Multi-element wave peak-based laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy rock fragment type identification method
A type identification and cuttings technology, applied in the field of cuttings type identification, can solve the problems of difficult description of cuttings, poor recognition effect, high recognition results, etc., and achieve the effect of taking into account the efficiency of data processing, the accuracy of recognition results, and the increase in time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
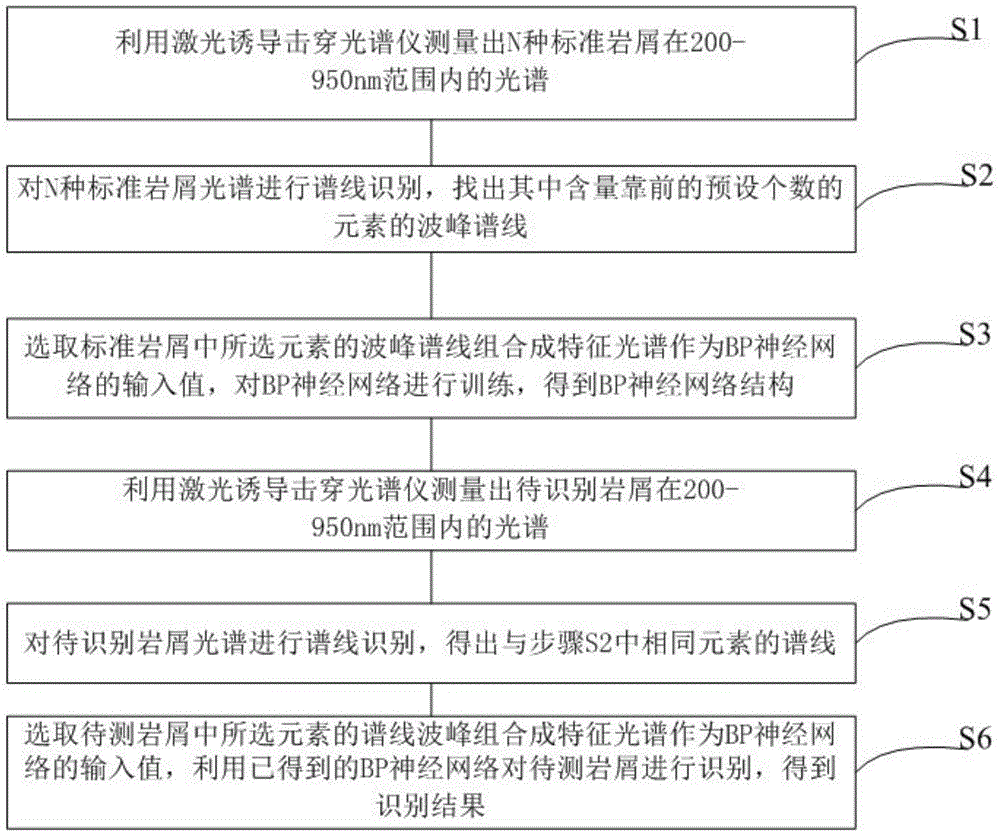
[0014] Such as figure 1 Shown, a kind of cuttings type identification method, it comprises the following steps:
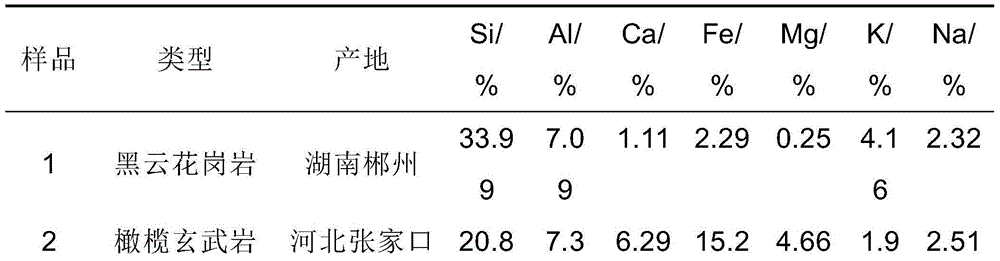
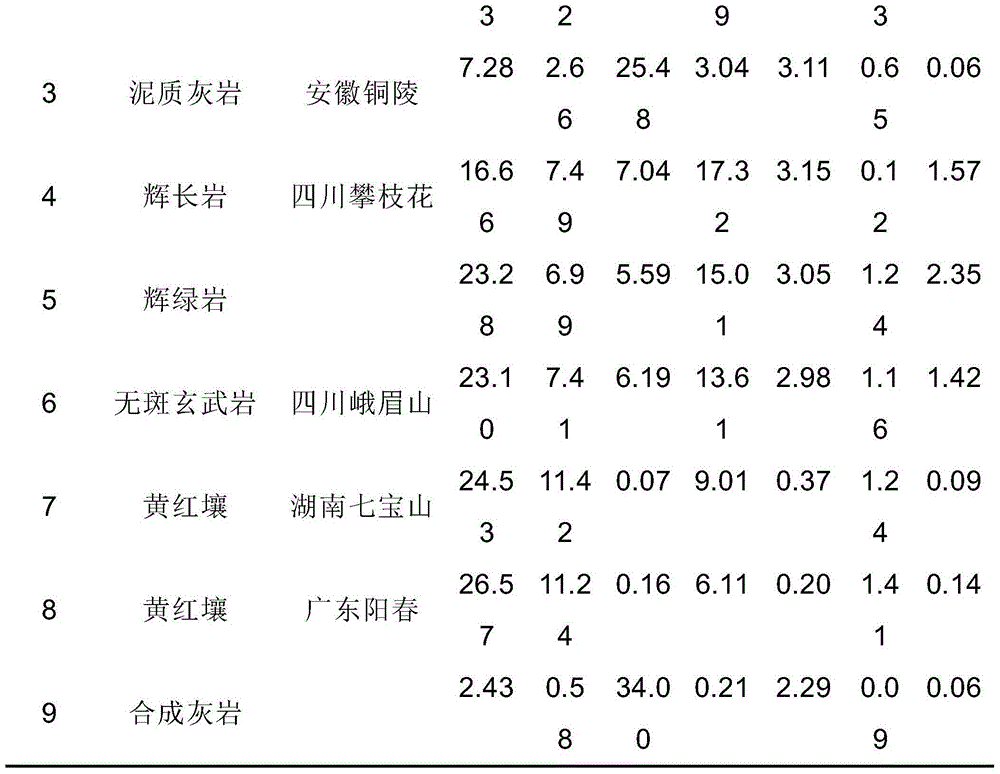
[0015] S1. Use a laser-induced breakdown spectrometer to measure the spectra of N standard cuttings in the range of 200-950nm. Optionally, the following 9 rock samples can be selected and pressed into standard cuttings by a tablet press. The types, origins and contents of major elements in the rock samples are listed in the table below.
[0016]
[0017]
[0018] S2. Carry out spectral line identification on N kinds of standard cuttings spectra, and find out the peak spectral lines of the preset number of elements with the highest content among them. Optionally, the selected elements in the standard cuttings include Mn, Mg, Si, Fe, Al, Ti, Ca, Na, K.
[0019] S3. Select the peak spectral lines of the selected elements in the standard cuttings to form a characteristic spectrum as the input value of the BP neural network, and train the BP neural network to o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com