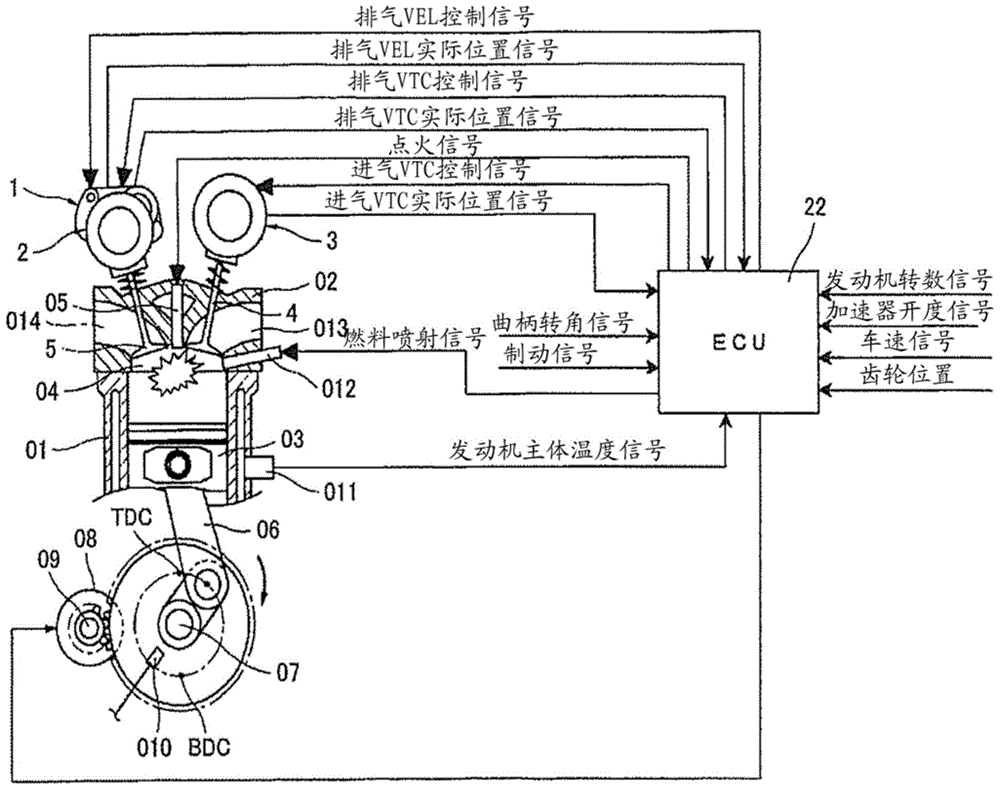
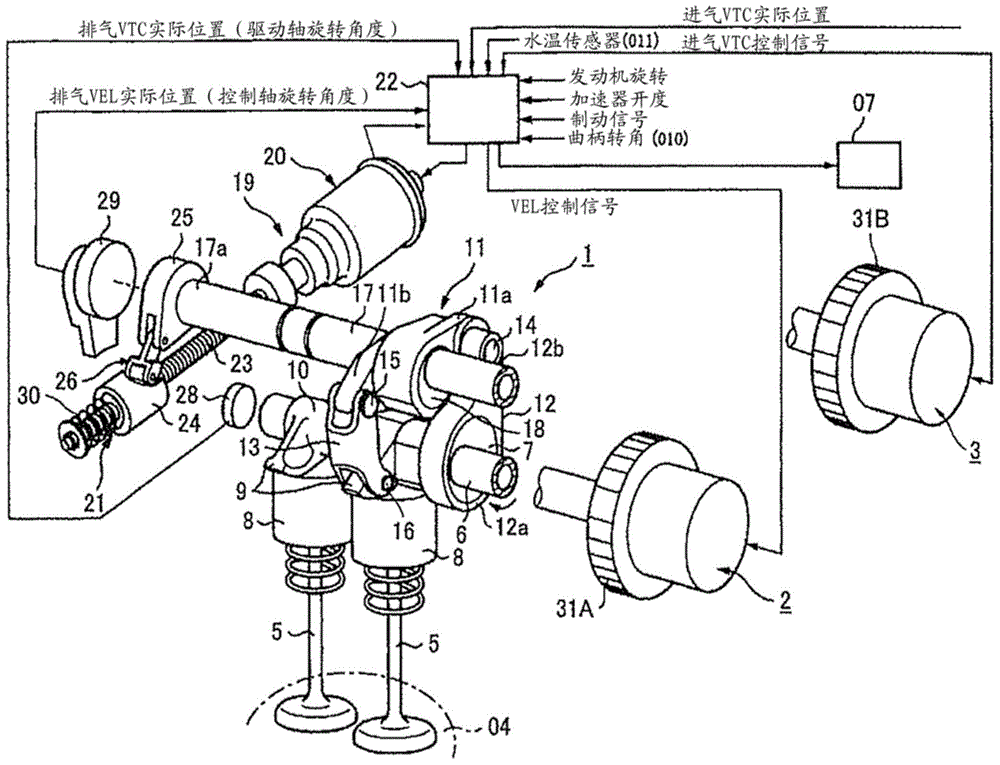
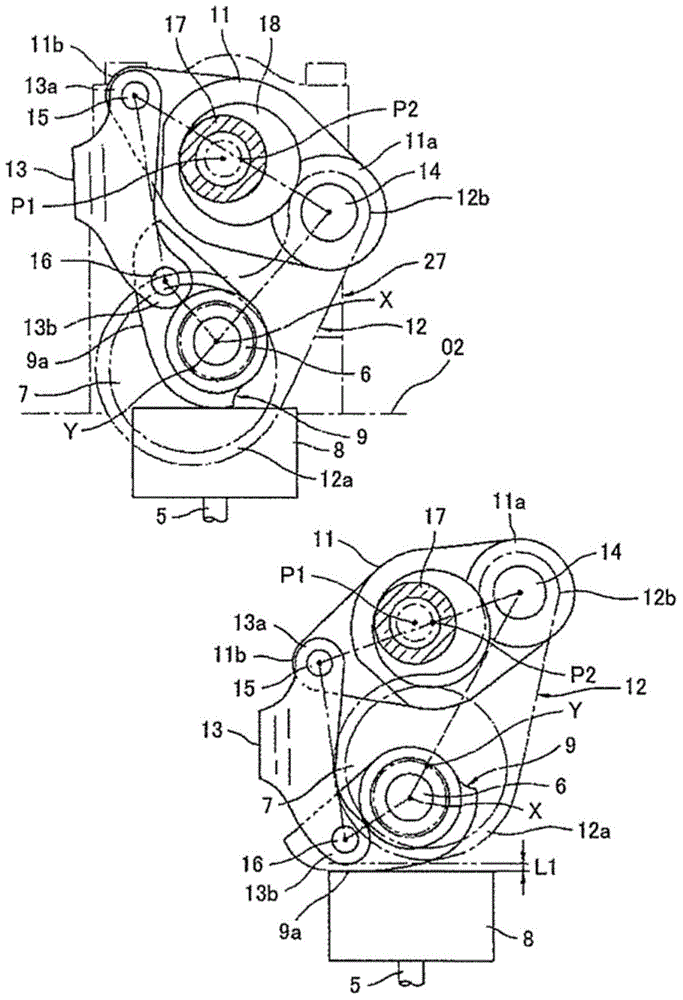
Automatic stop/restart control system for internal combustion engine and variable valve actuating apparatus
An automatic stop and control system technology, applied in engine control, engine start, internal combustion piston engine, etc., can solve the problems of high peak combustion pressure, increased internal combustion engine rotation change, passenger discomfort, etc., to increase the ratio, reduce The effect of lower limit rotation speed and improved combustion torque
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0109] In the internal combustion engine having the above-mentioned variable valve device, then using Fig. 8 to Figure 11 The first embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail. Here, in the embodiment described below, both the valve opening timing ( EVO1 ) of the exhaust valve 5 and the valve closing timing ( IVC1 ) of the intake valve 4 at the time of restart are default positions, which are mechanically stable positions.
[0110] Figure 8A , Figure 8B The operation of the exhaust valve 5 and the intake valve 4 during transition from the automatic stop state (when fuel injection is stopped) to the restart state in this embodiment is shown. Here, the exhaust valve 5 is controlled by the exhaust VEL1, and the intake valve 4 is controlled by the intake VTC3.
[0111] Figure 8A The figure on the left shows the exhaust valve 5 and the intake valve 4 in the low-rotation running state before transitioning to the automatic stop state, or in the automatic s...
Embodiment 2
[0177] Next, use Figure 12A , Figure 12B The second embodiment of the present invention will be described, but in Example 1, when a restart request is generated at a speed equal to or less than the first predetermined speed Nk1, the valve opening timing of the exhaust valve 5 and the closing time of the intake valve 4 are changed. However, in Embodiment 2, when the number of revolutions N falls below the fourth predetermined number of revolutions Nk4 at time Ta, the output changes the valve opening timing of the exhaust valve 5 and the closing valve of the intake valve 4 without waiting for a restart request. Period control signal, which is the difference between embodiment 2 and embodiment 1. In addition, in Figure 12B in the flow chart, because with Figure 11 The same symbols in the control steps of the shown flowcharts denote the same processing, so the description will be simplified.
[0178] Such as Figure 12A As shown, the motor vehicle is in a running (cruisin...
Embodiment 3
[0189] Next, use Figure 13A , Figure 13B The third embodiment of the present invention will be described, but in Example 1, the exhaust VEL1 is used to control the opening timing of the exhaust valve 5, but in Example 3, the difference is that the exhaust VTC2 is used instead of the exhaust VEL1. Therefore, the exhaust valve 5 does not control the valve lift, but controls the valve timing (phase) similarly to the intake VTC3.
[0190] The exhaust VTC2 and the intake VTC3 in this embodiment have actually the same structure, and the two VTC2, 3 are different from the intake VTCs of Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2, and the most retarded angle position is the default position. That is, the coil springs 55 and 56 biasing the vane 32b of the vane member 32 bias the vane 32b to the retarded side, and are set to the most retarded angle phase when the hydraulic pressure is not supplied. The status at this time is Figure 13A Phase shown on the right. In the present embodiment, as de...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com