High-performance sintered neodymium-iron-boron rare-earth permanent magnetic material and preparation method thereof
A rare-earth permanent magnet and NdFeB technology, which is applied in the direction of magnetic materials, inorganic materials, magnetic objects, etc., can solve the problems of failing to meet the requirements of the main phase of the design, achieve small impact on residual magnetism, reduce dosage, and improve coercivity force effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
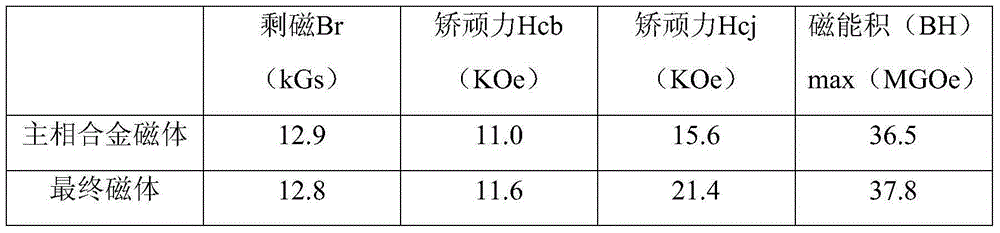
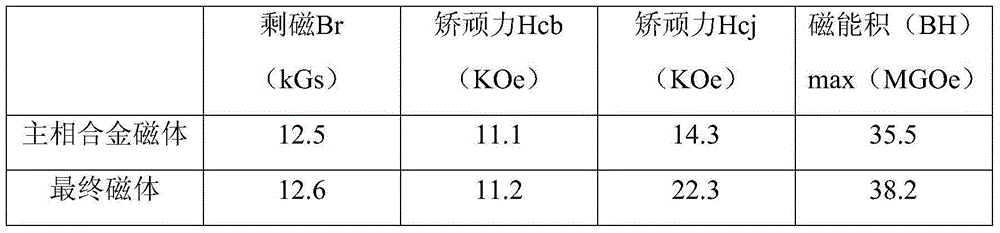
[0030] The first main phase magnetic powder alloy composition Nd 24 PR 6 co 1.8 Fe 61.1 Nb 0.6 al 0.30 Cu 0.2 B 1.0(mass percentage content), use the SC process to make flakes, use hydrogen explosion treatment to make the average particle size of the powder below 100 μm, and use hydrogen crushing and jet milling to make magnetic powder with an average particle size of 3.0-5.0 μm. Orientation press molding in 2T orientation magnetic field, isostatic pressing under 180MPa pressure. Sintering at 1050°C*2h, secondary heat treatment, 880°C*2h and 550°C*2h to obtain the first main phase sintered NdFeB magnet.
[0031] Alloy composition Dy of the second boundary zone structure 30 Fe 68.2 Nb 0.6 al 0.3 Cu 0.2 B 1.0 (mass percentage content), using the SC process to make flakes, using hydrogen explosion treatment to make the average particle size of the powder below 100 μm, and using hydrogen crushing and jet milling to make magnetic powder with an average particle size of...
Embodiment 2
[0037] The first main phase magnetic powder alloy composition Nd 24 PR 6 Fe 62.9 Nb 0.6 al 0.30 Cu 0.2 B 1.0 (mass percentage content), use the SC process to make flakes, use hydrogen explosion treatment to make the average particle size of the powder below 100 μm, and use hydrogen crushing and jet milling to make magnetic powder with an average particle size of 3.0-5.0 μm. Orientation press molding in 2T orientation magnetic field, isostatic pressing under 180MPa pressure. Sintering at 1050°C*2h, secondary heat treatment, 880°C*2h and 550°C*2h to obtain the first main phase sintered NdFeB magnet.
[0038] Alloy composition Dy of the second boundary zone structure 30 Fe 68.8 al 0.3 Cu 0.2 B 1.0 (mass percentage content), using the SC process to make flakes, using hydrogen explosion treatment to make the average particle size of the powder below 100 μm, and using hydrogen crushing and jet milling to make magnetic powder with an average particle size of 2.5-4.0 μm.
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com