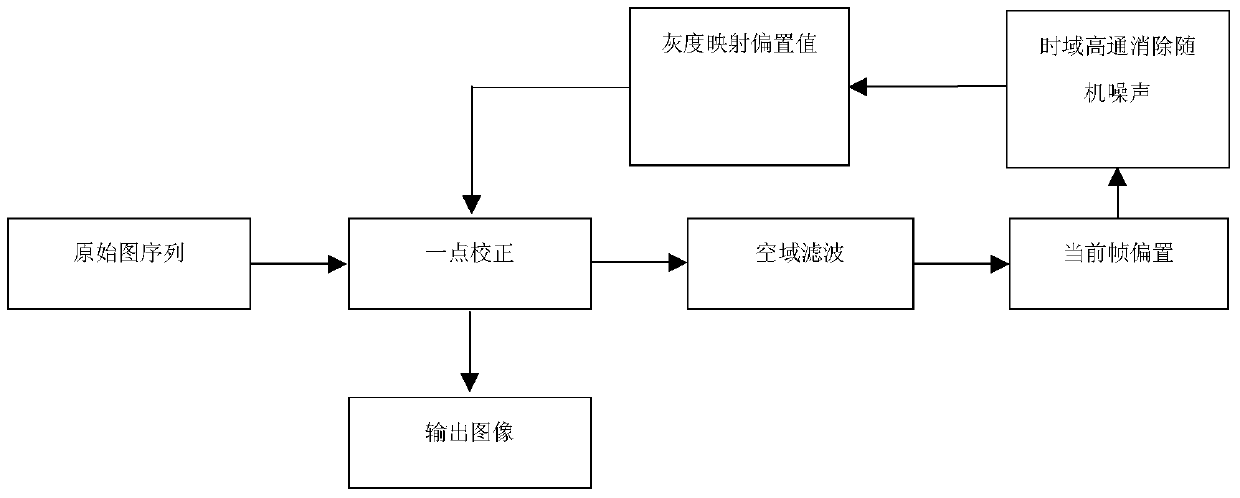
A time-domain high-pass non-uniformity correction method based on gray-scale correlation
A non-uniformity correction and grayscale technology, applied in the field of infrared imaging, can solve problems such as difficulty in correct update of neural network correction parameters, loss of filter window, improper details, etc., to preserve image details, prevent over-correction, and eliminate ghosts. shadow effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0056] In this example, a video sequence collected by a domestic 384×288 VOx focal plane detector is used to conduct a comparative test to verify the processing effect of the present invention on the non-uniformity of the "stripe" of a real detector. The image and video sequence is for the detector to shoot the still radiator, and constantly cut into the field of view by hand to verify the processing effect and convergence speed of the algorithm.
[0057] Using a time-domain high-pass non-uniformity correction method based on gray-scale correlation disclosed in this embodiment to correct the above-mentioned image and video sequences, and compare the corrected infrared imaging quality with the neural network non-uniformity of the prior art The infrared imaging quality of the correction algorithm, the constant statistical non-uniformity correction algorithm, and the time-domain high-pass filter algorithm correction processing are compared to illustrate the beneficial effects of a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com