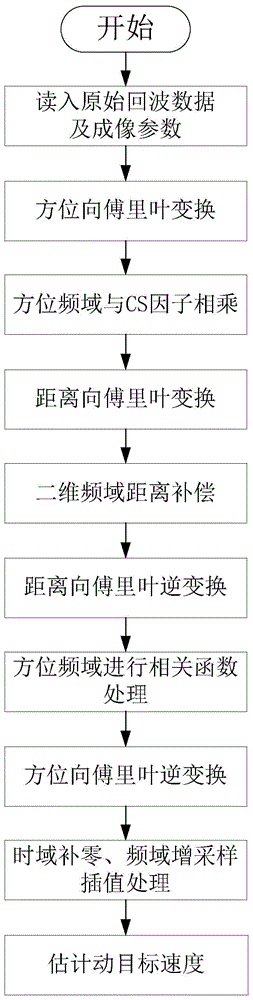
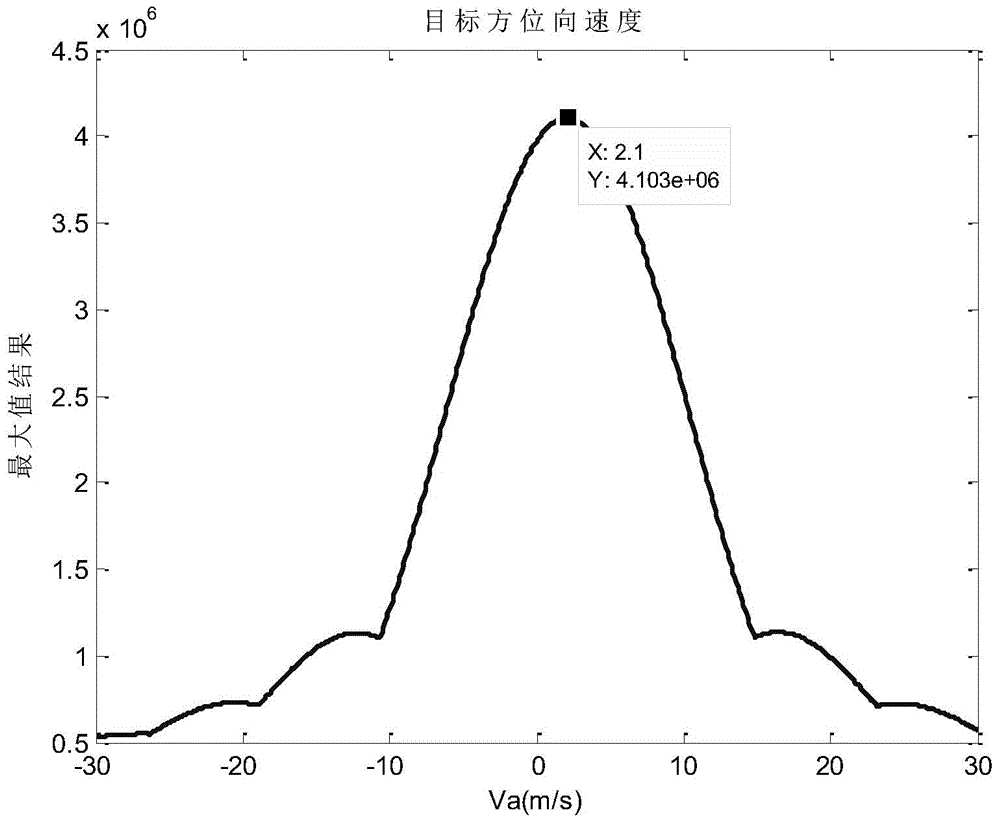
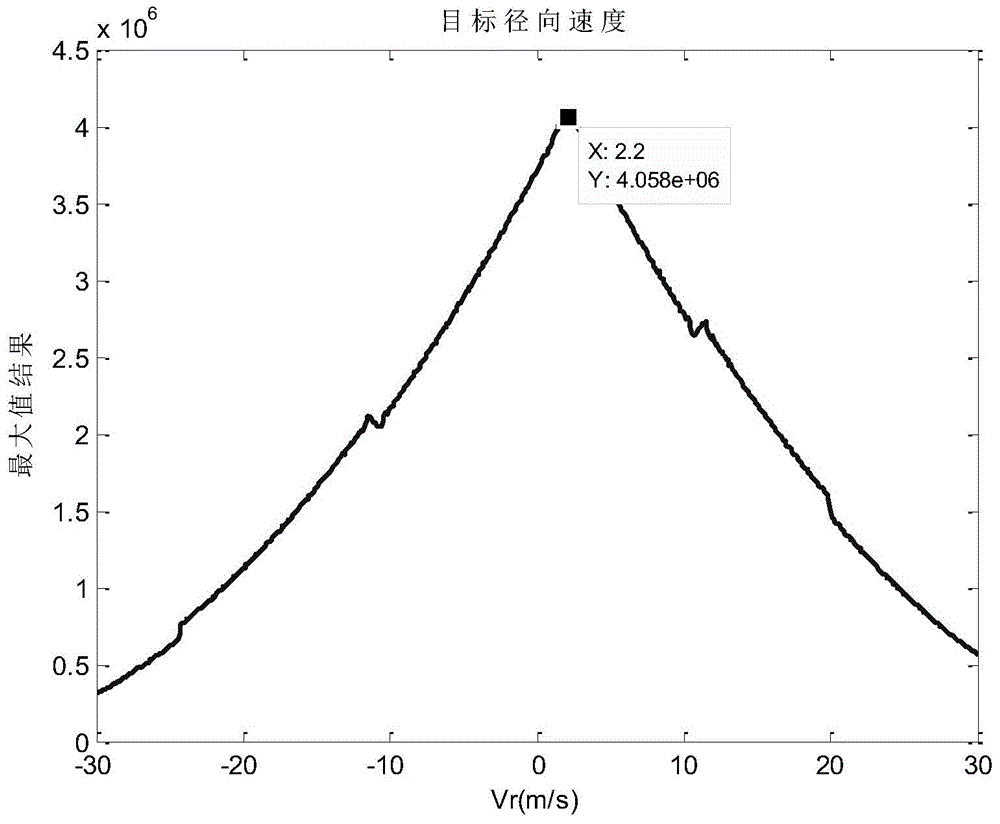
Correlation function-based moving-target parameter estimation method
A correlation function and parameter estimation technology, which is applied in the field of signal processing, can solve problems such as system complexity, blind speed of detection methods, and difficult image focus, and achieve high-precision speed parameter estimation, high speed detection accuracy, and strong applicability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0118] This embodiment proposes a method for estimating moving target parameters based on correlation functions. The simulation scene is a 1×1 dot matrix. According to the actual speed and direction of the point target, the detection is divided into three situations: assuming that the target only has azimuth speed; assuming that the target has only Radial Velocity; assume the target has both azimuth and radial velocities. The imaging parameters involved in the imaging process are shown in Table 1.
[0119] Table 1 embodiment parameters
[0120]
[0121]
[0122] This embodiment specifically includes the following steps:
[0123] Step 1: Read in the simulation complex data S based on the two-dimensional original echo simulation of the moving target in the spaceborne side-looking strip SAR mode 0 and the corresponding imaging parameters. Among them, S 0 is a two-dimensional complex array with a size of 8192×4096, and the specific imaging parameters are shown in Table 1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com