Page management method based on embedded system mixed main memory
An embedded system and page management technology, applied in website content management, special data processing applications, memory address/allocation/relocation, etc., can solve problems such as increased power consumption of write operations, page error migration, long write delay, etc. Achieve the effect of reducing execution time, prolonging service life, and reducing the number of writes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
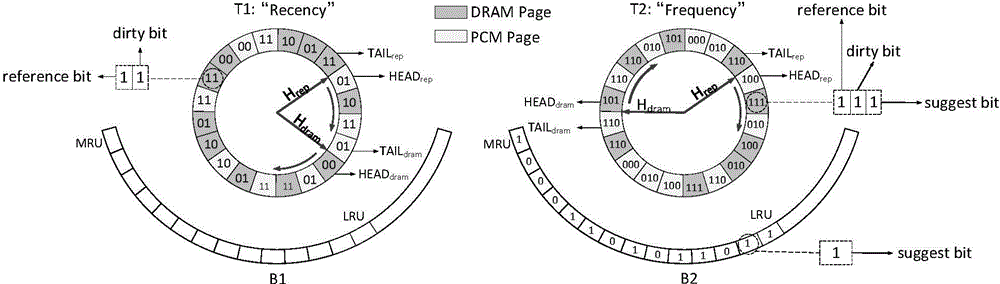
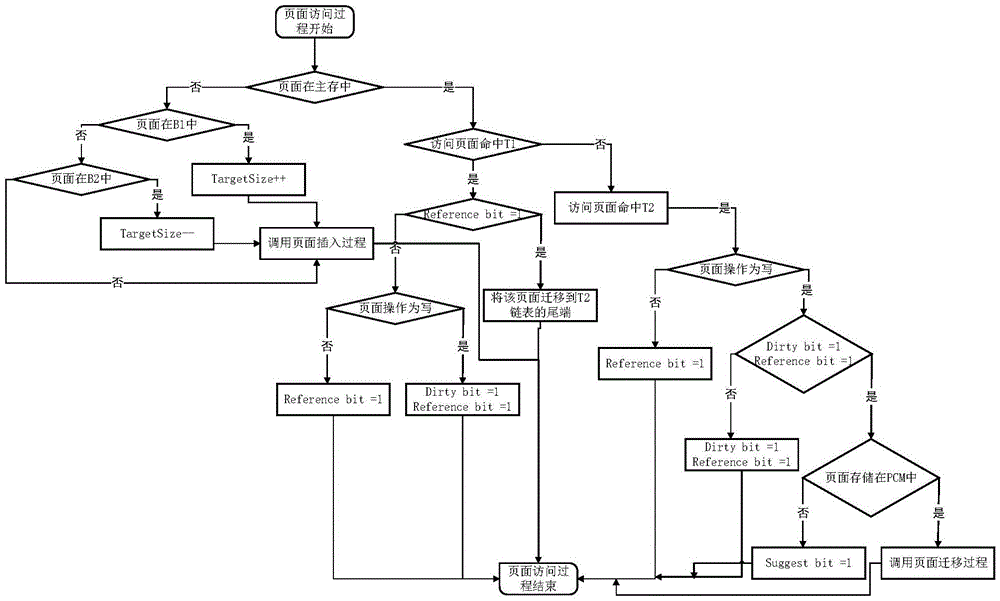
[0068] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing, the page management method based on embedded system hybrid main memory that the present invention proposes is described in further detail:
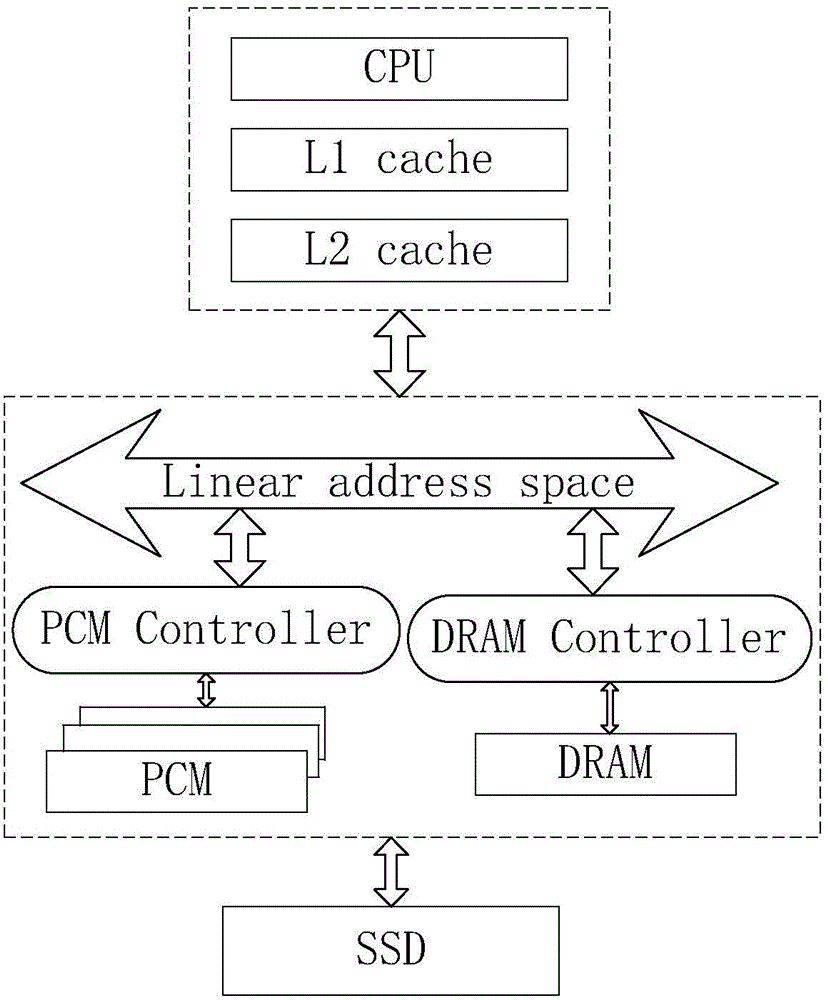
[0069] figure 1 It shows the mixed main memory architecture applied by the page management method based on the mixed main memory of the embedded system proposed by the present invention. In this architecture, DRAM and PCM are part of the main memory at the same time, but due to their different physical properties, different memory controllers - DRAM Controller and PCM Controller are respectively provided. At the relatively upper operating system level, DRAM and PCM are in the same address space, and are managed by the operating system in a unified page manner. The present invention designs the page management strategy at the operating system level. When the CPU fetches memory, it first needs to find the L1Cache, and if the L1Cache misses, it needs to find the L2Cache. Here L2Cache ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com