Water-soluble ammonium polyphosphate NPK compound fertilizer and preparation method thereof
A water-soluble poly and ammonium phosphate technology, applied in the field of compound fertilizers, can solve the problems of serious ammonia loss of ammonium polyphosphate, fast decay of product polymerization rate, poor bubble control effect, etc., so as to improve the utilization rate of phosphate fertilizer and slow the decay of polymerization rate. , The effect of strong product stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
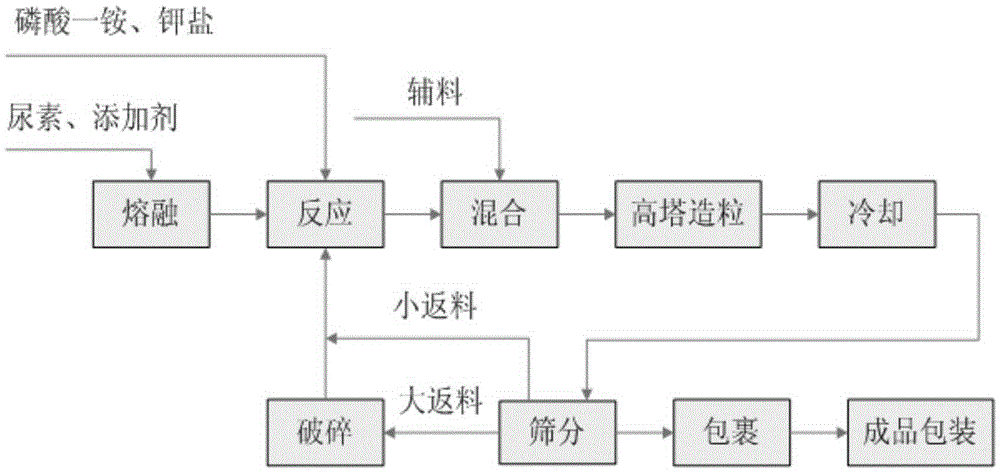
[0025] And, the embodiment of the present invention provides a kind of preparation method of water-soluble ammonium polyphosphate NPK compound fertilizer, comprises the following steps:
[0026] S01. Provide urea and additives to form a low-melt mixture, and melt the low-melt mixture to obtain a first melt;
[0027] S02. Adding a blend formed by monoammonium phosphate, potassium sulfate or potassium chloride to the first melt, and performing a heating reaction;
[0028] S03. Granulation.
[0029] Specifically, in the above step S01, the melting point of the urea is lowered by adding the additive, thereby lowering the heating reaction temperature. On the one hand, make described heating reaction temperature to 110-150 ℃, reduce the polymerization degree of synthetic ammonium polyphosphate to 2-10, be soluble in water, can be used for producing compound fertilizer (conventional reaction is with urea, monoammonium phosphate as raw material, in At a temperature of 200-300°C, amm...
Embodiment 1
[0043] A kind of water-soluble ammonium polyphosphate NPK compound fertilizer, comprises monoammonium phosphate, potassium sulfate or potassium chloride, low melting mixture, wherein, described low melting mixture comprises urea and additive, and described additive is ammonium chloride, potassium chloride 1. At least one of dicyandiamide, the mass ratio of the urea, monoammonium phosphate, potassium sulfate or potassium chloride is 1.0:1.0:1.0, and the mass ratio of the additive to the urea is 0.1:1.
[0044] The preparation method of described water-soluble ammonium polyphosphate NPK compound fertilizer, comprises the following steps:
[0045] S11. Provide urea and additives to form a low-melt mixture, and melt the low-melt mixture to obtain a first melt;
[0046] S12. Adding a blend formed by monoammonium phosphate, potassium sulfate or potassium chloride to the first melt, and performing a heating reaction, wherein the temperature of the heating reaction is 110° C., and the...
Embodiment 2
[0049] A water-soluble ammonium polyphosphate NPK compound fertilizer, comprising monoammonium phosphate, potassium sulfate or potassium chloride, a low-melt mixture and auxiliary materials, wherein the low-melt mixture includes urea and additives, and the additives are ammonium chloride, chlorine Potassium chloride, dicyandiamide at least one, described auxiliary material is at least one in ammonium sulfate, zinc sulfate, magnesium sulfate, borax, and the mass ratio of described urea, monoammonium phosphate, potassium sulfate or potassium chloride is 7.0:1.0:2.0, the mass ratio of the additive to the urea is 0.3:1.
[0050] The preparation method of described water-soluble ammonium polyphosphate NPK compound fertilizer, comprises the following steps:
[0051] S21. Provide urea and additives to form a low-melt mixture, and melt the low-melt mixture to obtain a first melt;
[0052] S22. Add a blend formed by monoammonium phosphate, potassium sulfate or potassium chloride to th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com