Systems and methods for encoding and decoding of check-irregular non-systematic ira codes
An irregular and non-systematic technology, applied in the field of systems and methods for encoding and decoding irregular non-systematic IRA codes, can solve problems such as non-convergence, and achieve the effect of improving the convergence rate of decoding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
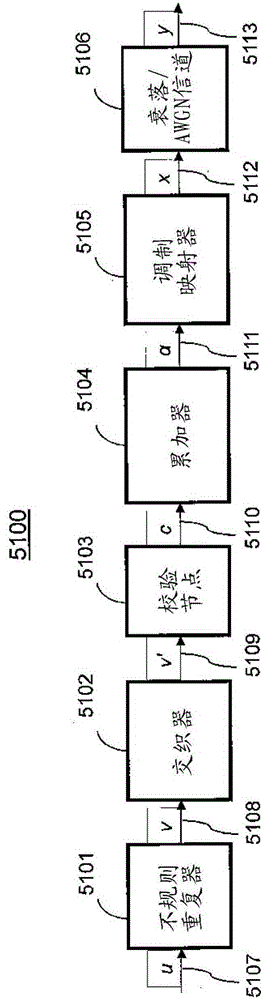
[0041] Check irregular non-systematic IRA encoders and transmitters
[0042] According to some implementations in figure 1 A typical simplified transmitter with a check-irregular non-systematic IRA encoder is shown in . Transmitter 5100 includes a set of bit repeaters of different degrees, also referred to as bit repeater nodes, collectively referred to as irregular bit repeaters 5101, wherein irregular bit repeaters 5101 combine the information on line 5107 in an irregular form The bit sequence u repeats. For example, a bit repeater of degree m produces m identical copies of an information bit, as is known in the art. These repeated information bits represent the first level coded bits. The interleaver 5102 performs a pseudo-random permutation on the repeated sequence of bits v on line 5108 and produces interleaved first-level coded bits v' on line 5109 .
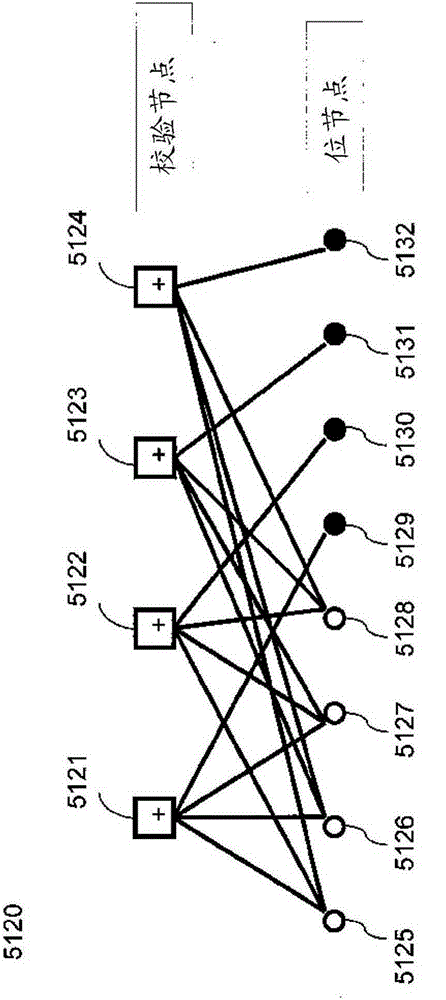
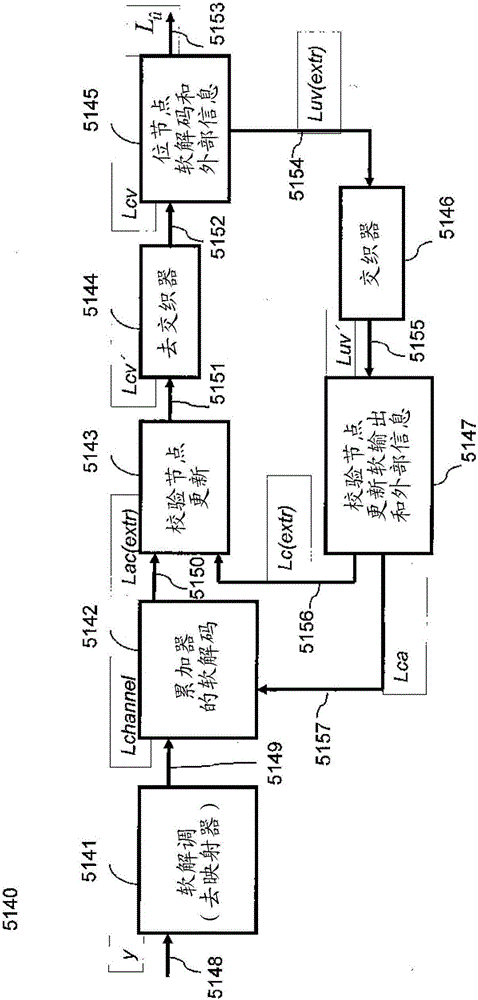
[0043] A set of check node combiners of different degrees, collectively referred to as check nodes 5103, operates on...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com