A device and method for coaxial double-beam laser preheating and slow cooling stress release
A stress-releasing, dual-beam technology, applied in the field of additive manufacturing, to solve the problem of low laser absorption rate, improve forming efficiency, and protect lenses
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
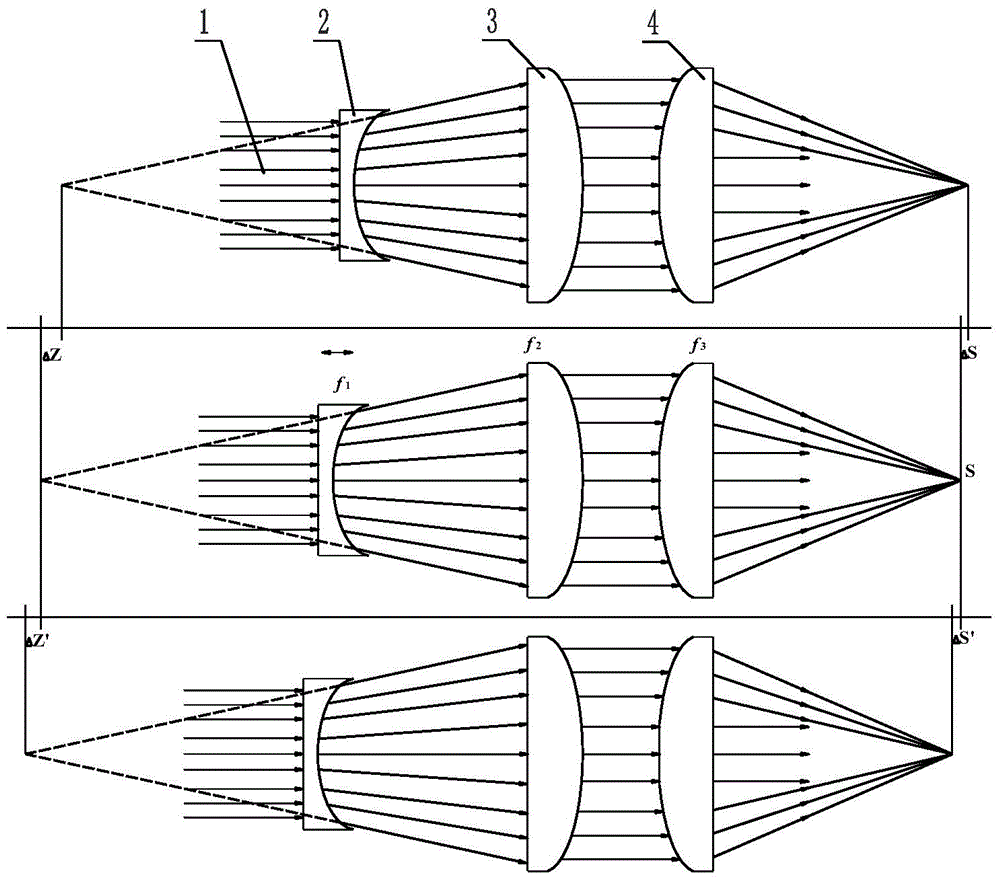
[0048] refer to figure 1 , the optical lens used in this embodiment includes a beam expanding concave lens 2 without a plane B, a collimating convex lens 3 without a plane D, and a focusing convex lens 4 with a plane A. Among them, refer to Figure 5 (a), the diameter of the beam expanding concave lens 2 is D1, and the effect of the beam expanding concave lens 2 is to expand the incident quasi-parallel laser beam 1 to reduce the laser energy density on the collimating convex lens 3 and the focusing concave lens 4 to protect The role of the lens. refer to Figure 7 (a), the diameter of the collimating convex lens 3 is D3, and the function of the collimating convex lens 3 is to output the laser beam 1 expanded by the beam expanding convex lens 2 in parallel. refer to Figure 8 , the diameter of the focusing convex lens 4 is D, and the central position of its convex surface is ground and polished to form a plane A with a diameter of d. The function of the plane A of the focu...
Embodiment 2
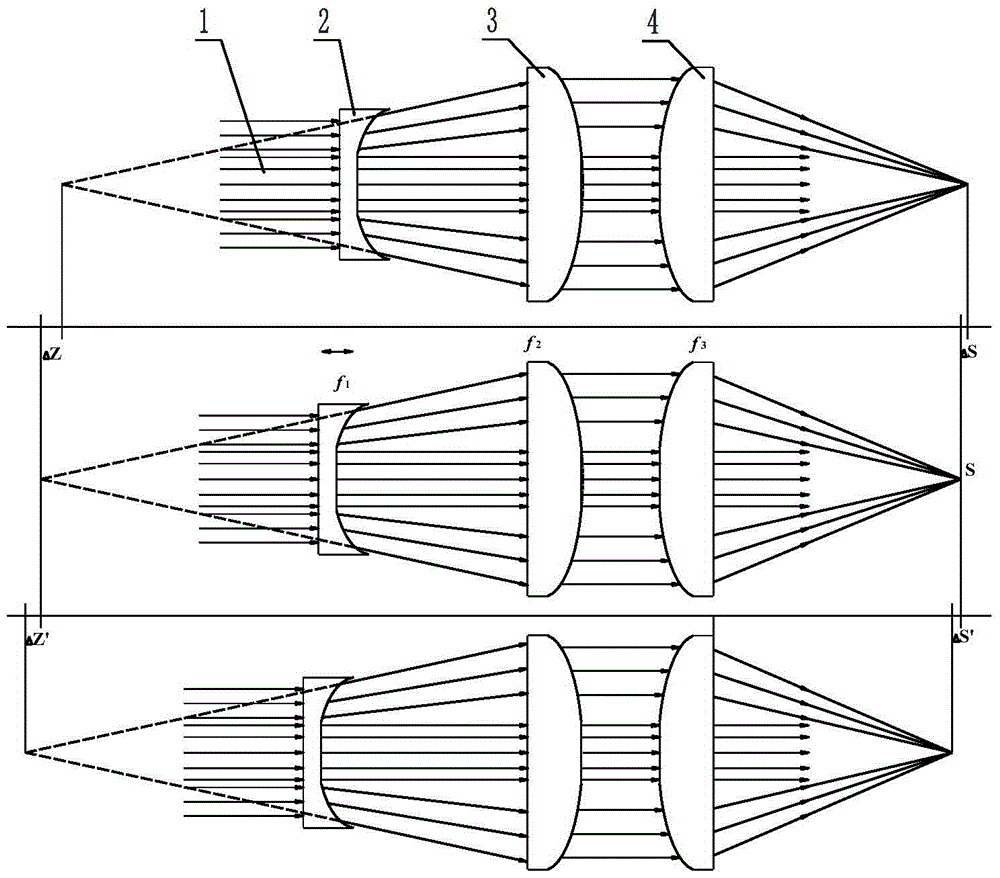
[0050] refer to figure 2 , the optical lens used in this embodiment includes a beam expanding concave lens 2 with a plane B, a collimating convex lens 3 with a plane D and a focusing convex lens 4 with a plane A. Among them, refer to Figure 5 (b), the diameter of the beam expander concave lens 2 is D1, and the center of the concave surface is ground and polished to form a plane B with a diameter of d1. The plane B allows the laser beam 1 to pass through directly in parallel without beam expansion. The beam expander concave lens 2 The function of the concave part of the laser beam is to expand the incident quasi-parallel laser beam, so as to reduce the laser energy density on the collimating convex lens 3 and the focusing concave lens 4, and protect the lens. refer to Figure 7 (b), the diameter of the collimating convex lens 3 is D3, and the central position of its convex surface forms a plane D with a diameter of d3 after being ground and polished, and the plane D makes t...
Embodiment 3
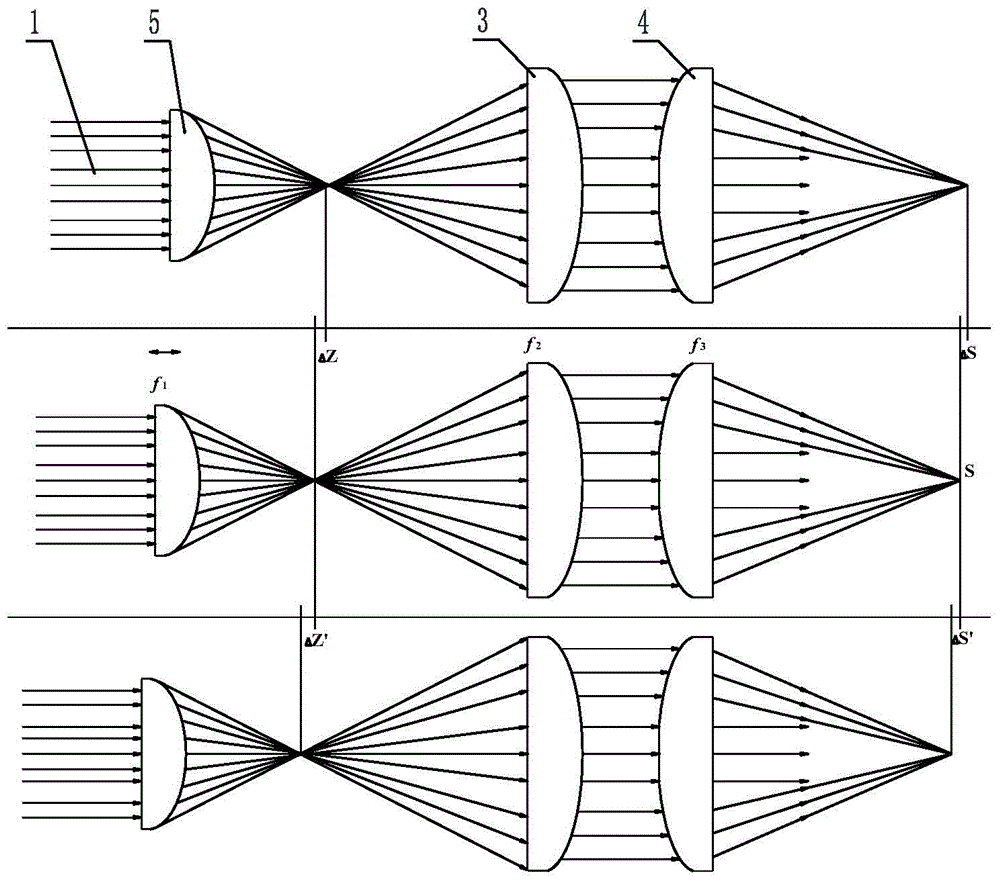
[0052] refer to image 3 , the optical lenses used in this embodiment include a beam expander convex lens 5 without a plane C, a collimating convex lens 3 without a plane D, and a focusing convex lens 4 with a plane A. Among them, refer to Figure 6 (a), the diameter of the beam expanding convex lens 5 is D2, and the effect of the beam expanding convex lens 5 is to expand the beam of the incident quasi-parallel laser beam 1, to reduce the laser energy density on the collimating convex lens 3 and the focusing concave lens 4, to protect The role of the lens. refer to Figure 7 (a), the diameter of the collimating convex lens 3 is D3, and the function of the collimating convex lens 3 is to output the laser beam 1 expanded by the beam expanding convex lens 2 in parallel. refer to Figure 8 , the diameter of the focusing convex lens 4 is D, and the central position of its convex surface is ground and polished to form a plane A with a diameter of d. The function of the plane A ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com