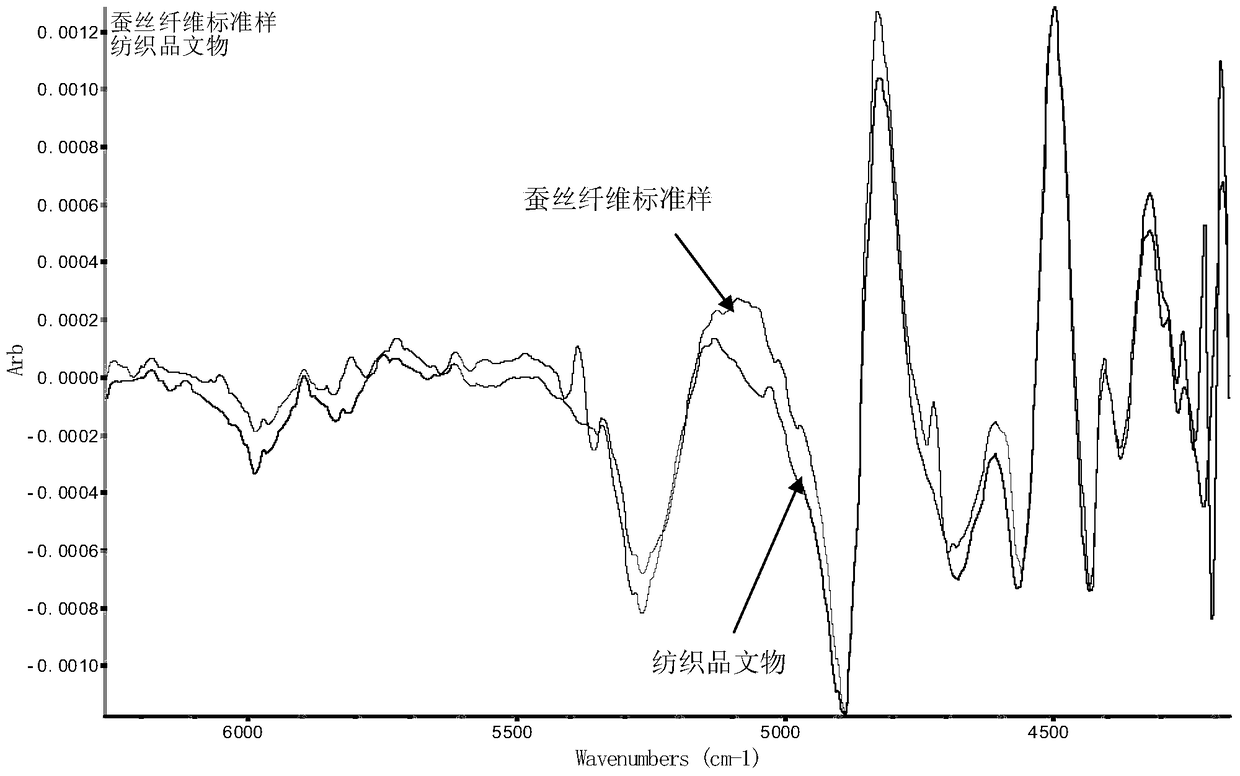
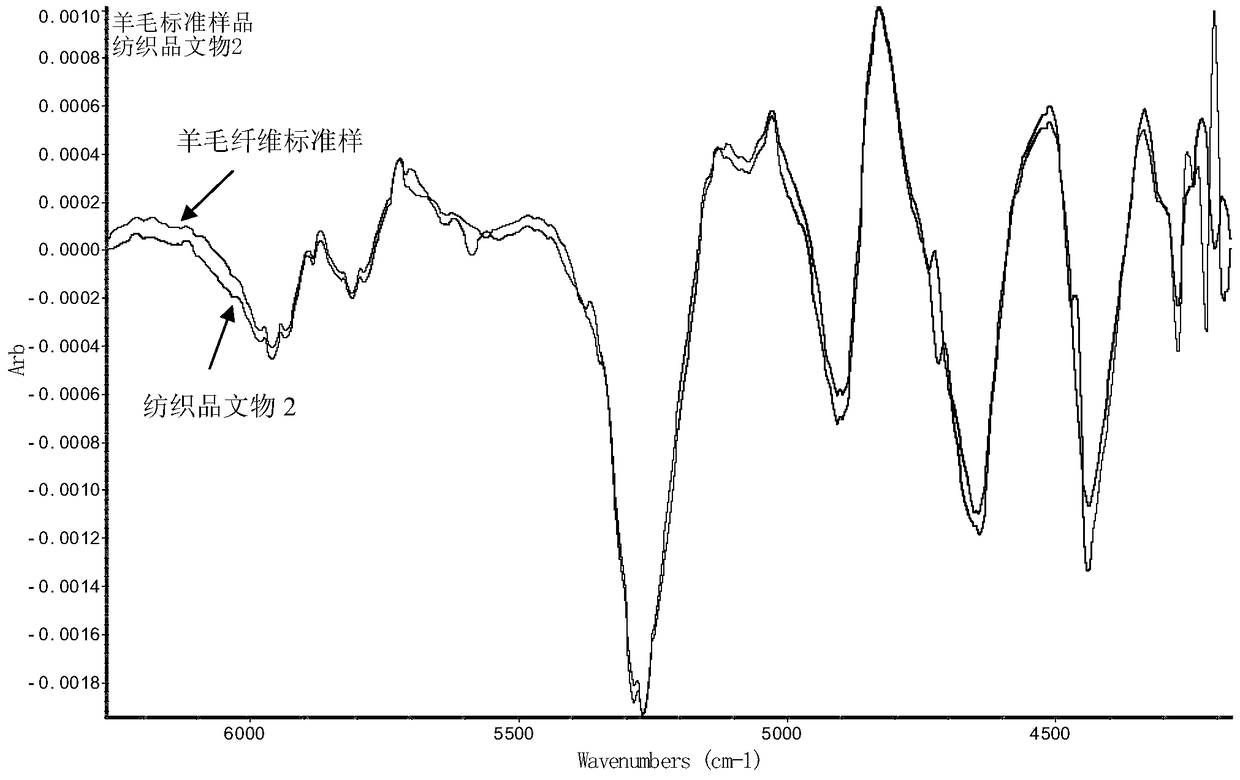
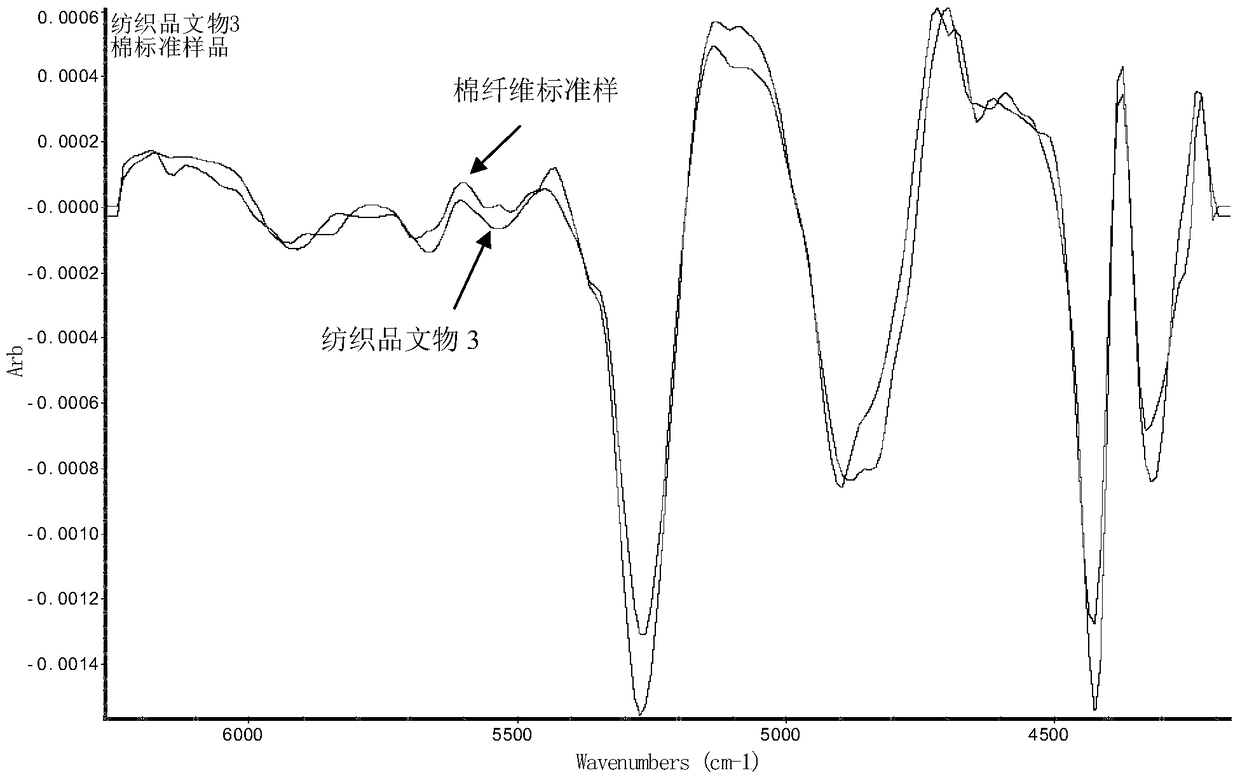
A method for non-destructive and pressure-free identification of textile cultural relic materials based on infrared spectroscopy
A technology of infrared spectroscopy and near-infrared spectroscopy, which is applied in the field of identifying textile cultural relic materials, can solve the problems of destroying integrity, quickly and non-destructively detecting textile cultural relics, and affecting the accuracy of infrared spectroscopy, so as to improve near-infrared light reflectance and material identification. The process is fast and accurate, and the effect of high infrared reflectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] A method for non-destructive and pressure-free identification of textile cultural relic materials based on infrared spectroscopy, comprising the following steps:
[0031] 1) Place a flat reflective sheet on the detection table of the infrared spectrometer, and spread the textile cultural relics to be tested on the reflective sheet. The surface of the reflective sheet is plated with gold, and the thickness of the coating on the reflective sheet is 0.7 mm.
[0032] 2) Adjust the detection probe of the near-infrared spectrometer, control the distance between the detection probe and the textile cultural relics at 0.6mm, control the ambient temperature at 22°C, and control the relative humidity at 55%, and then conduct near-infrared spectral information Collect and obtain the near-infrared spectrum of textile cultural relics.
[0033] 3) The obtained near-infrared spectrum is subjected to S.Golay smoothing filtering by microPHAZIR software, and the smoothness is 1, and then...
Embodiment 2
[0037] A method for non-destructive and pressure-free identification of textile cultural relic materials based on infrared spectroscopy, comprising the following steps:
[0038] 1) Use a brush dipped in ethanol to wet and clean the parts to be tested on the textile cultural relics, then use a brush dipped in acetone to continue wetting the wetted parts of the textile cultural relics, and then place the textile cultural relics at a temperature of Dry for 30 minutes at 25°C and 30% relative humidity. Wherein, the consumption of described ethanol is 1mL / cm 3 , the amount of acetone is 1.5mL / cm 3 .
[0039] A flat reflective sheet is placed on the detection table of the infrared spectrometer, and the textile cultural relic to be tested is flatly spread on the reflective sheet. The surface of the reflective sheet is coated with aluminum oxide. The thickness of the coating on the reflective sheet is 0.6mm.
[0040] 2) Adjust the detection probe of the near-infrared spectrometer...
Embodiment 3
[0045] A method for non-destructive and pressure-free identification of textile cultural relic materials based on infrared spectroscopy, comprising the following steps:
[0046] 1) Use a brush dipped in ethanol to wet and clean the parts to be tested on the textile cultural relics, then use a brush dipped in acetone to continue wetting the wetted parts of the textile cultural relics, and then place the textile cultural relics at a temperature of Dry at 30°C and 40% relative humidity for 15 minutes. Wherein, the consumption of described ethanol is 2mL / cm 3 , the amount of acetone is 2.5mL / cm 3 .
[0047] A flat reflective sheet is placed on the detection table of the infrared spectrometer, and the textile cultural relic to be tested is flatly spread on the reflective sheet. The surface of the reflective sheet is coated with silicon dioxide. The thickness of the coating on the reflective sheet is 0.8mm.
[0048] 2) Adjust the detection probe of the near-infrared spectromete...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com