Preparation method for microvesicle composite regenerative medical material
A technology of microbubbles and scaffold materials, applied in medical science, prostheses, etc., can solve the problems of seed cell growth and premature apoptosis, and achieve the effect of promoting angiogenesis, simple cryopreservation method, and less immune rejection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1 Preparation of microbubble / decalcified bone matrix composite regenerative medical material
[0026] 1. Extraction of rat bone marrow MSC-derived MV
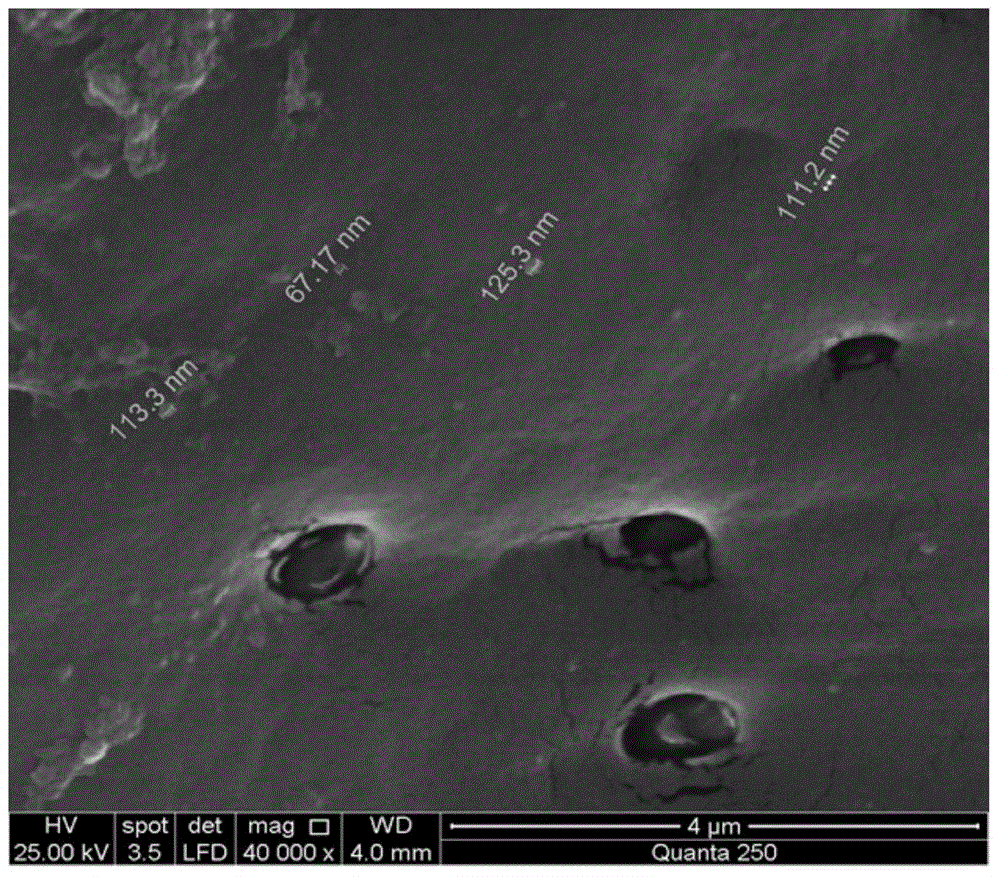
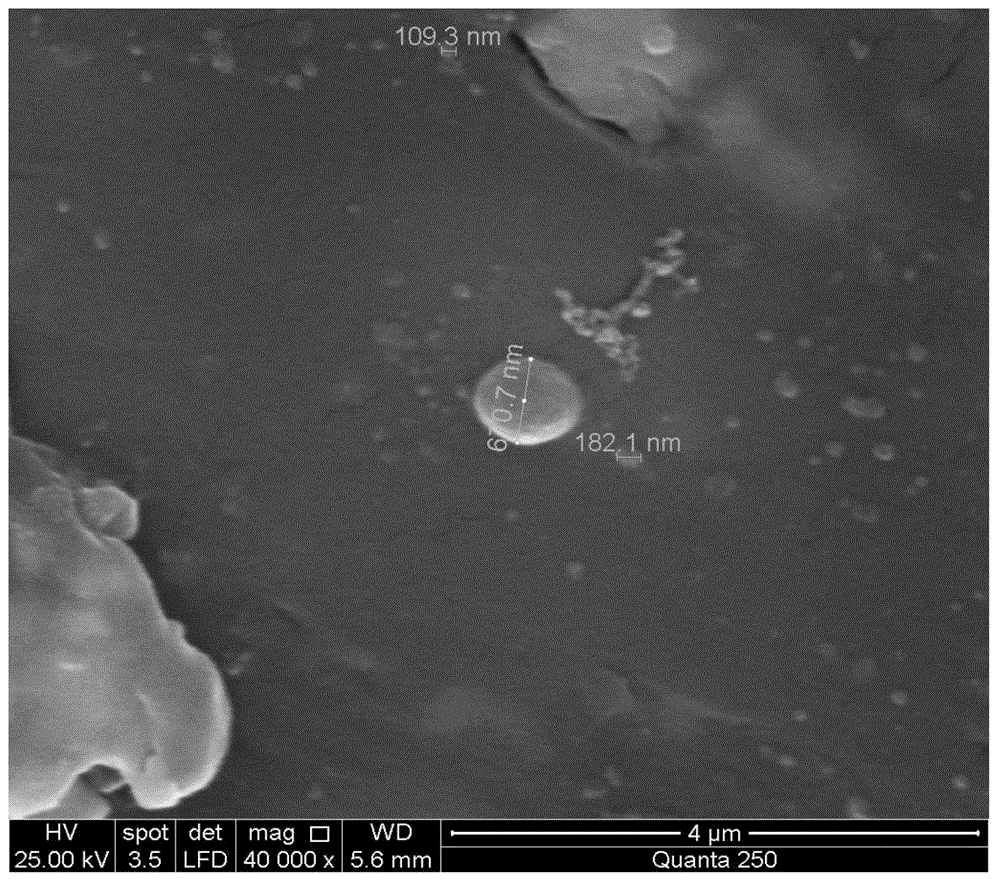
[0027] SD rat bone marrow-derived MSCs were cultured in primary culture, and MSCs from the 3rd to 5th passages were used to extract MVs. Before extracting MVs, the MSC medium was replaced with a serum-free medium to continue culturing for 24 h. Collect the cell supernatant, centrifuge at 2,000×g for 20 minutes, discard the pellet and take the pellet, centrifuge at 100,000×g, 4°C for 1 hour, discard the supernatant, resuspend the pellet in PBS, and freeze at minus 80°C for later use.
[0028] 2. Preparation of MV / DBM composite regenerative medical materials
[0029] 1) The biological material used in this example is the decalcified bone matrix (DBM) commonly used in tissue engineering bone. The scaffold material was cut into a size of 3×3×3 mm, soaked in 75% alcohol for 2 hours, Wash 3 times with PBS and dry at...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Example 2 Preparation of the composite regenerative medical material of microbubble / polycaprolactone
[0034] 1. Extract mouse bone marrow MSC-derived MV
[0035]BALB / c mouse bone marrow-derived MSCs were cultured in primary culture, and MSCs from the 3rd to 5th passages were used to extract MVs. Before extracting MVs, the MSC medium was replaced with a serum-free medium to continue culturing for 24 h. Collect the cell supernatant, centrifuge at 2,000×g for 20 minutes, discard the pellet and take the pellet, centrifuge at 100,000×g, 4°C for 1 hour, discard the supernatant, resuspend the pellet in PBS, and freeze at minus 80°C for later use.
[0036] 2. Preparation of MV / PCL composite regenerative medical materials
[0037] 1) The biological material used in this example is polycaprolactone (polycaprolactone, PCL), which is commonly used in tissue engineering bone. The scaffold material was cut into a size of 3×3×3 mm, soaked in 75% alcohol for 2 hours, and washed with...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com