Fixable oxycarbide and microorganism capable of performing fermentation reaction and preparation method and application thereof
一种氧化物、固定碳的技术,应用在基于微生物的方法、生物化学设备和方法、微生物等方向,能够解决有机化合物产率不佳、成本及资源浪费、碳源损失等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0071] Embodiment 1: the preparation of fusion strain
[0072] (1-1) Selection of parental strains
[0073] Clostridium ljungdahlii strain BCRC17797 capable of fixing carbon dioxide and Clostridium tyrobutyricum strain BCRC14535 capable of fermentation to produce organic acids were selected as parental strains.
[0074] (1-2) Preparation of protoplasts
[0075] Mix glucose and mRCM medium to provide a mixed medium with a glucose concentration of 10 g / L, and deoxygenate the mixed medium, and then inject 40 ml of deoxygenated centrifuge tubes into two deoxygenated centrifuge tubes mixed media. Next, inoculate the two parental strains selected in (1-1) into the mixed culture medium of the centrifuge tube, and cultivate them in an anaerobic incubator at 37°C until the Dassostella grows to OD 600 (the absorbance value when the wavelength is 600 nanometers) is about 0.8, Clostridium tyrobutyricum grows to OD 600 About 1.5 (ie, both parental strains grew to mid-log phase). The b...
Embodiment 2
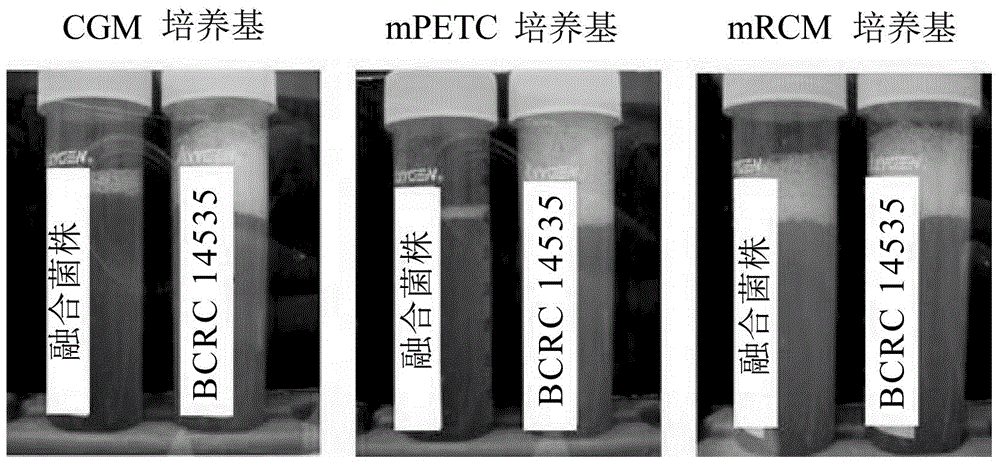
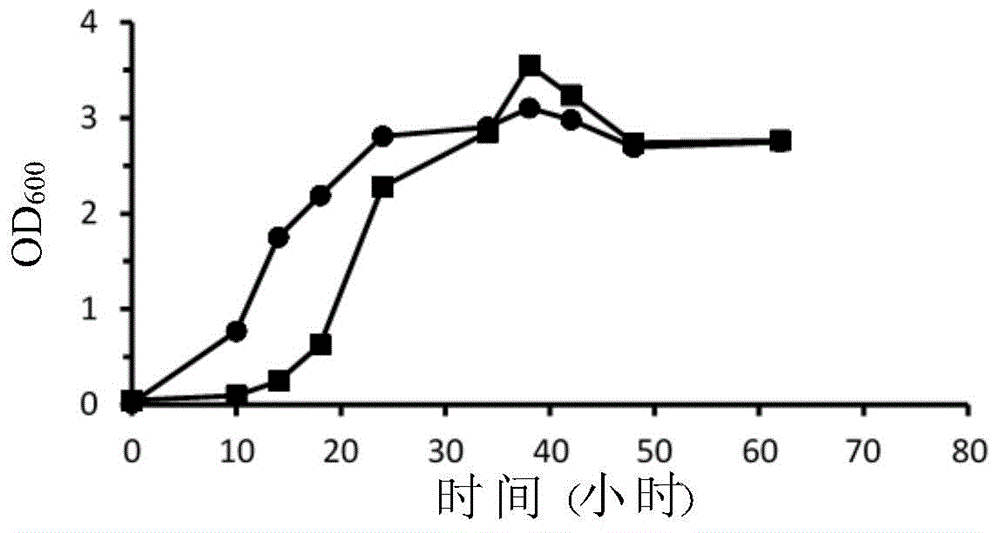
[0084] Example 2: Test the physiological properties of Clostridium tyrobutyricum strain ITRI02001 and Clostridium tyrobutyricum strain BCRC14535
[0085] Glucose was mixed with the mRCM medium to provide a mixed medium with a glucose concentration of 10 g / L, and the mixed medium was deoxygenated for subsequent use.
[0086] Inject 40 ml of the aforementioned deoxygenated mixed medium into two 50 ml centrifuge tubes. Next, the Clostridium tyrobutyricum strain BCRC14535 and the Clostridium tyrobutyricum strain ITRI02001 were respectively inoculated in the aforementioned mixed medium, and cultured in an anaerobic incubator at 37°C. When the strains grow to the mid-logarithmic phase (that is, the OD of Clostridium tyrobutyricum strain BCRC14535 and Clostridium tyrobutyricum strain ITRI02001 600 Respectively about 1.5 o'clock), the bacterium liquid of this two bacterial strains is with the volume ratio of 1: 200 (bacteria liquid: mRCM medium), is diluted in the two airtight bottle...
Embodiment 3
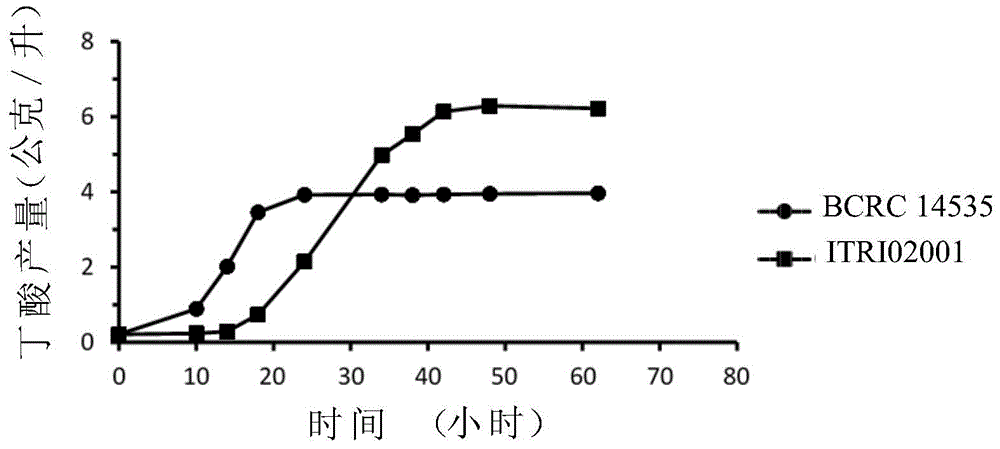
[0089] Example 3: Testing the effectiveness of Clostridium tyrobutyricum strain ITRI02001 in producing organic compounds
[0090] (3-1) Comparison of carbon conversion rate between Clostridium tyrobutyricum strain BCRC14535 and ITRI02001
[0091] Glucose and mRCM medium were mixed to provide a mixed medium with a glucose concentration of 10 g / L and an acetic acid concentration of 4 g / L, and the mixed medium was deoxygenated for subsequent use.
[0092] Inject 40 ml of the aforementioned deoxygenated mixed medium into two 50 ml centrifuge tubes. Next, the Clostridium tyrobutyricum strain BCRC14535 and the Clostridium tyrobutyricum strain ITRI02001 were respectively inoculated in the aforementioned mixed medium, and cultured in an anaerobic incubator at 37° C. for fermentation reaction for 48 hours. Next, the contents of glucose, acetic acid and butyric acid in the aforementioned medium were analyzed with an Agilent 1100 series high-performance liquid chromatography coupled wit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com