Method for diagnosing pneumatic asymmetric fault of impeller of doubly-fed wind turbine generator system
A technology of doubly-fed wind power generation and diagnostic methods, which is applied to wind power generator components, wind power engines, engines, etc., to achieve the effect of easy implementation and improved accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
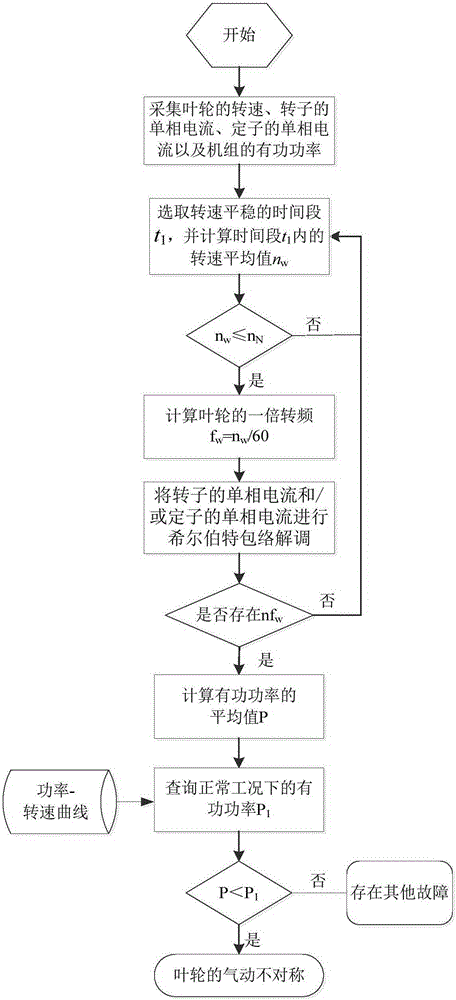
[0026] Such as figure 1 As shown, the method for diagnosing the aerodynamic asymmetry fault of the impeller of the doubly-fed wind power generating set according to the specific embodiment of the present invention includes the following steps:
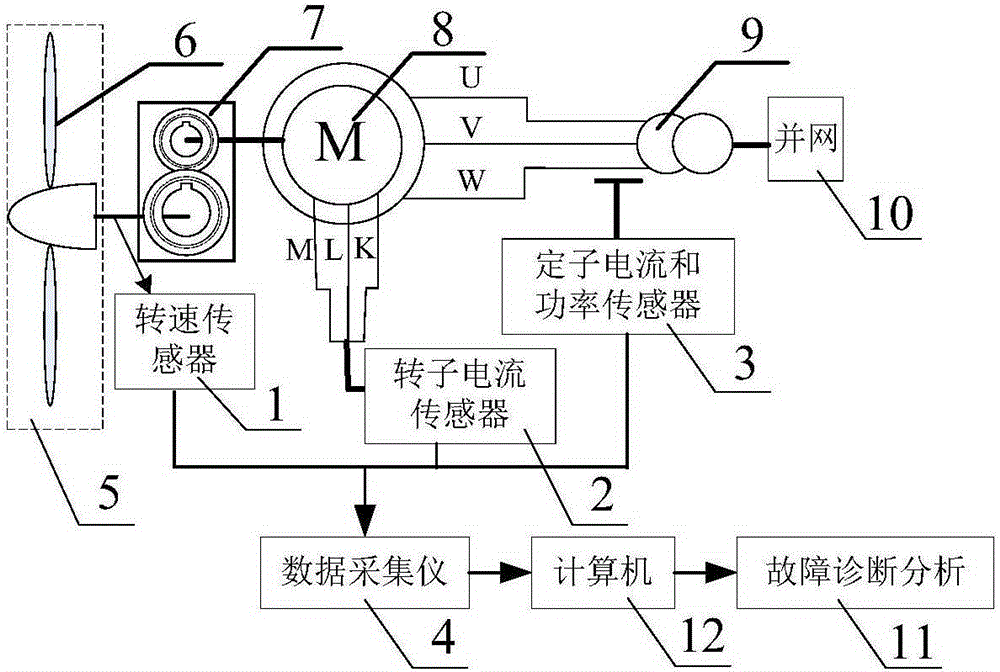
[0027] 1) Use the rotational speed sensor, current sensor and power sensor to synchronously collect the rotational speed of the impeller 6 of the DFIG, the single-phase current of the rotor of the DFIG, the single-phase current of the stator, and the DFIG synchronously within the time period t, respectively. The active power of the wind turbine, and save the collected data to the computer for fault diagnosis and analysis.
[0028] 2) In the time period t, select the time period t when the speed of the impeller 6 is stable 1 (t 1 1 The average speed of the impeller 6 within n w .
[0029] 3) Judging the average speed n w Is it less than the rated speed n of the impeller 6 N .
[0030] 4) If the average speed n w Less than the ra...
Embodiment 2
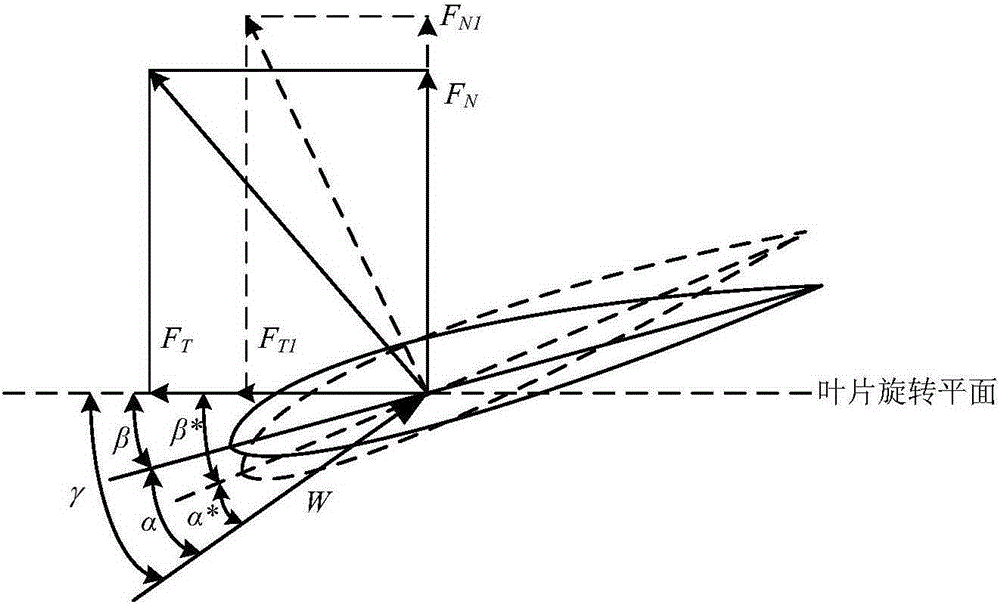
[0037] The influence of the aerodynamic asymmetry fault of the impeller of the doubly-fed wind turbine on the aerodynamic torque and active power is analyzed below through the speed and force in the plane of the blade element airfoil.
[0038] This embodiment is based on the blade element theory of momentum (BEM). The leaf element theory divides the blade into N equal parts, assuming that the airfoil of each leaf element is the same. The schematic diagram of the speed and force in the airfoil plane of the blade element is as follows: image 3 shown. For the wind turbine 5 in the rotating state (such as figure 2 As far as the impeller 6 is shown), the blade element aerodynamic force only considers the tangential traction force F parallel to the impeller rotation plane T and the axial thrust F perpendicular to the plane of impeller rotation N , where F TThe function is to generate aerodynamic torque and output it to the doubly-fed wind generator 8 (such as figure 2 shown...
Embodiment 3
[0050] The following is an analysis of the influence of the aerodynamic asymmetry fault of the impeller 6 on the current of the rotor and the current of the stator when the doubly-fed wind turbine is running at maximum wind energy.
[0051] In order to improve the utilization rate of wind energy and the efficiency of wind power generation, the Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) control strategy is commonly used in doubly-fed wind power generation systems. Among them, the optimal power-speed curve method is commonly used by most doubly-fed wind turbines in MPPT control. It means that when the unit is connected to the grid and operates below the rated speed, in order to capture the maximum wind energy, the wind energy utilization coefficient of the wind turbine 5 must always maintain the maximum value C pmax , while the pitch angle of the wind turbine 5 is not adjusted, and the speed of the unit is indirectly adjusted by controlling the output power of the generator, so as to m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com