Patents
Literature
469results about "Valve camshafts" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Valve timing control apparatus
ActiveUS20110259289A1Valve camshaftsMachines/enginesElectrical and Electronics engineeringValve timing
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
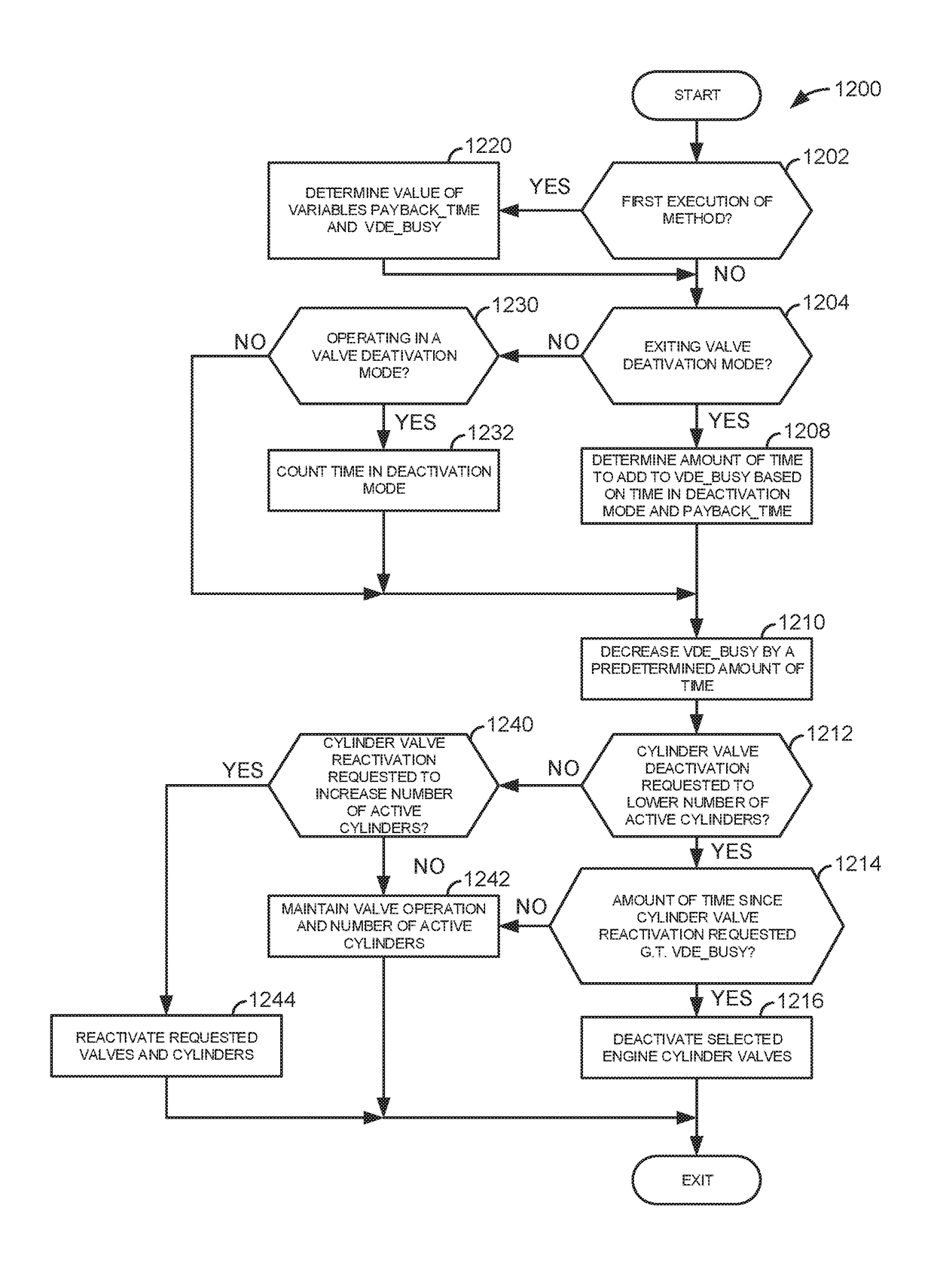
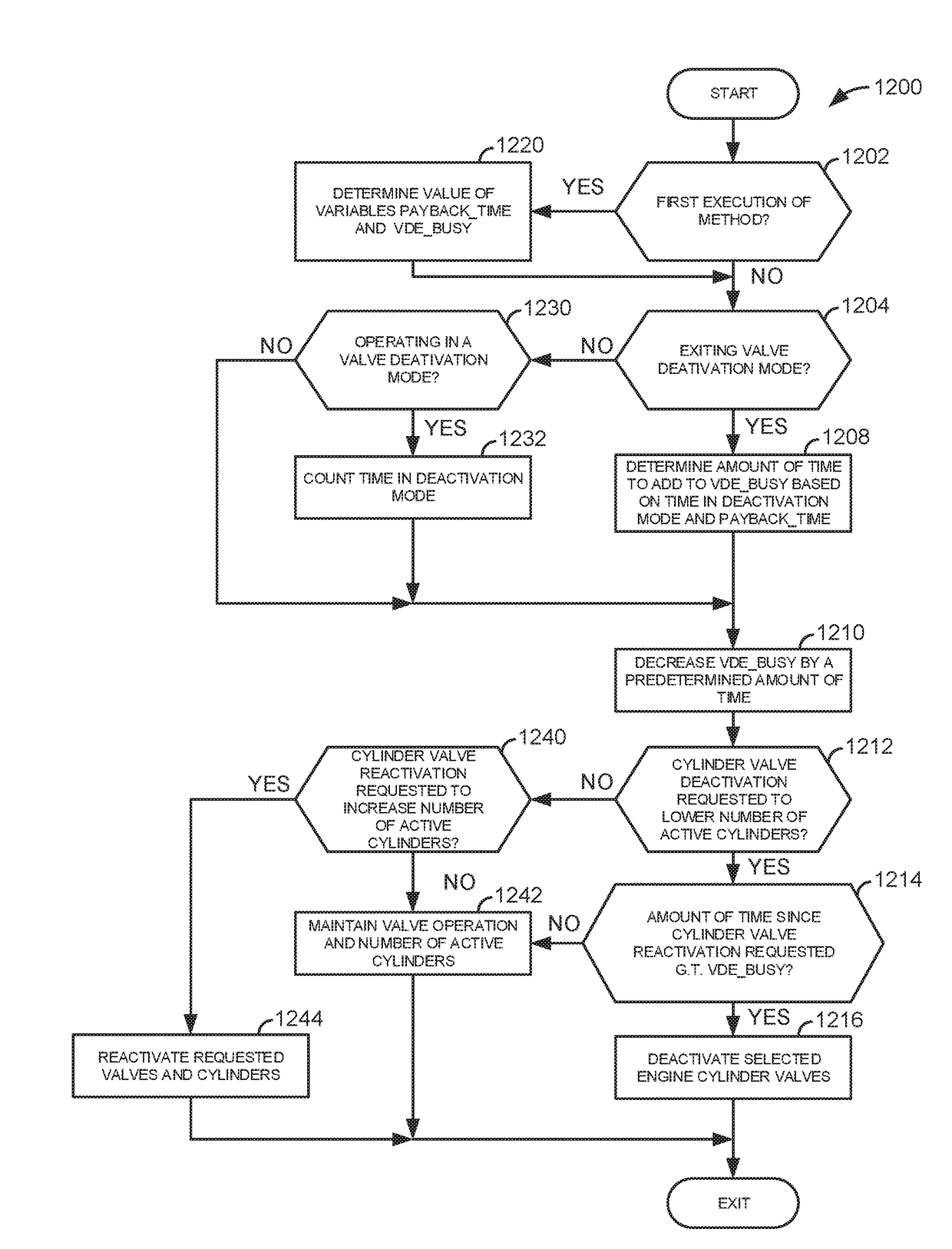
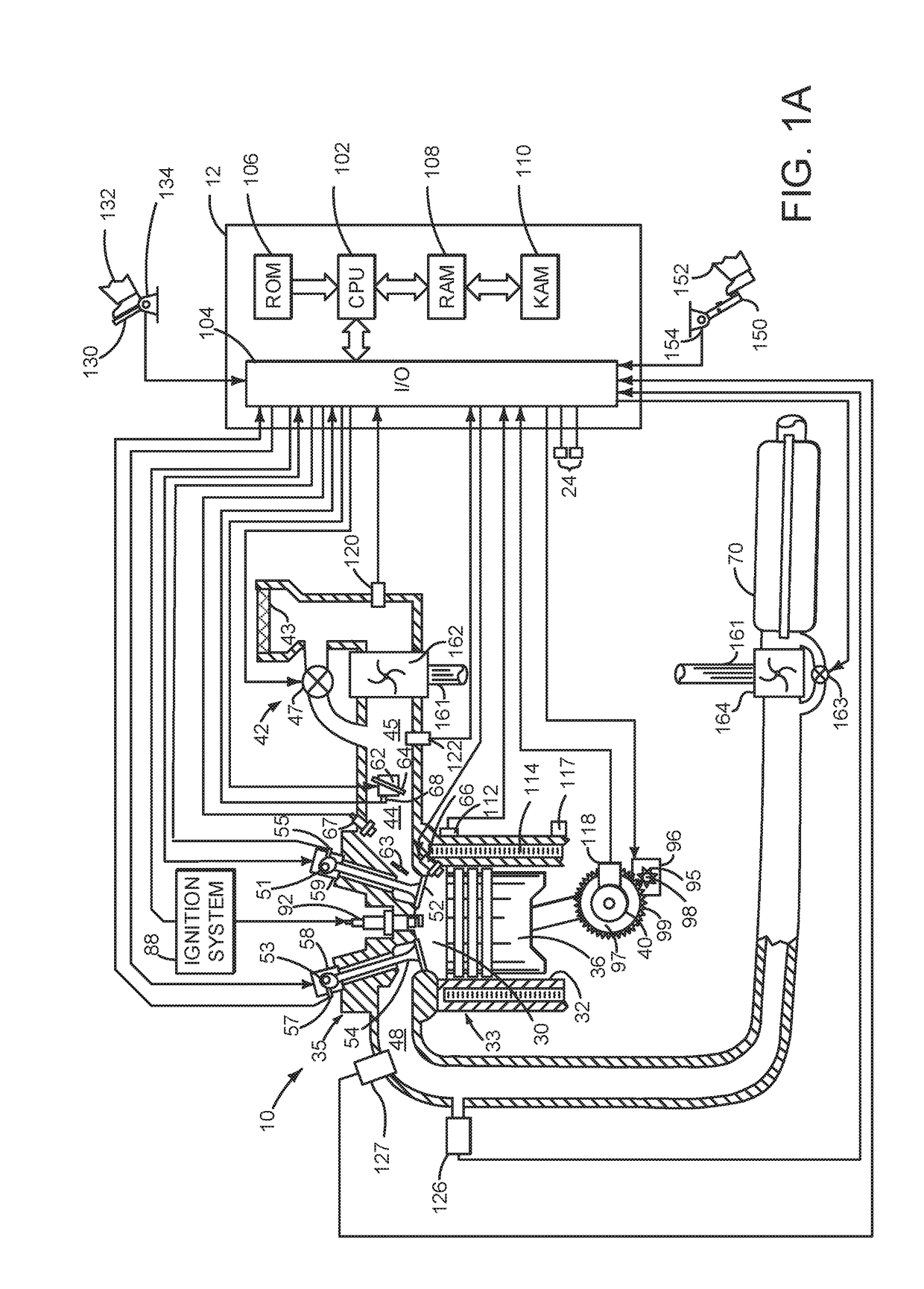
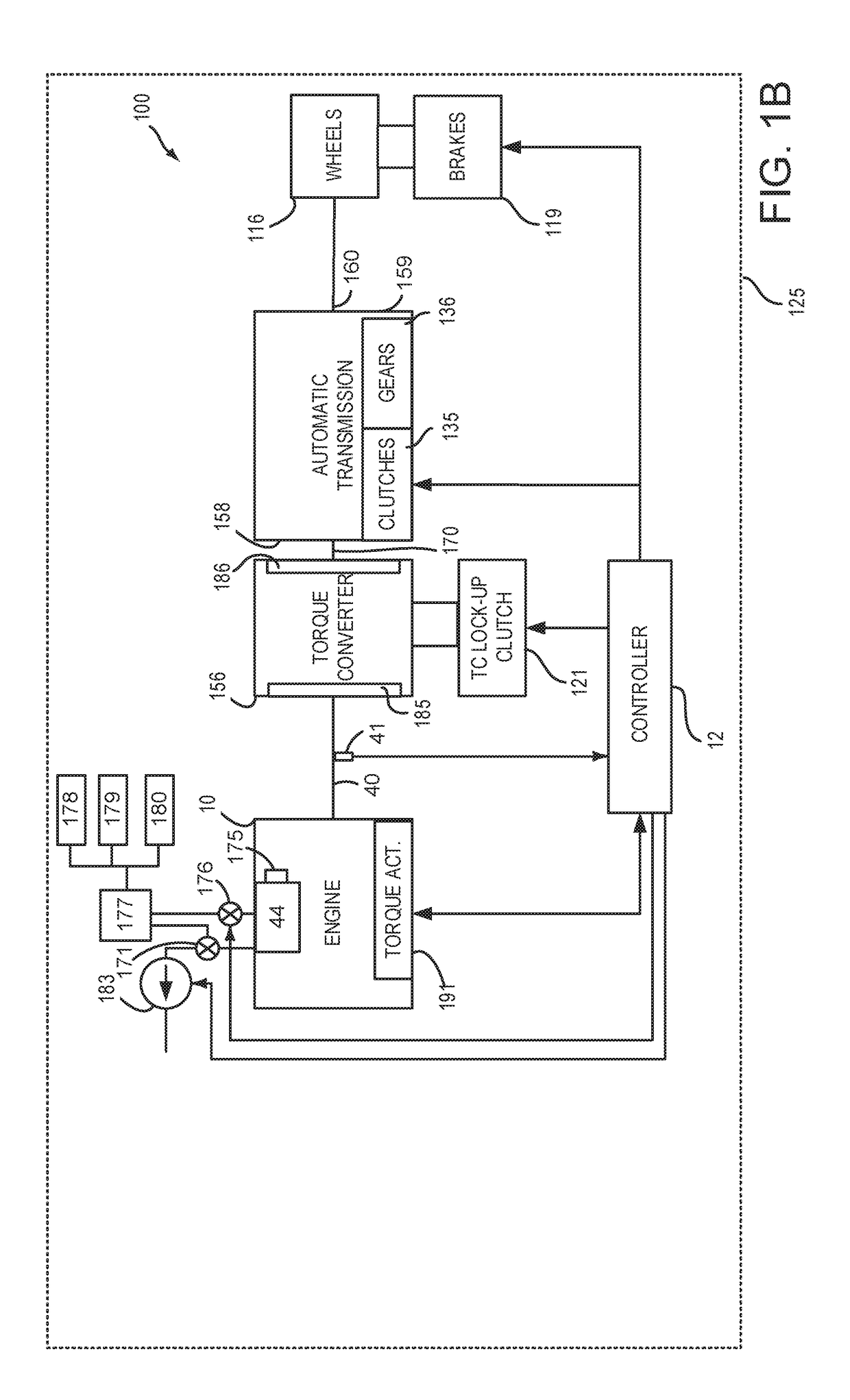
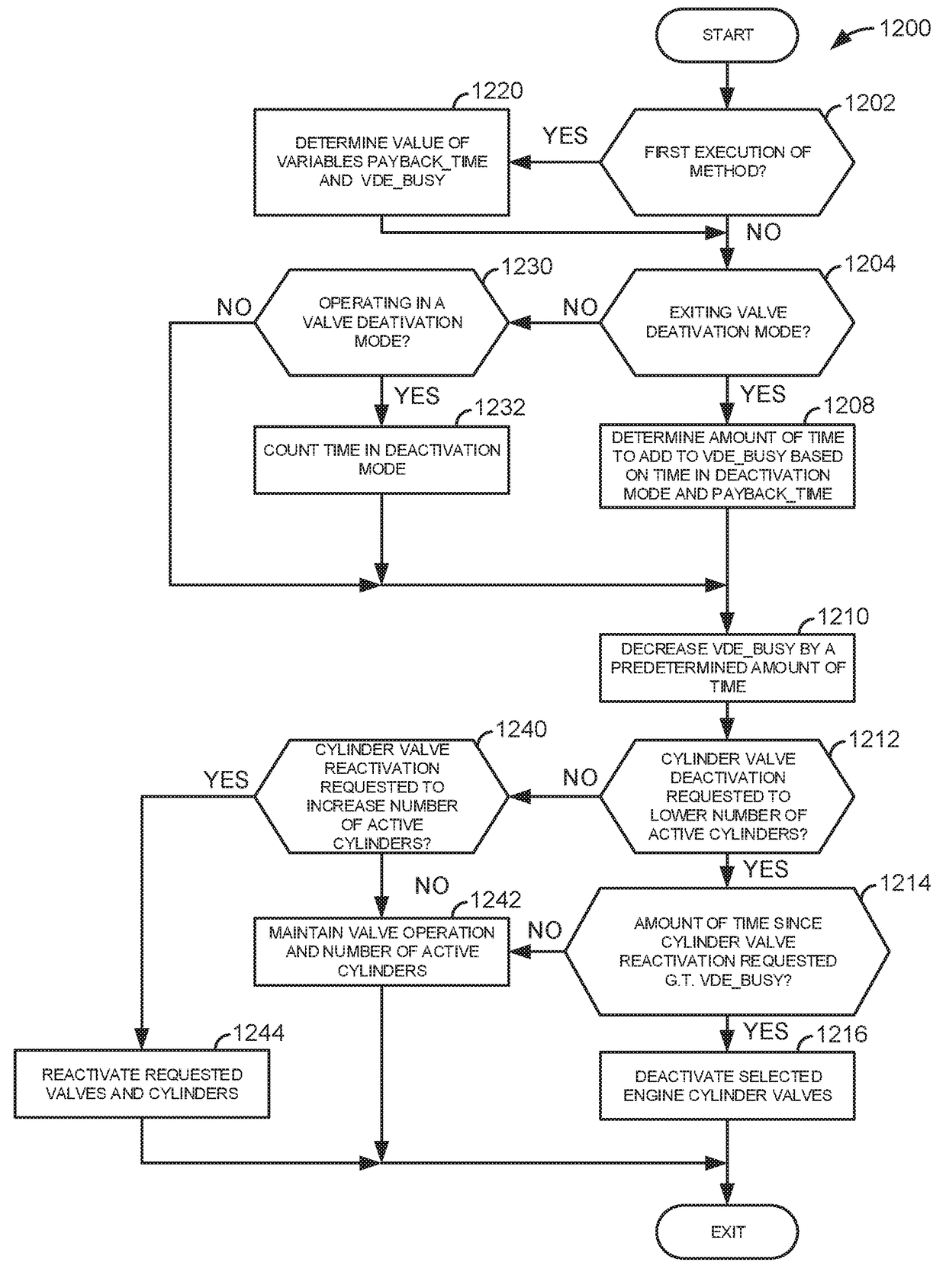
System and method for mitigating cylinder deactivation degradation
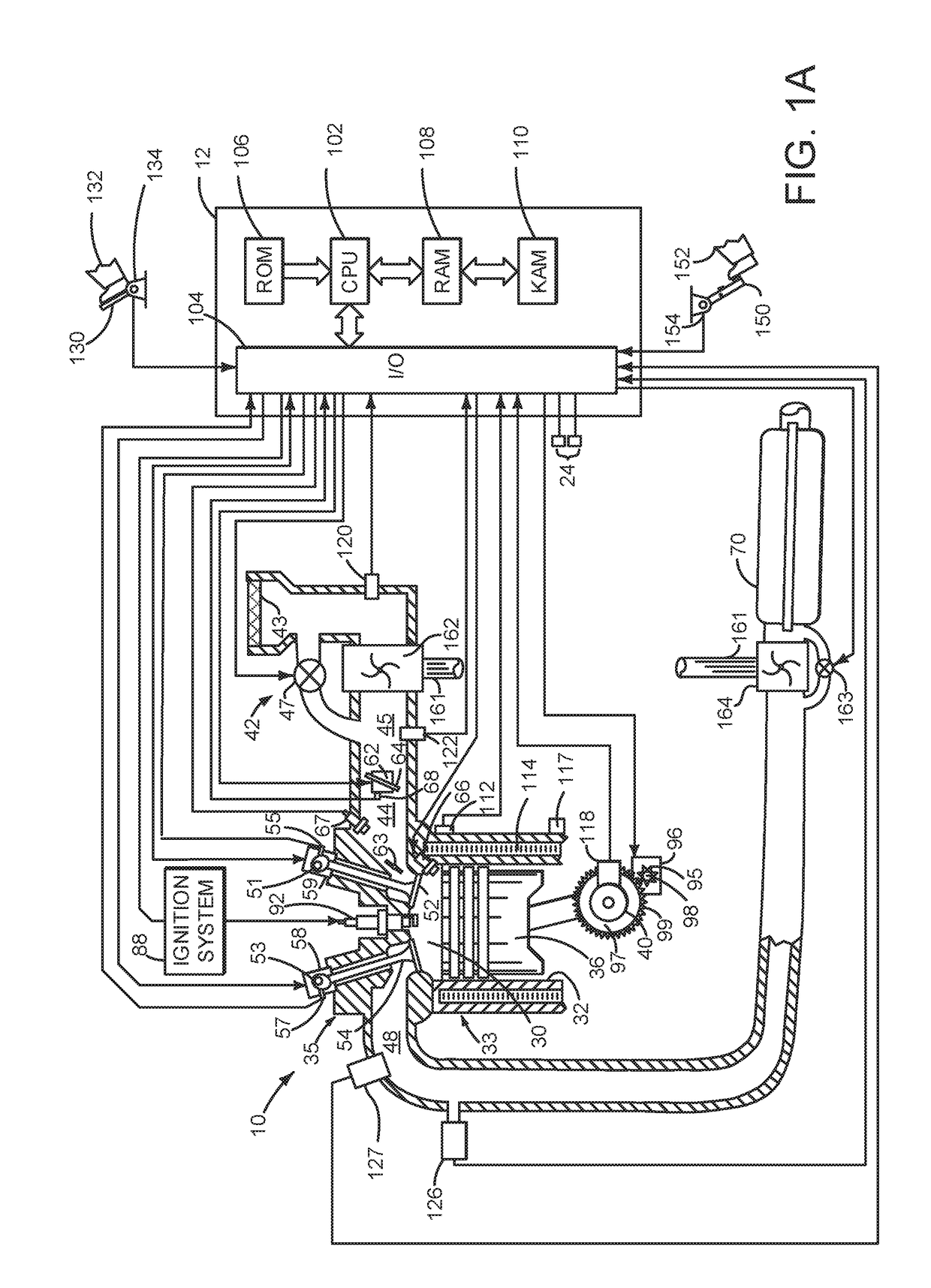
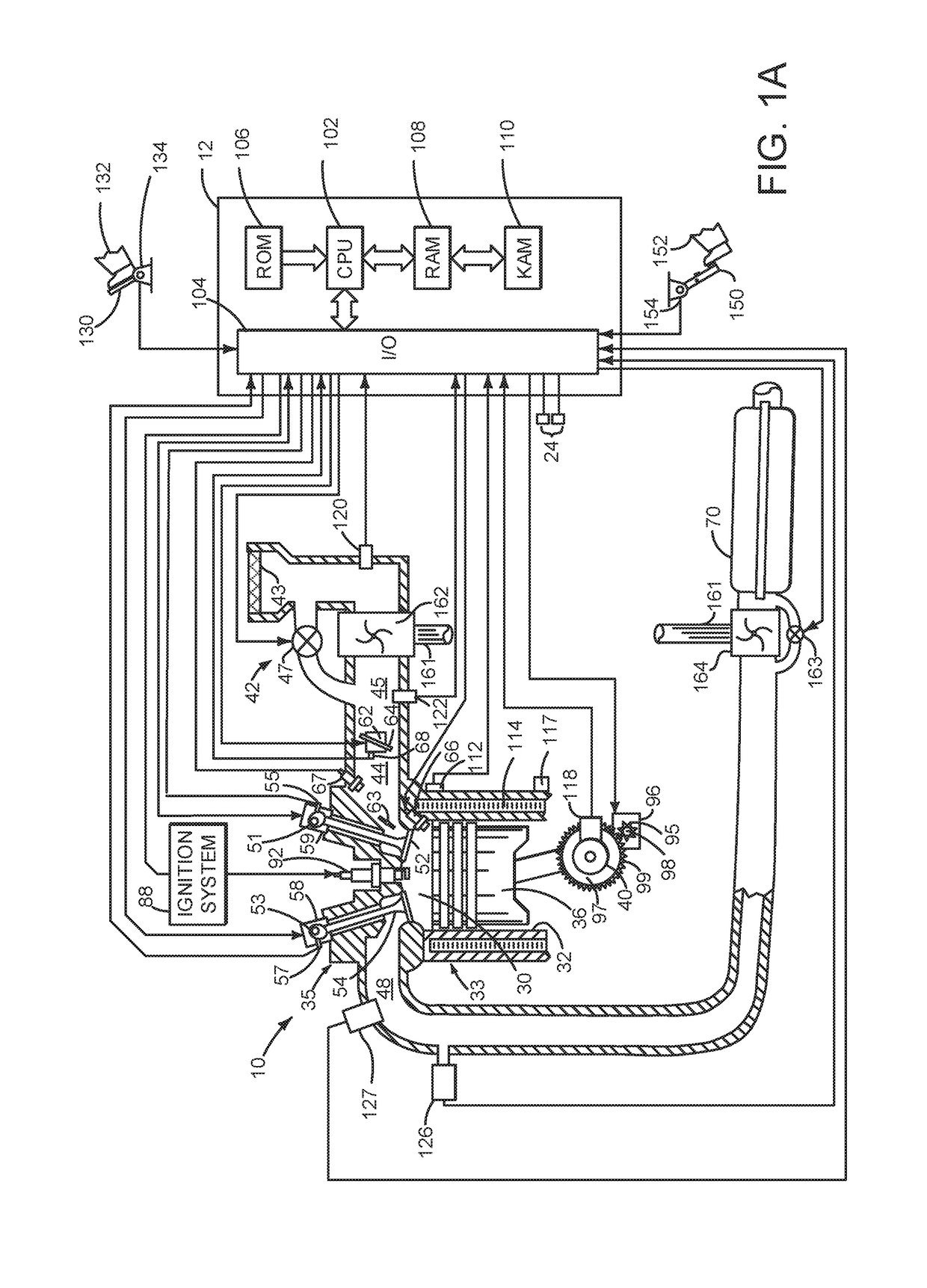
ActiveUS20170356374A1Reduce the possibilityBalance is upsetElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesEngineeringClosed state
Systems and methods for operating an engine with deactivating and non-deactivating valves are presented. In one example, valves of a cylinder are deactivated in a closed state in response to an indication of degradation of a valve of the cylinder. Further, fuel flow to the cylinder may be stopped via ceasing to inject fuel to the cylinder.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
System and method for improving cylinder deactivation
ActiveUS20170356375A1Improving engine fuel economyReduce engine noiseElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesMotor fuelAutomotive engineering
Systems and methods for operating an engine with deactivating and non-deactivating valves are presented. In one example, estimates of engine fuel consumption for operating the engine with a plurality of cylinder modes or patterns while a transmission is engaged in different gears are determined and are used as a basis for deactivating engine cylinders.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Variable valve timing control apparatus
ActiveUS20120055429A1Internal combustion piston enginesOutput powerVariable valve timingPhase control
A variable valve timing control apparatus includes an abnormality determining portion and a valve controller. The abnormality determining portion determines whether there is an abnormality in a system of a VCT phase control in which an oil pressure control valve is controlled in a manner that an actual VCT phase coincides with a target phase. The valve controller controls the oil pressure control valve to drive a lock pin in a locking direction so as to lock the VCT phase when the abnormality determining portion determines that there is an abnormality in the system of the VCT phase control.
Owner:DENSO CORP
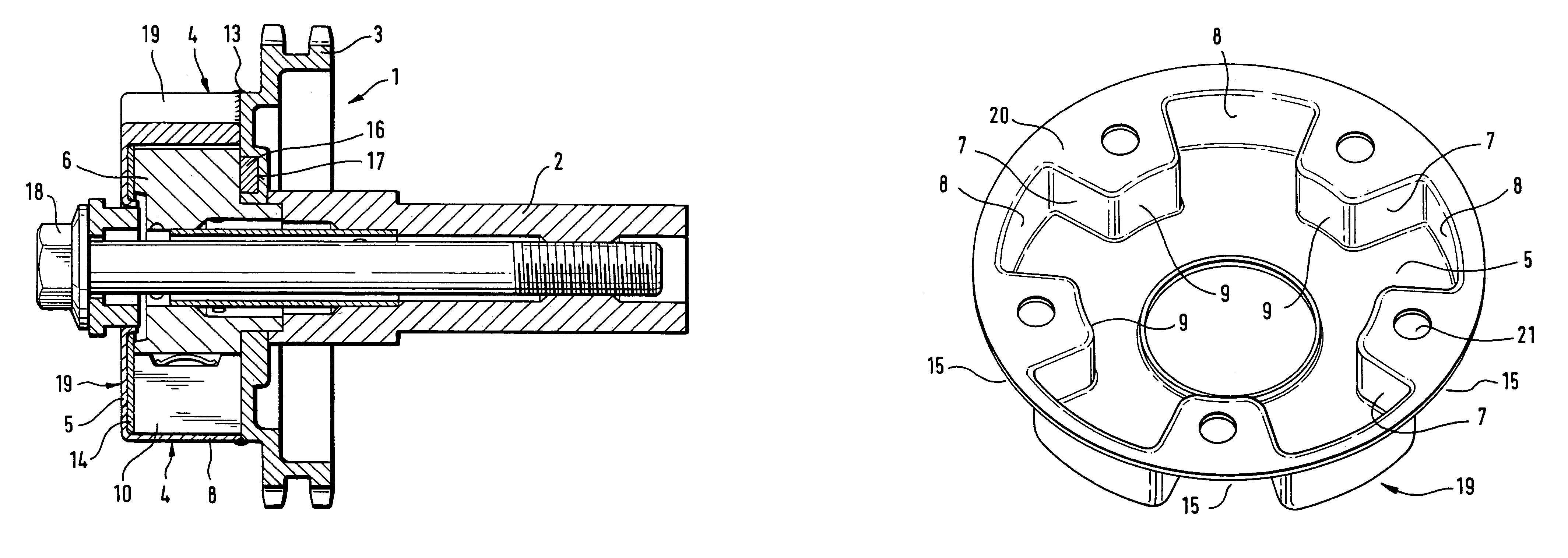
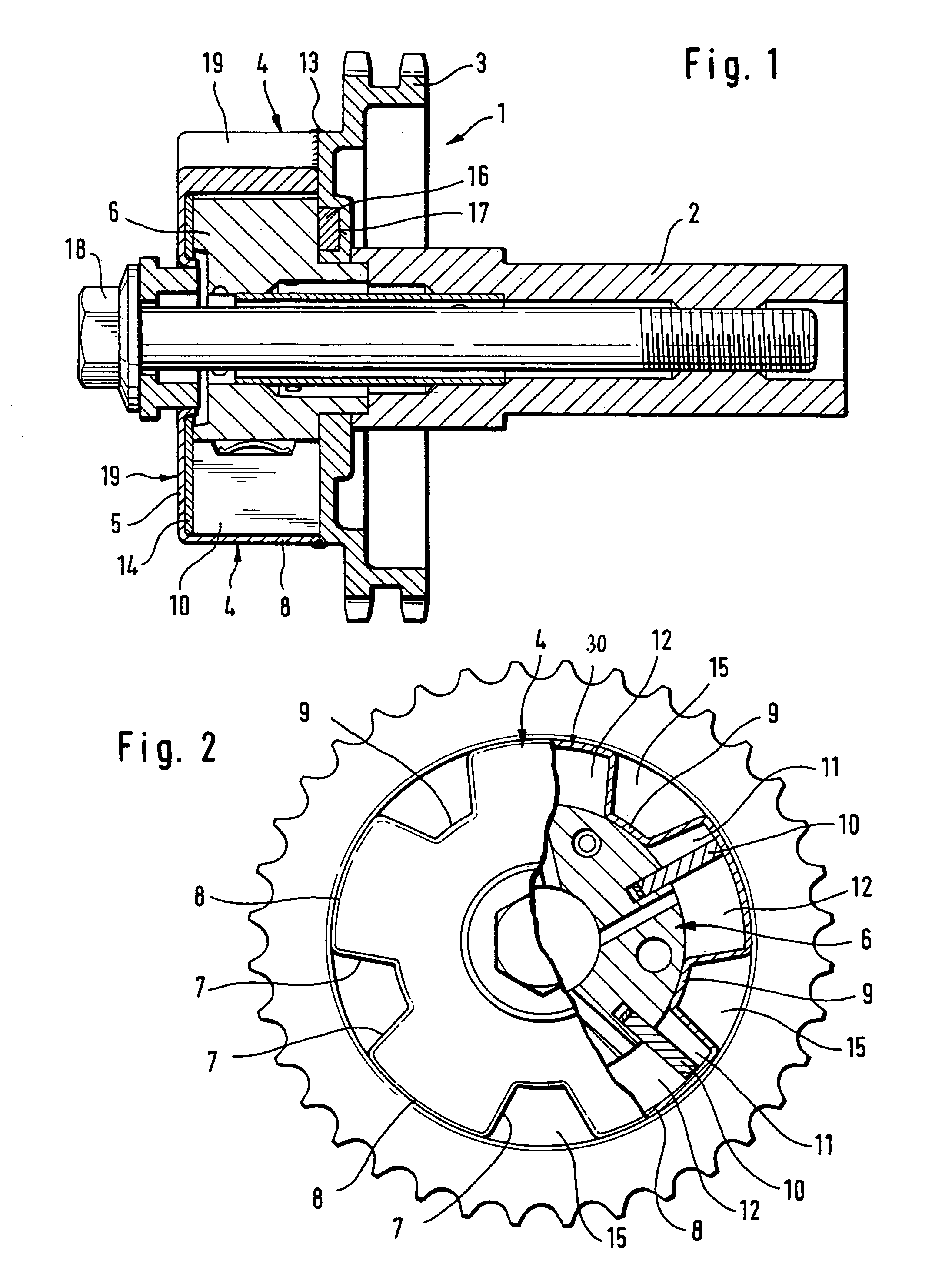
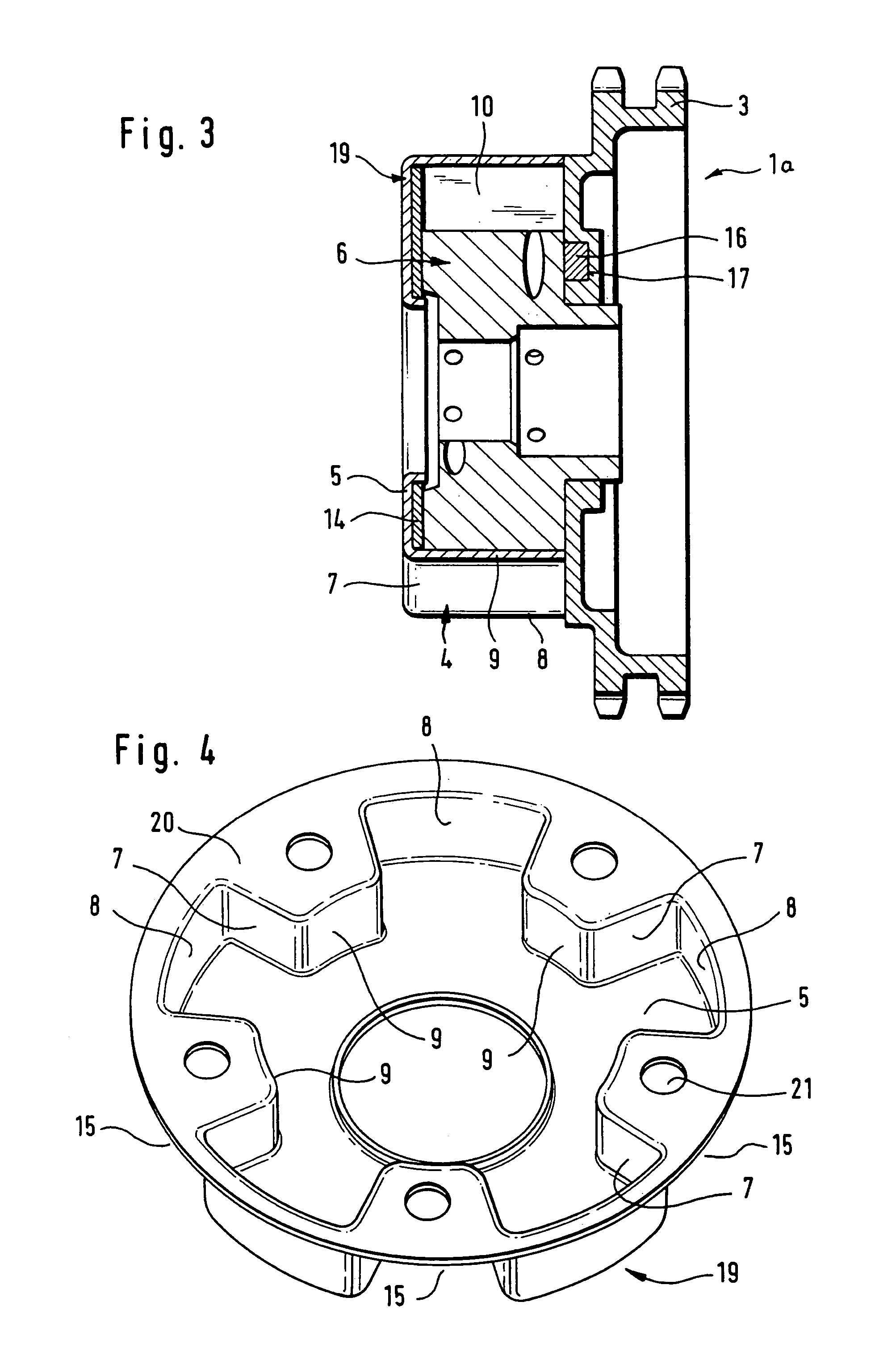
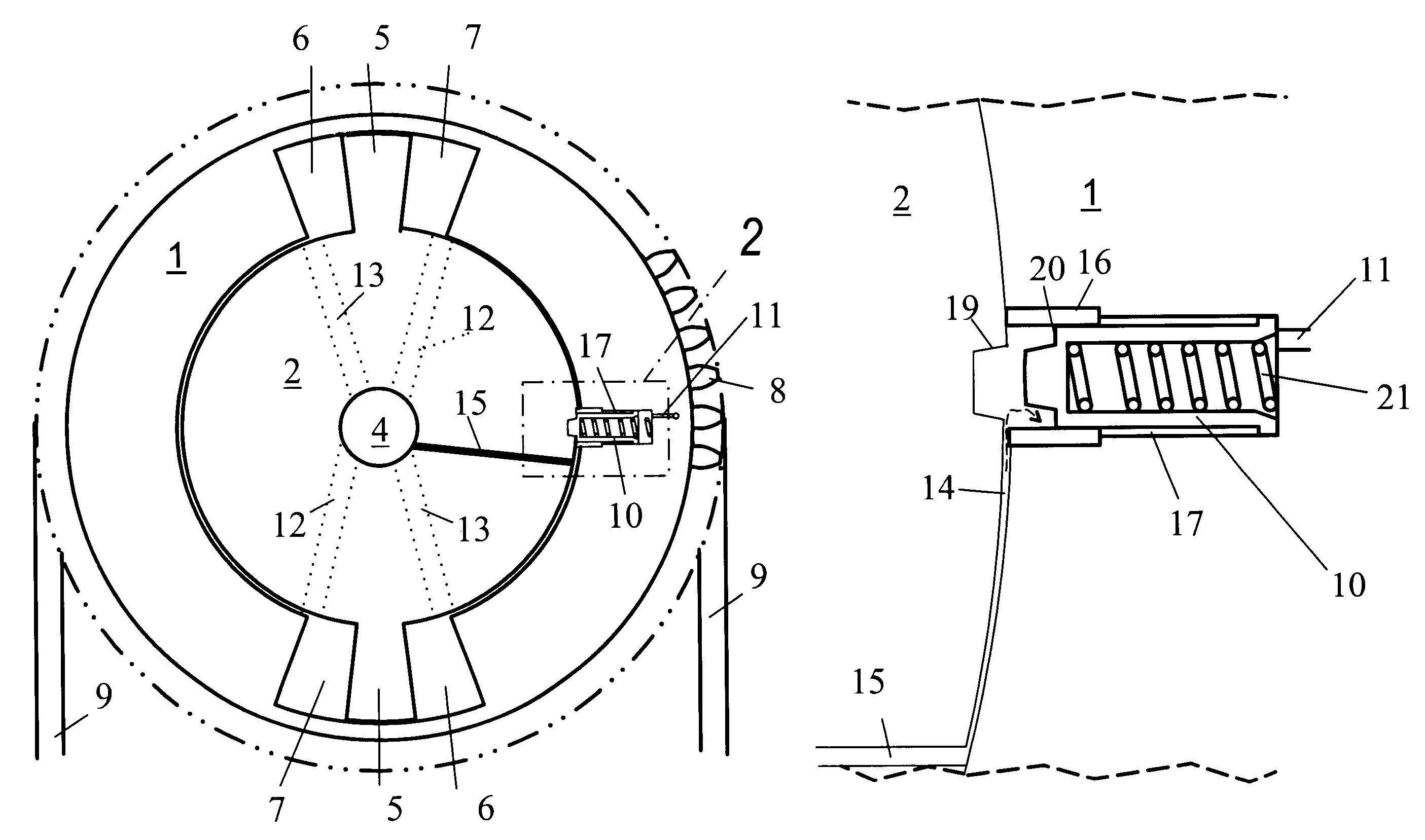
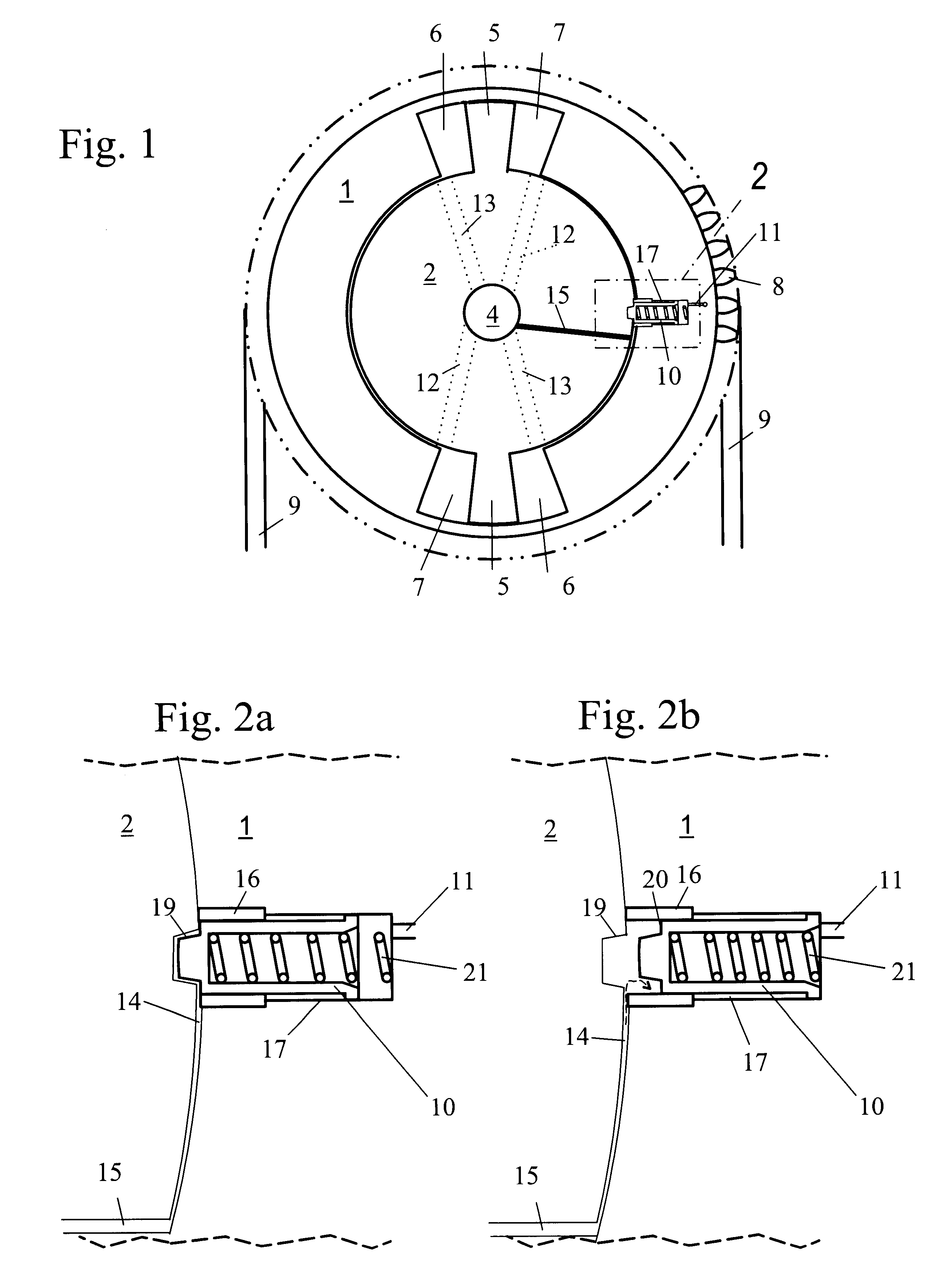
Camshaft adjuster for internal combustion engines of motor vehicles
A camshaft adjuster for motor vehicles has a stator and a rotor rotatable relative thereto between which pressure chambers are provided. Pressure medium is supplied in a controlled way via a valve to the pressure chambers in order to rotate the rotor relative to the stator. Mounting of the valve in the internal combustion engine of the motor vehicle is often difficult when mounting conditions are tight, sometimes even impossible. In order for the camshaft adjuster to be usable even in tight spatial conditions, the valve is arranged on the side facing away from the camshaft connection. The valve can therefore be arranged stationarily axially outside of the engine of the motor vehicle. The camshaft adjuster requires thus only little mounting space.
Owner:HYDRAULIK RING
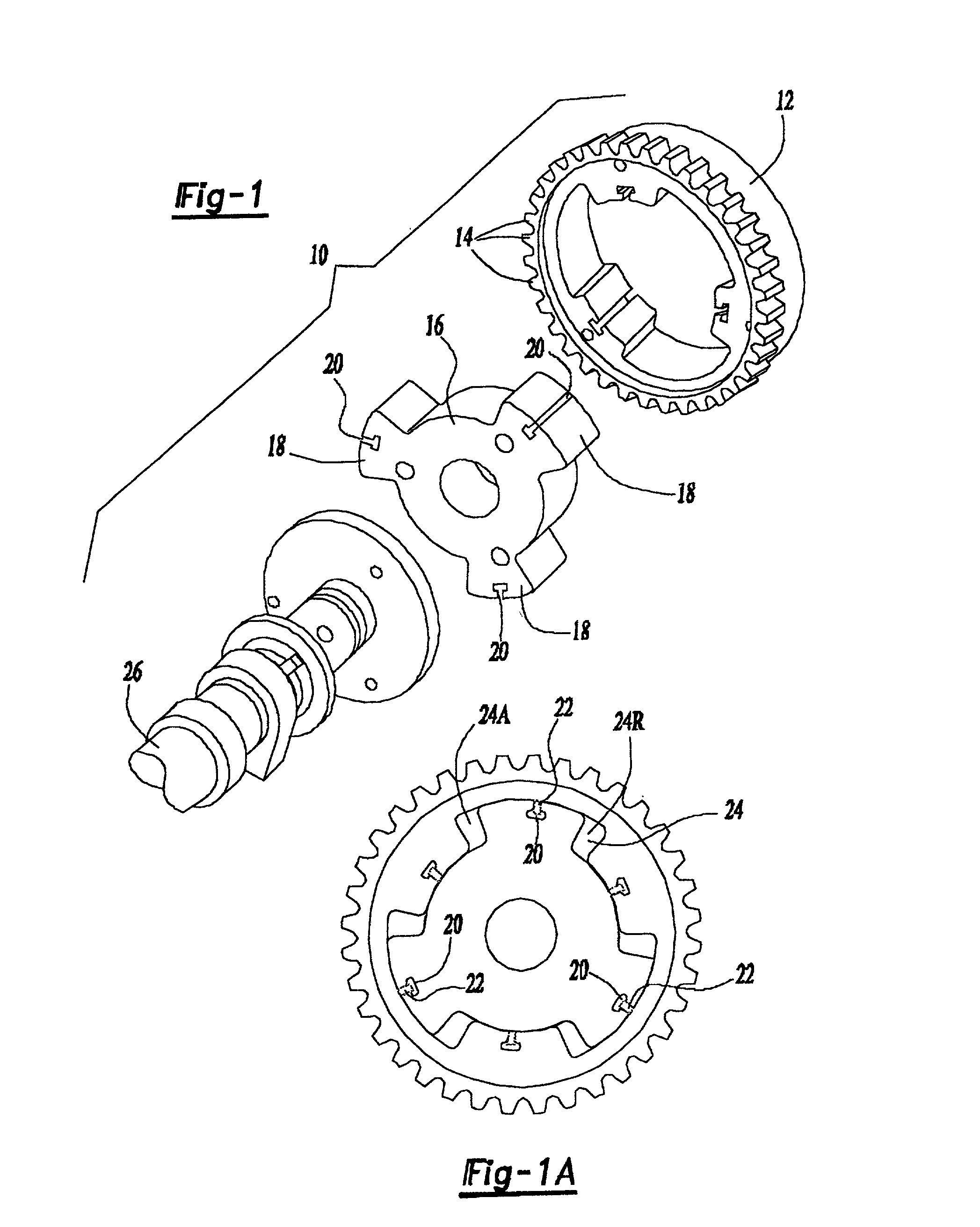
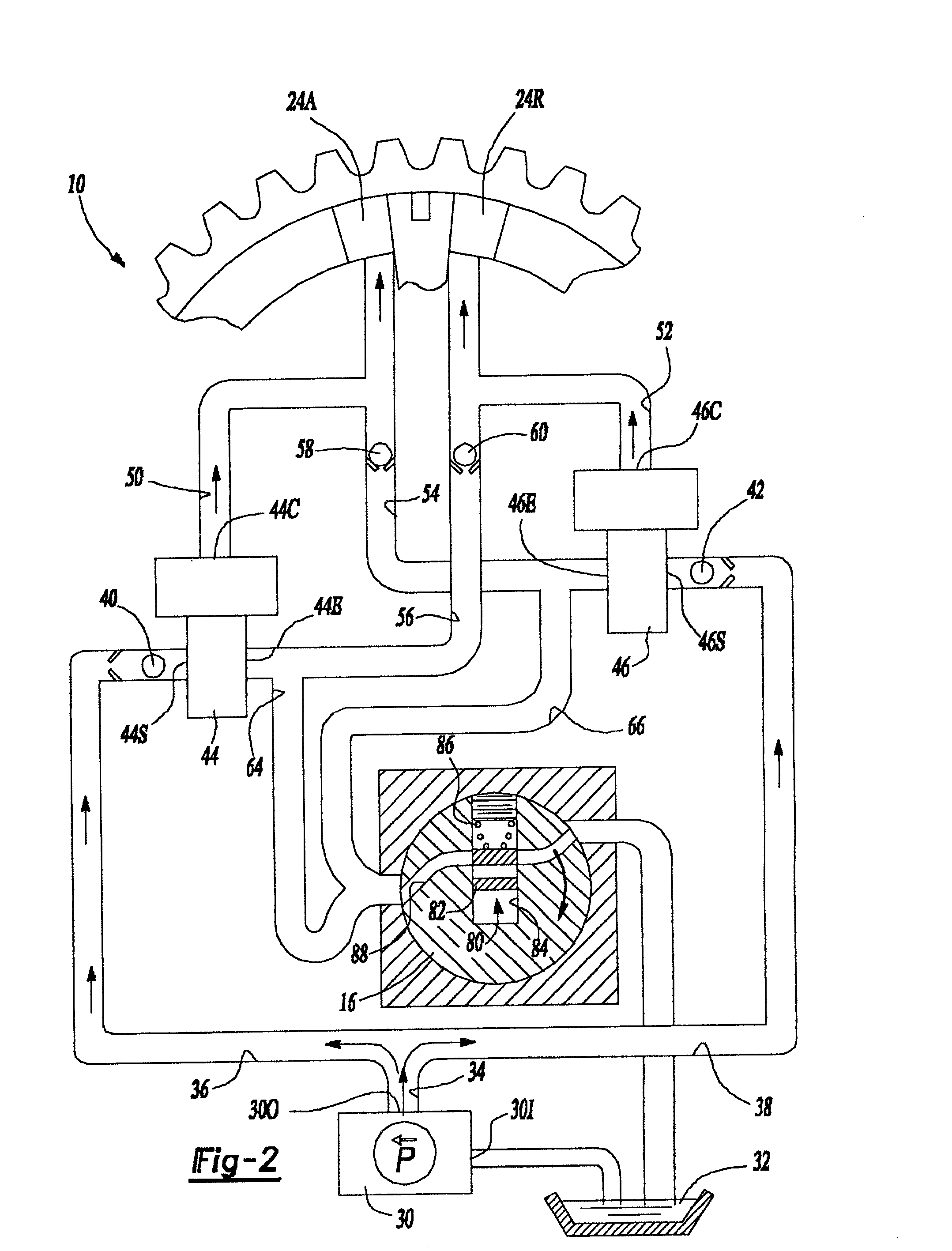
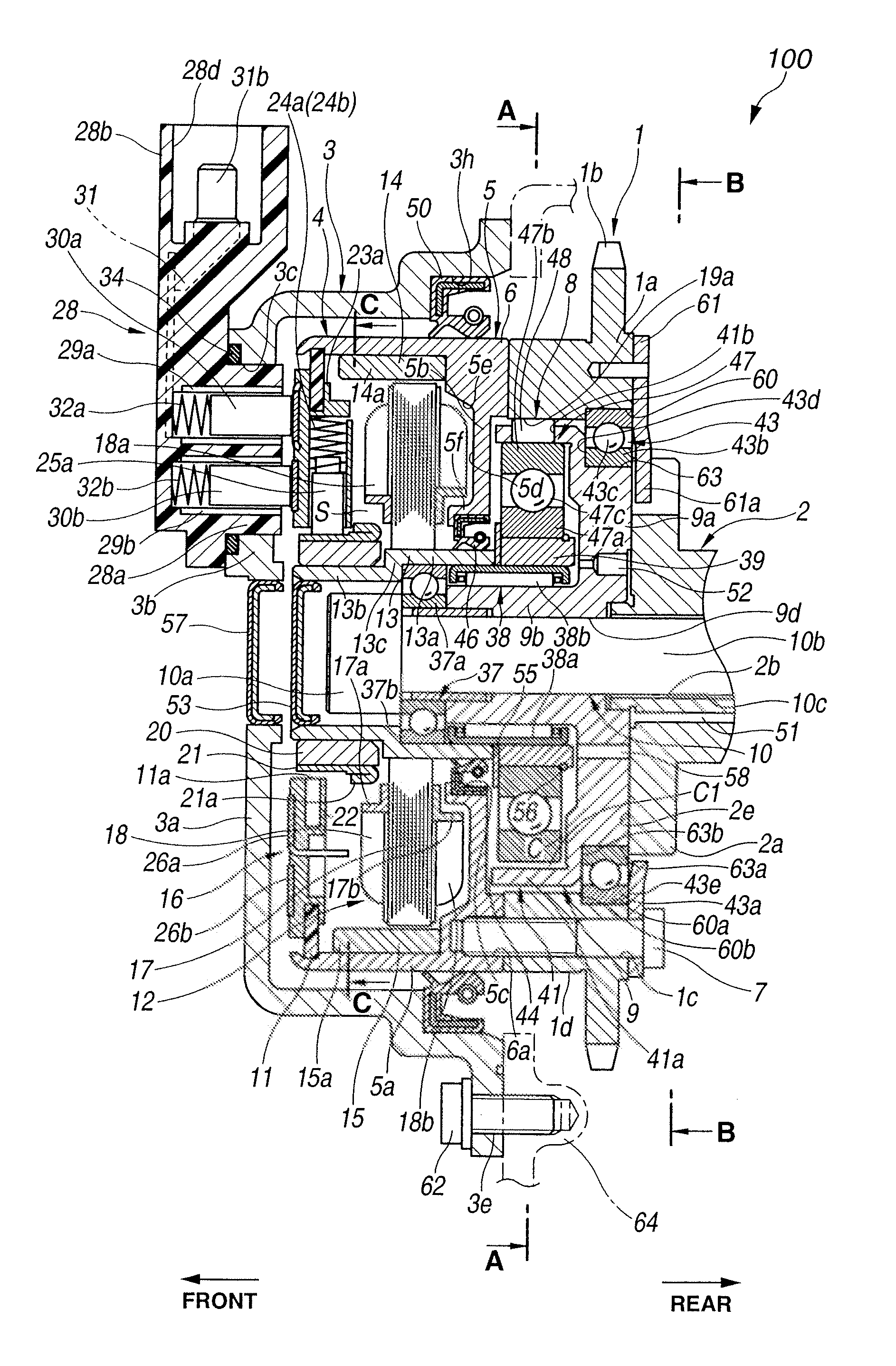
Multi-mode control system for variable camshaft timing devices
A variable camshaft timing apparatus (10) includes a pulse actuating circuit (24A, 50, 44, 56, 60, 24R and 24R, 52, 46, 54, 58, 24A) for oscillating the variable camshaft timing apparatus in reaction to fluid under pulsation, and includes a pressure actuating circuit (30, 34, 36, 40, 44, 50, 24A, 24R, 52, 46, 66, 80 / 180, 32 and 30, 34, 38, 42, 46, 52, 24R, 24A, 50, 44, 64, 80 / 180, 32) for oscillating the variable camshaft timing device in reaction to fluid under pressure. Advance and retard valves (44, 46) are interconnected with the pulse and pressure actuating circuits for independently and simultaneously activating the pulse and pressure actuating circuits. Finally, an exhaust valve (80, 180, 280) is positioned in fluid communication with the pulse and pressure actuating circuits, such that the variable camshaft timing device may be oscillated using one or both of the pulse actuating and pressure actuating circuits, and may be maintained in position using one or both of the pulse actuating and pressure actuating circuits.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
Flow rate control valve
A flow rate control valve includes a housing having an accommodation chamber in communication with oil passages, and a spool accommodated in the accommodation chamber movably in a reciprocating manner. The housing includes a bolt for fastening a movable member of a variable valve timing mechanism, and a sleeve inserted in an insertion portion provided in the bolt and having the accommodation chamber. The bolt is provided with a port through which the oil passages communicate with the insertion portion. The sleeve is provided with a through hole penetrating the sleeve. Furthermore, an annular protrusion and a recess are provided as a phase adjustment portion that adjusts a phase of rotation of the sleeve with respect to the bolt to a phase in which the port coincides in position with the through hole and holds the phase of rotation of the sleeve with respect to the bolt equal thereto.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Valve timing adjusting device
InactiveUS6848401B2Increased durabilityEasy constructionMachines/enginesValve camshaftsGear wheelEngineering
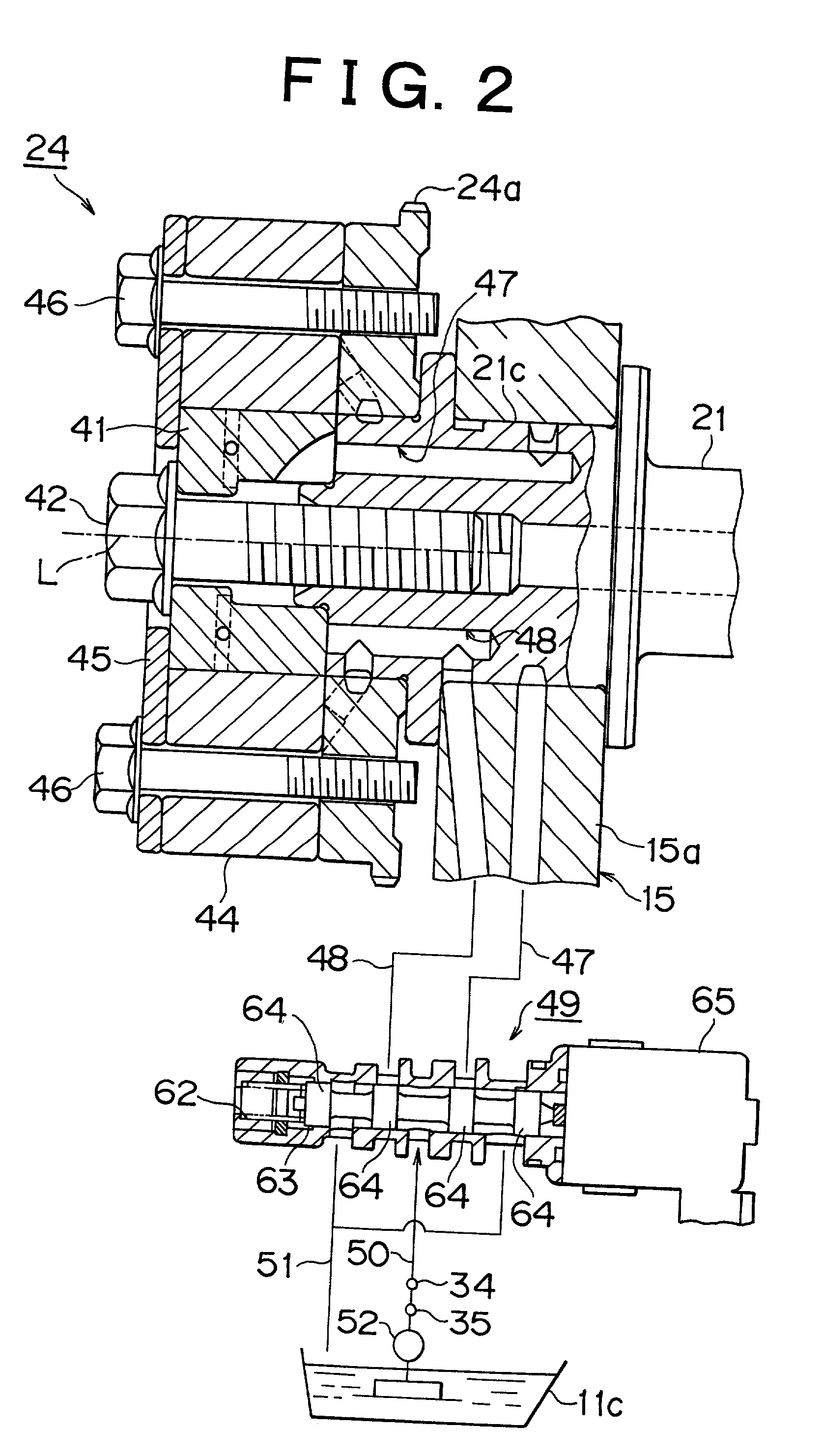
A valve timing adjusting device adjusts valve timing by shifting rotational phase of a camshaft relative to a crankshaft. The device has an electric motor for rotating a rotor member that drives and moves a phase defining member to a required position. The phase defining member defines the rotational phase of the camshaft in accordance with the position itself. The phase defining member may be a planetary gear rotatably supported on an eccentric shaft as the rotor member. The planetary gear works as both a reduction mechanism and a phase shifting mechanism. The phase defining member may be a control pin slidably supported on a rotatable member as the rotor member. A planetary gear may be additionally used as the reduction mechanism for rotating the rotatable member. It is possible to control the phase with high accuracy and durability.
Owner:NIPPON SOKEN +1
Multi-mode variable cam timing phaser
A variable camshaft timing device can operate using pressure generated by camshaft torque energy to transfer fluid from one working chamber to another work chamber or operate via an external fluid pressure source to fill one working chamber while simultaneously exhausting an opposing working chamber or operate using both modes simultaneously. The mode of the variable camshaft timing device is determined by the position of the control valve. The lock pin is controlled by fluid from one of the working chambers.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
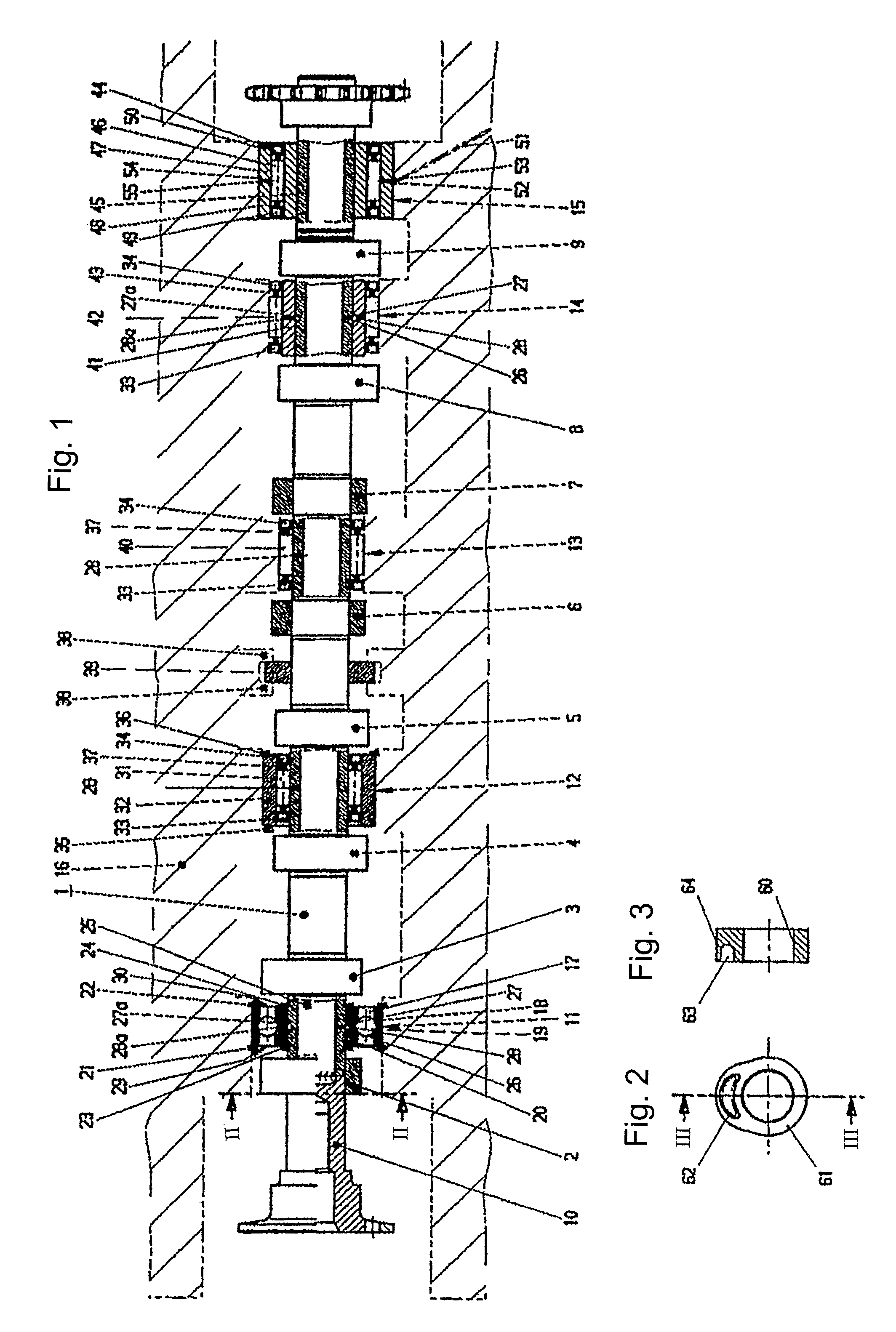
Shaft with functional bodies such as camshafts for internal combustion engines, method of producing them and engines equipped therewith
ActiveUS7992533B2Lower assembly costsLow costCamsRoller bearingsCombustionExternal combustion engine
A shaft comprising functional elements, such as an assembled camshaft for an internal combustion engine, a method for producing such shafts, and internal combustion engines equipped with such shafts. The functional elements each have a bore and are produced separately from the shaft main body, and the bore is subsequently press fit onto the shaft body to attach the functional element in an axially and rotationally fixed manner. The shaft is also provided with at least one roller bearing that includes at least one undivided roller bearing element which is mounted on the shaft body between two functional elements, for example, by press fitting.
Owner:NEUMAYER TEKFOR ENG GMBH
System for deactivating engine cylinders
ActiveUS20170356355A1High power outputIncrease displacementElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust valveInlet valve
Systems and methods for operating an engine with deactivating and non-deactivating valves is presented. In one example, the engine may include non-deactivating intake valves, deactivating intake valves, and only non-deactivating exhaust valves. The non-deactivating exhaust valves may operate to open and close during an engine cycle while deactivating intake valves remain closed during the engine cycle to prevent air flow through selected engine cylinders.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
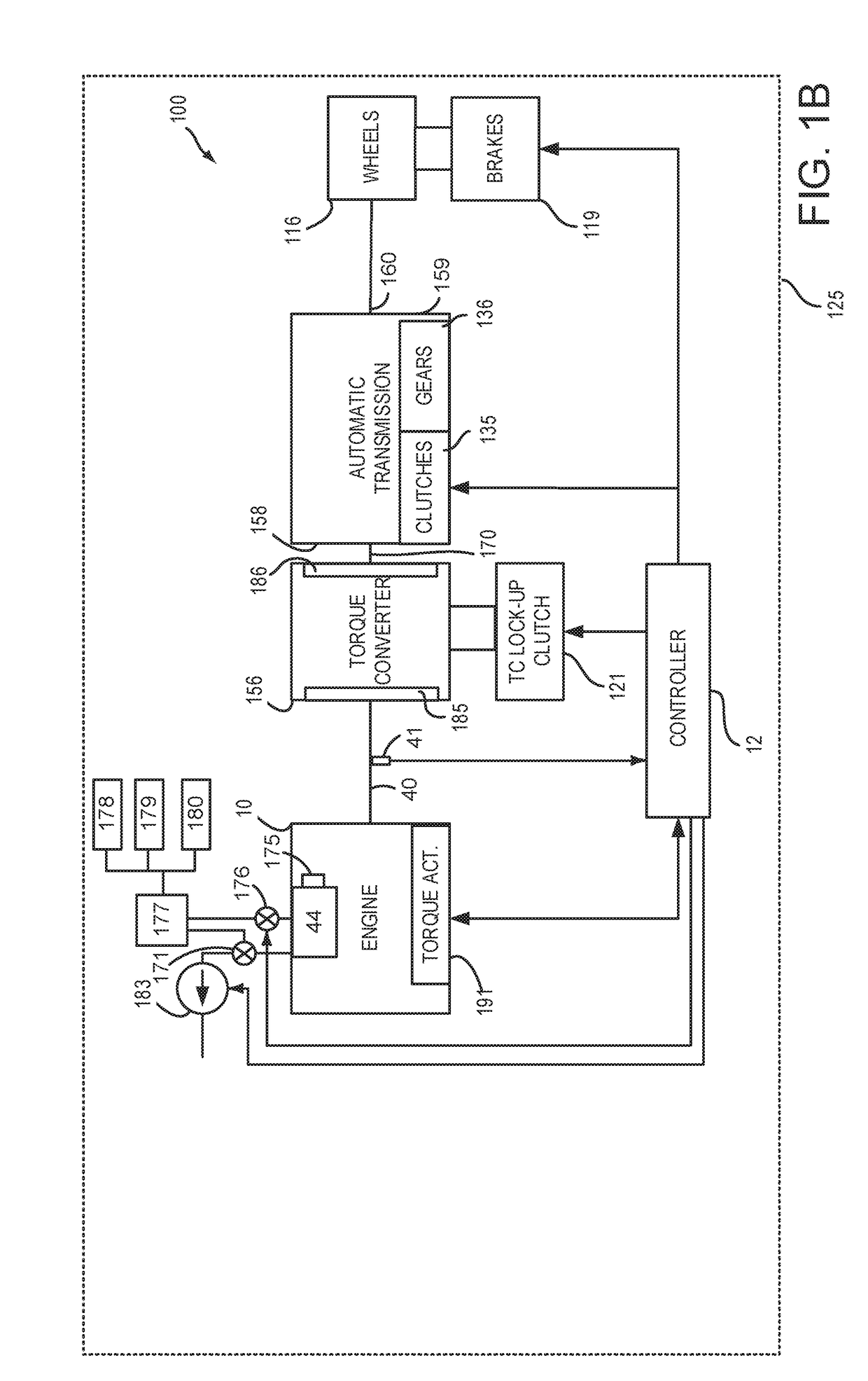
System and method for operating an engine oil pump
ActiveUS20170356373A1High output pressureEngine fuel consumption is lowElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesOil pressureMotor oil
Systems and methods for operating an engine with an oil pump that supplies engine oil to various oil consumers in an engine are presented. In one example, a displacement of a variable displacement engine oil pump is adjusted to provide sufficient oil pressure throughout the engine, but low enough to conserve fuel.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
System and method for intake manifold pressure control
ActiveUS20170356372A1Reduce engine 's responseProduce moreElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesEngineeringActuator
Systems and methods for operating an engine with deactivating and non-deactivating valves are presented. In one example, engine volumetric efficiency actuators are adjusted in response to a request to activate engine cylinders so that engine intake manifold pressure is drawn down quickly toward its normal state at the engine's present speed and torque.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Multi-mode variable cam timing phaser
A variable camshaft timing device can operate using pressure generated by camshaft torque energy to transfer fluid from one working chamber to another work chamber or operate via an external fluid pressure source to fill one working chamber while simultaneously exhausting an opposing working chamber or operate using both modes simultaneously. The mode of the variable camshaft timing device is determined by the position of the control valve. The lock pin is controlled by fluid from one of the working chambers.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
Shaft with Functional Bodies Such as Camshafts for Internal Combustion Engines, Method of Producing Them and Engines Equipped Therewith
A shaft comprising functional elements, such as an assembled camshaft for an internal combustion engine, a method for producing such shafts, and internal combustion engines equipped with such shafts. The functional elements each have a bore and are produced separately from the shaft main body, and the bore is subsequently press fit onto the shaft body to attach the functional element in an axially and rotationally fixed manner. The shaft is also provided with at least one roller bearing that includes at least one undivided roller bearing element which is mounted on the shaft body between two functional elements, for example, by press fitting.
Owner:NEUMAYER TEKFOR ENG GMBH
Camshaft phaser using both cam torque and engine oil pressure
A variable cam timing phaser with a control valve that can selectively user either CTA mode, TA mode or both CTA and TA mode simultaneously to actuate the phaser.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
System and method for reactivating engine cylinders
InactiveUS20170356364A1Good adjustment rateReduce spring forceElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesEngineeringCrankshaft
Systems and methods for operating an engine with deactivating valves are presented. In one example, deactivated valves may be reactivated to increase a rate of camshaft phase indexing relative to engine crankshaft position. However, if a desired rate of camshaft indexing is low, the engine cylinders may remain deactivated based on the low rate of desired camshaft indexing.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Valve gear for internal combustion engine
InactiveCN101802351AValve opening characteristic changesChange valve opening characteristicsMachines/enginesValve camshaftsEngineeringInternal combustion engine
A valve gear mechanism for an internal combustion engine, capable of changing valve-opening characteristics of a valve. The mechanism can smoothly change valve-opening characteristics by using a simplified structure without causing an increase in the number of parts and without causing an increase in sliding friction. A valve gear has a switching mechanism (24) for switching connection and disconnection between rocker arms (32, 34) arranged between a valve (18) and cams (14, 16). When a slide pin (58) reaches an displacement end (Pmax2) in the direction in which a slide pin (58) is retracted,the urging force of a return spring (56) acting on switching pins (48, 54L, 54R) is received by an engaging portion, formed between a notch (58e) provided in the slide pin (58) and a rock pin (70), with the engaging portion separated from a camshaft (12).
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Automatic stop/restart control system for an internal combustion engine and variable valve actuating apparatus
InactiveUS20150369199A1Low RPMEasy to useElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust valveControl system
Owner:HITACHI AUTOMOTIVE SYST LTD
Hydraulic control unit for use in valve timing control apparatus and controller for hydraulic control unit
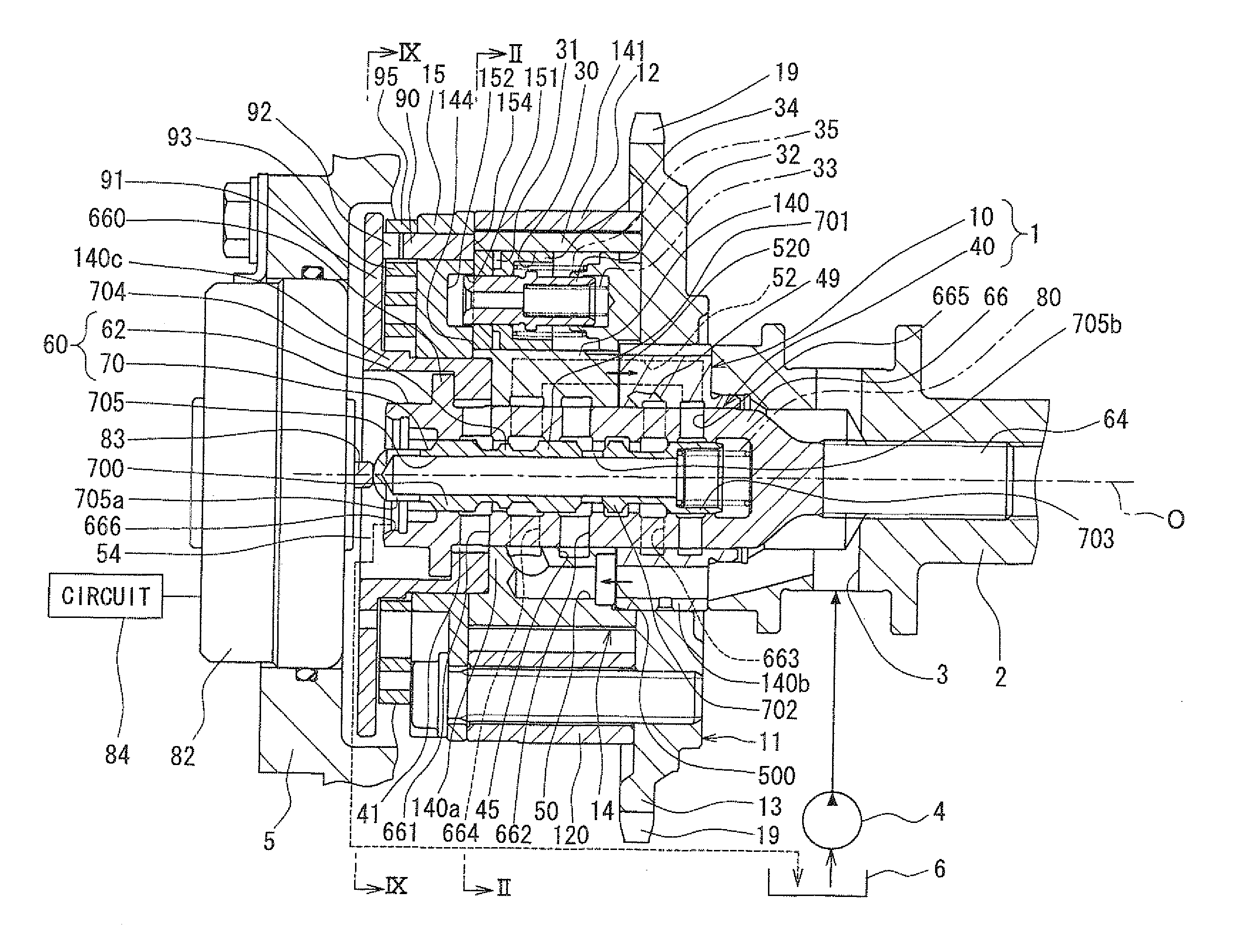
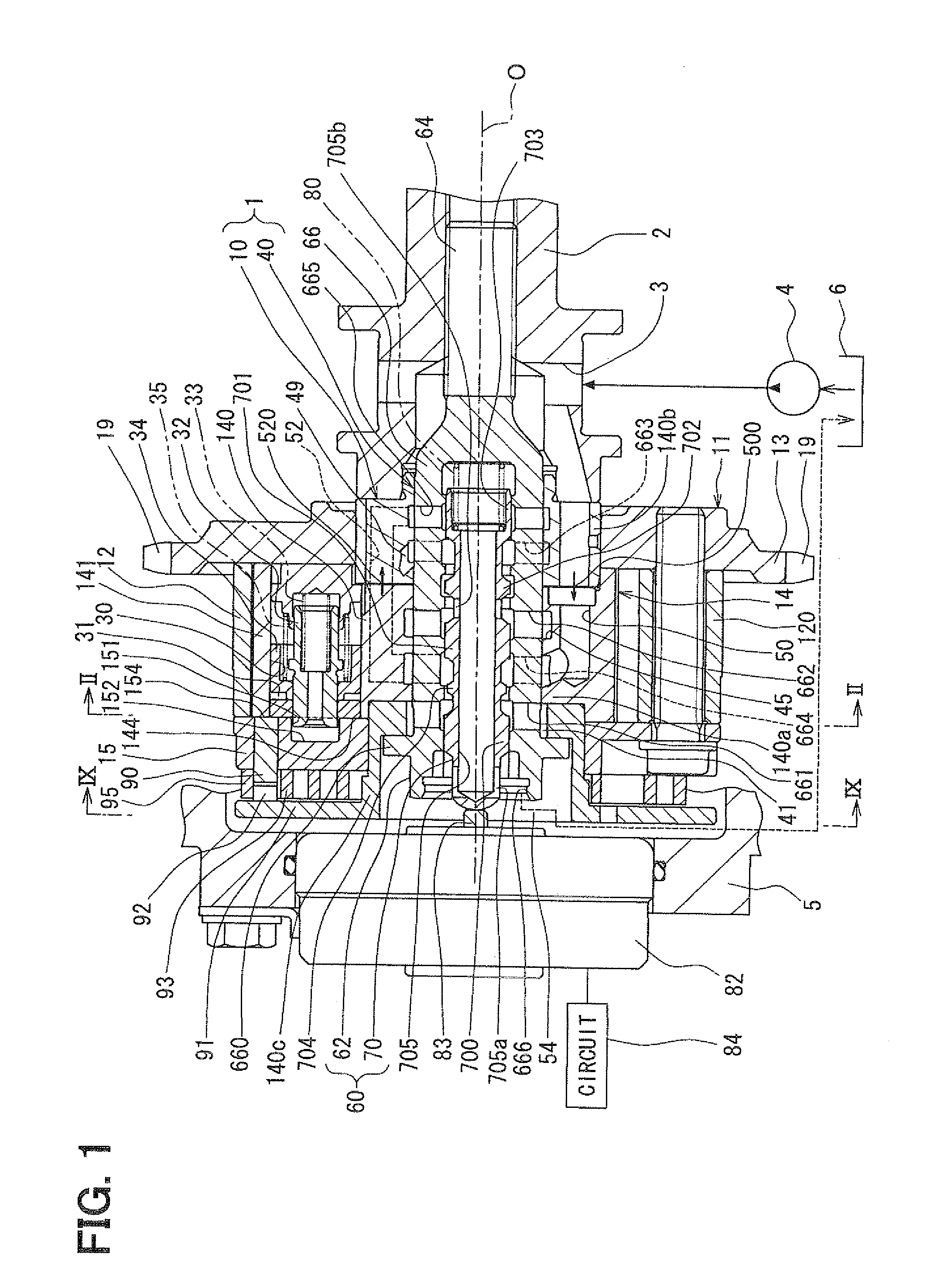
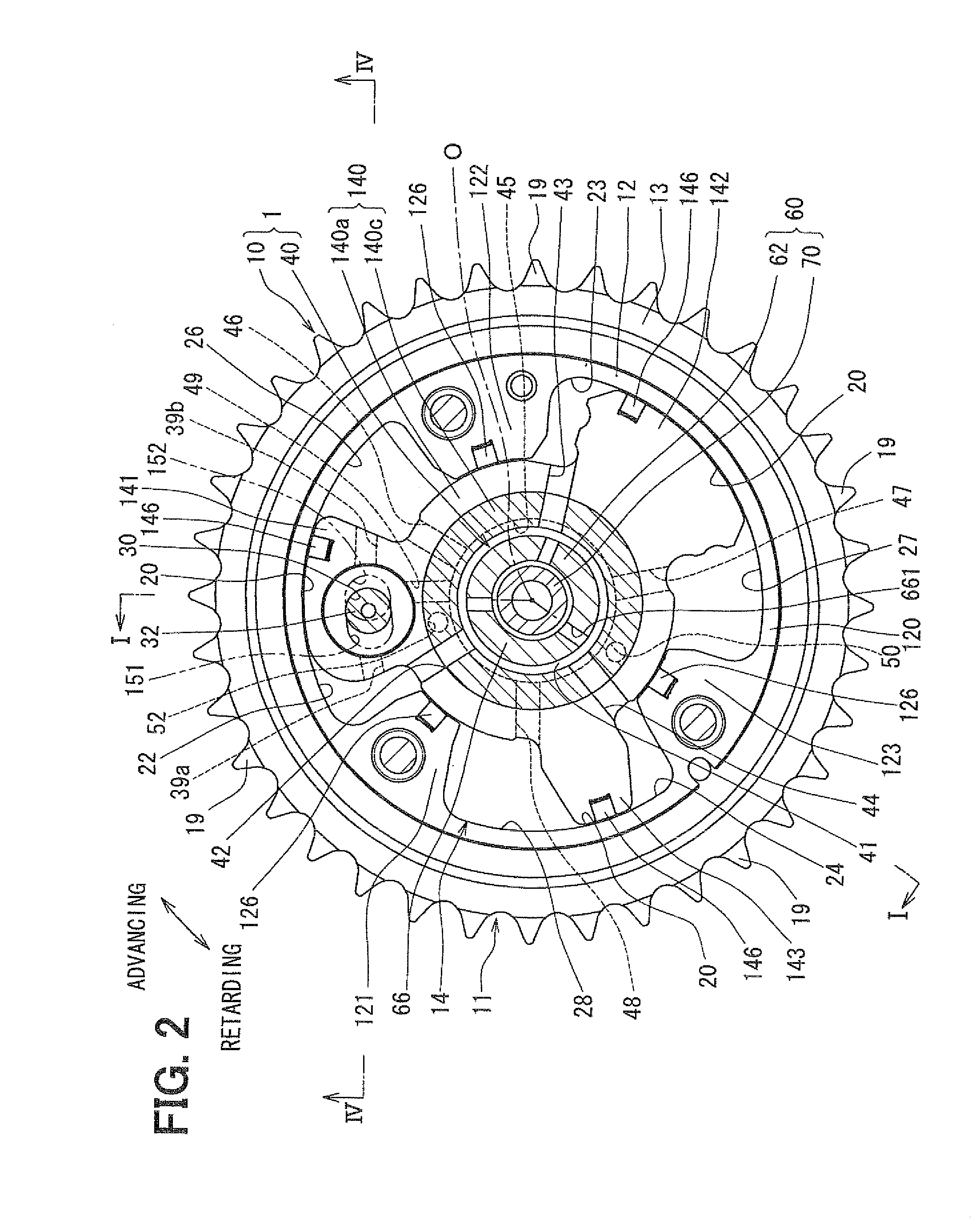
InactiveUS20130068183A1Rapidly lock mechanismLess time delayMachines/enginesValve camshaftsHydraulic control unitEngineering
A hydraulic control unit is configured to switch among a first state where a discharge passage of a pump driven by an internal combustion engine communicates with both a phase-advance passage and a lock passage and simultaneously a phase-retard passage communicates with a drain passage, a second state where the discharge passage communicates with both the phase-retard passage and the lock passage and simultaneously the phase-advance passage communicates with the drain passage, and a third state where the phase-advance passage, the phase-retard passage, and the lock passage all communicate with the discharge passage. The hydraulic control unit is further switchable to a fourth state where the discharge passage communicates with both the phase-advance passage and the phase-retard passage and simultaneously the lock passage communicates with the drain passage.
Owner:HITACHI AUTOMOTIVE SYST LTD
Control device and control method for internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20150211424A1Easy to controlElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesVariable valve timingSafety control
A control device for an internal combustion engine includes an intake-side variable valve timing mechanism and a controller. The intake-side variable valve timing mechanism is configured to continuously advance or retard a phase of a cam that actuates an intake valve. The controller is configured to actuate the intake-side variable valve timing mechanism toward a retardation side and position the intake-side variable valve timing mechanism at a prescribed position, and execute fail-safe control on the basis of a signal from a cam position sensor instead of a signal from the crank position sensor, when it is determined that there is a failure in a crank position sensor of the internal combustion engine.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Camshaft adjuster and stator cover unit for automatic adjustment of a locking device
ActiveUS20150013636A1Easy to assembleNon-fuel substance addition to fuelValve camshaftsEngineeringInternal combustion engine
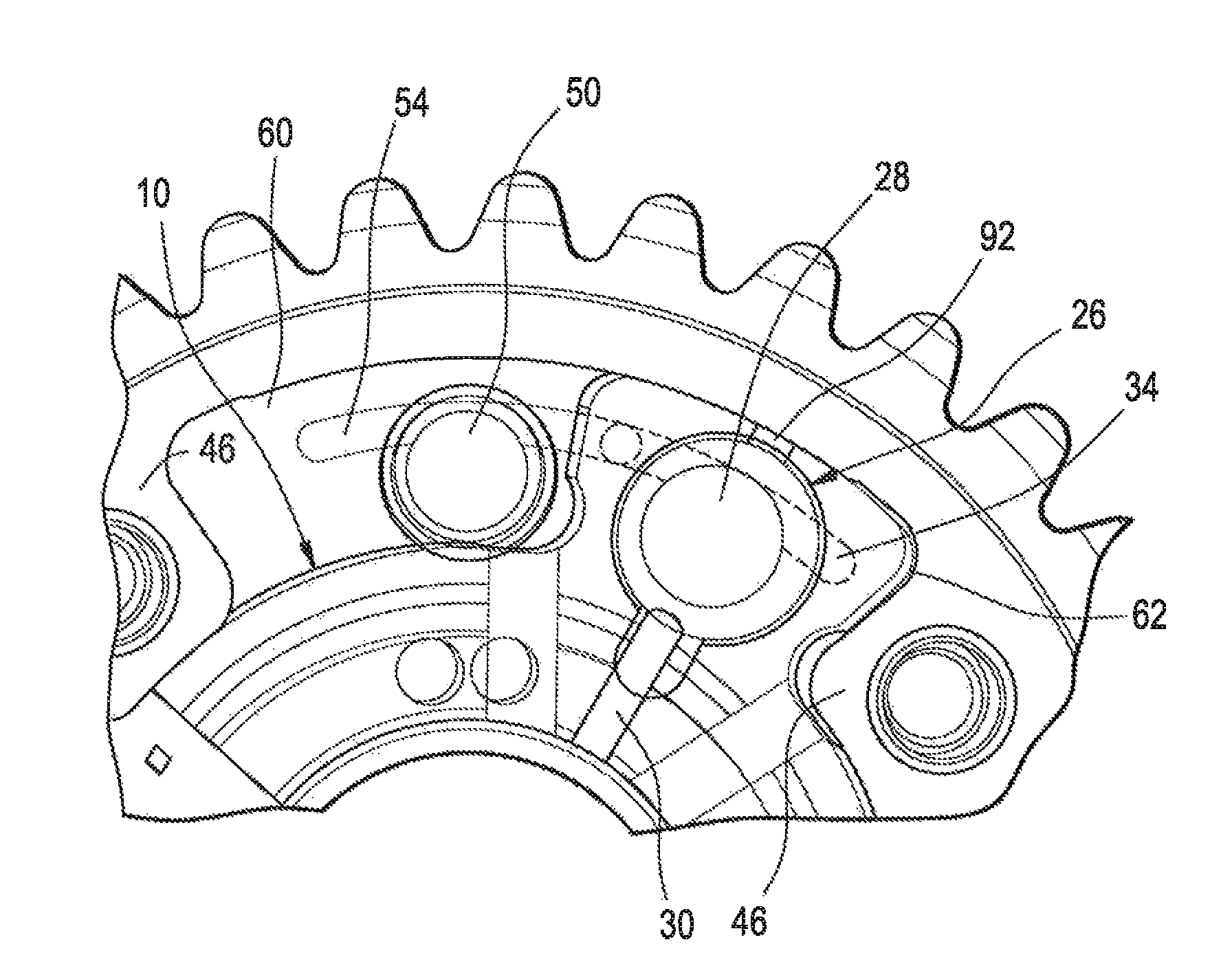
A stator-cover unit (1) for a camshaft adjuster designed for use in an internal combustion engine, having a toothed ring (2) for receiving a torque, there being integrally connected to said toothed ring a stator (3) in the form of a housing, having a locking cover (4) which is separate from the stator (3), wherein the locking cover (4) is connected rotationally conjointly to the stator (3), wherein the stator (3) and the locking cover (4), at least during assembly, are held rotationally conjointly secured in said position by means of a projection (9) on one of the two components, which projection engages with a form fit into a recess (11) on the other of the two components. A camshaft adjuster having a rotor and having a correspondingly designed stator-cover unit (1), wherein a piston can be introduced, movably in an axial direction, into an opening of the locking cover (4).
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
Internal combustion engine with hydraulic device for adjusting the rotation angle of a camshaft in relation to a crankshaft
ActiveUS6964250B2Reduce in quantityReduce riskInternal combustion piston enginesValve drivesExternal combustion engineMaterial removal
A hydraulic device in an internal combustion engine for adjusting a rotation angle of a camshaft in relation to a crankshaft includes a tubular stator and a rotor connected in fixed rotative engagement with the camshaft and having plural vanes in spaced apart relationship to define pressure chambers on both sides of the vanes. The stator is connected in fixed rotative engagement with a crankshaft-drive timing pulley and formed in single-piece construction with an end wall to thereby exhibit a pot-shaped structure. The pot is made without material removal from a sheet metal part and constructed to define with the rotor vanes the pressure chambers. Pressure medium is supplied to or purged from the pressure chambers to selectively adjust the position of the rotor in relation to the stator and thereby the position of the camshaft in relation to the crankshaft.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
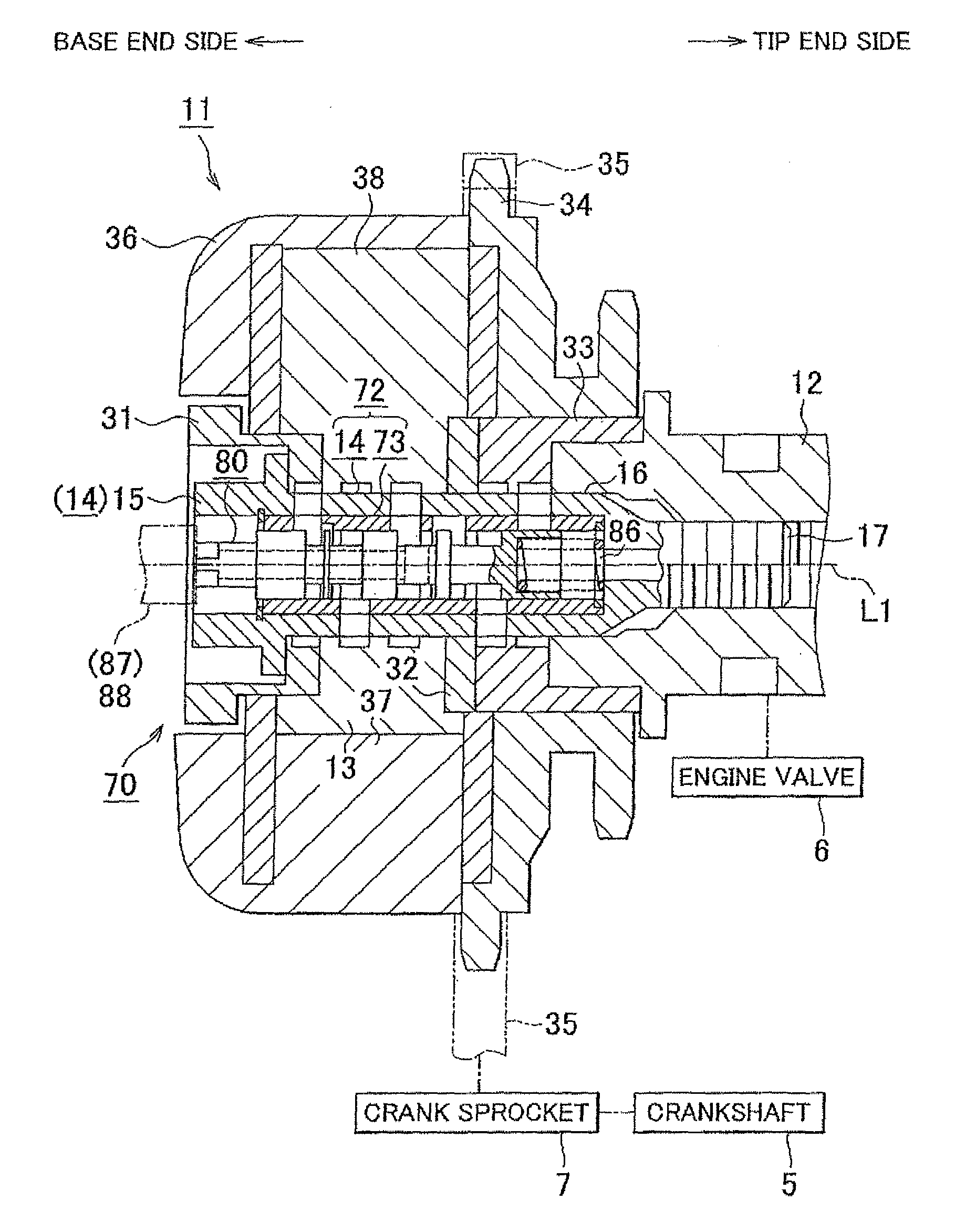
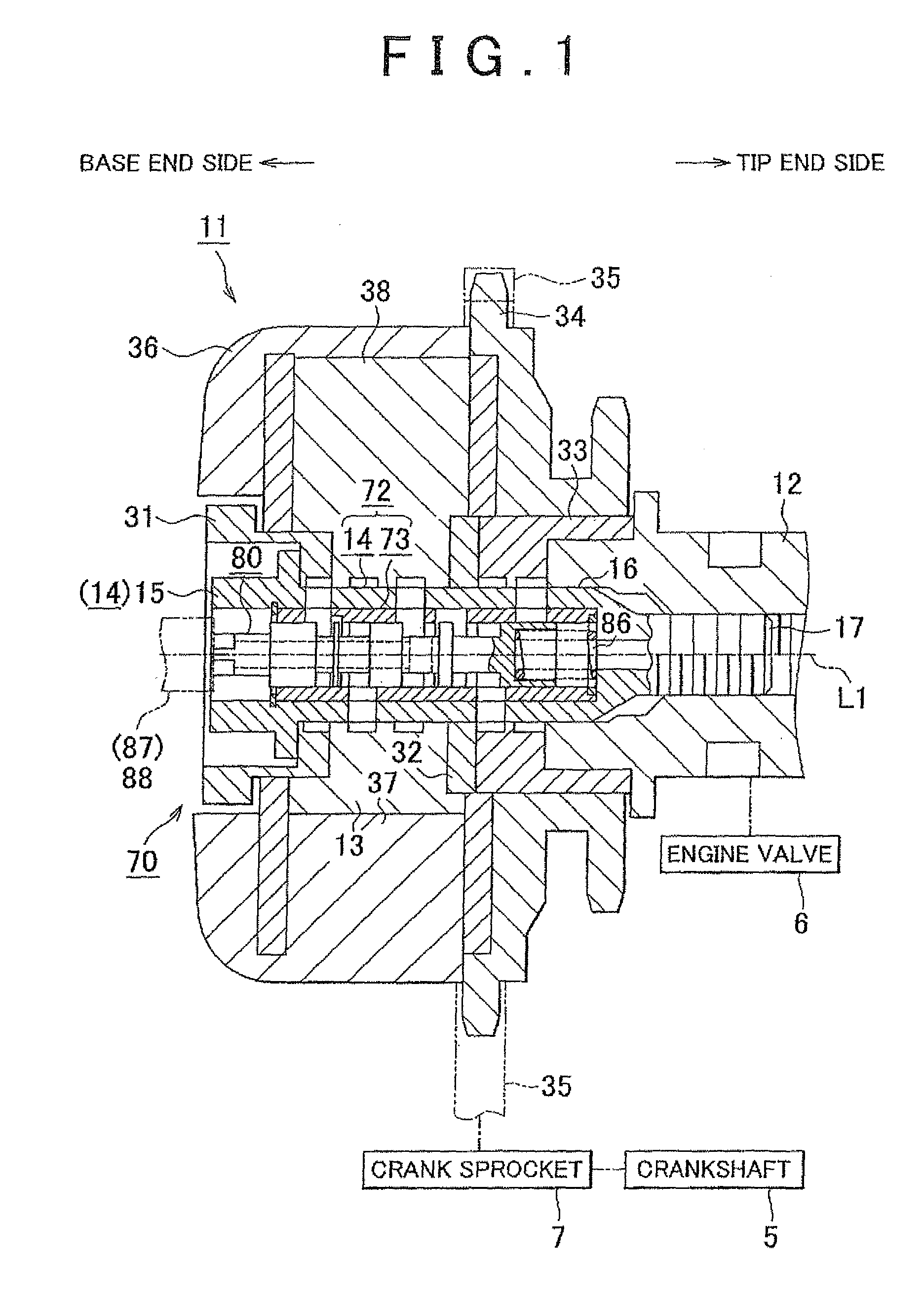
Valve timing control apparatus for internal combustion engine
A valve timing control apparatus for an internal combustion engine, including a drive rotation member, a follower rotation member, an electric motor, and a speed reducer including an internal gear portion, an eccentric cam on an inner peripheral side of the internal gear portion, rollers disposed between the internal gear portion and the eccentric cam, and a cage rotatable relative to the internal gear portion by rotation of the eccentric cam. A motor output shaft is arranged in series relative to the eccentric cam in an axial direction thereof. A needle bearing is rollably disposed on a part of an outer peripheral surface of the follower rotation member. The eccentric cam and the motor output shaft are press-fitted onto an outer peripheral portion of the needle bearing. The needle bearing extends over both the eccentric cam and the motor output shaft.
Owner:HITACHI AUTOMOTIVE SYST LTD
Valve timing control apparatus and method of internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20020010540A1Easy to controlAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlExhaust valveExternal combustion engine
A valve timing control apparatus of an internal combustion engine that includes a biasing device that applies bias force to a camshaft of intake or exhaust valves so as to bring the valve timing of the engine into a predetermined state when the valve timing is in a predetermined range, for example, when the valve timing is on the retard side of the engine start valve timing with which the engine is started is controlled by a controller that controls the valve timing in view of the bias force of the biasing device.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method and system for variable cam timing device
ActiveUS20160108773A1Improve emission performanceImprove fuel economy performanceElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesSpool valveEngineering
Methods and systems are described for an engine with a cam torque actuated variable cam timing phaser. Phaser positioning control is improved by reducing inaccuracies resulting from inadvertent spool valve and / or phaser movement when the spool valve is commanded between regions. In addition, improved spool valve mapping is used to render phaser commands more consistent and robust.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
VCT lock pin having a tortuous path providing a hydraulic delay
A variable cam timing phaser having a tortuous path from the supply of pressurized oil to the tapered recess into which the locking pin fits, that introduces a delay between when the engine starts and when the locking pin moves to an unlocked position. The tortuous path restricts fluid flow, preventing the locking pin from unlocking during engine start-up with the initial oil pressurization, prior to the variable cam timing phaser having sufficient oil to operate. The delay ensures that the chambers of the variable cam timing phaser have time to fill with operating fluid before the phaser is unlocked.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
Centering slot for internal combustion engine
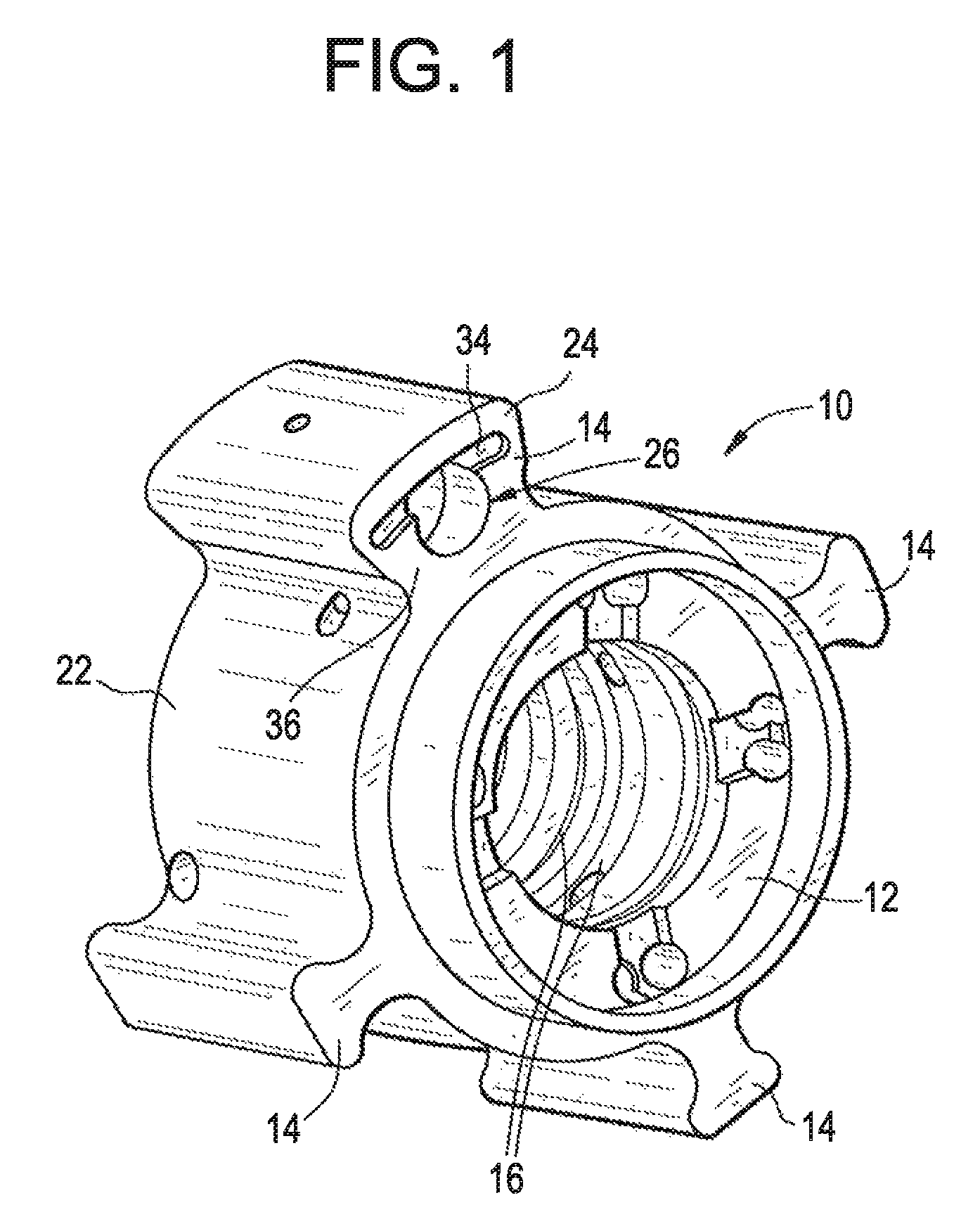
InactiveUS8973542B2Shorten the counting processReduce complexityMachines/enginesValve camshaftsExternal combustion engineInternal combustion engine
Owner:HILITE GERMANY
Starting device of spark-ignition multi-cylinder engine
InactiveCN103939223APremature ignition avoidanceElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesInlet valveStop time
A starting device of a spark-ignition multi-cylinder engine is provided. When the supplied hydraulic pressure is lower than a predetermined value, the variable valve phase mechanism locks the close timing of the intake valve to a predetermined timing that is between the most advanced timing and the most retarded timing and enables a cold start of the engine. When the engine in the engine start is in a high temperature state in which a temperature thereof is higher than a predetermined temperature, the start controller performs retard-setting on the cylinder that is on the intake stroke at an engine stopped timing among the plurality of cylinders to set a fuel injection timing thereof to an early stage of expansion stroke, and the start controller retards an ignition timing of the cylinder to a timing in the early stage of the expansion stroke and after the fuel injection is completed.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
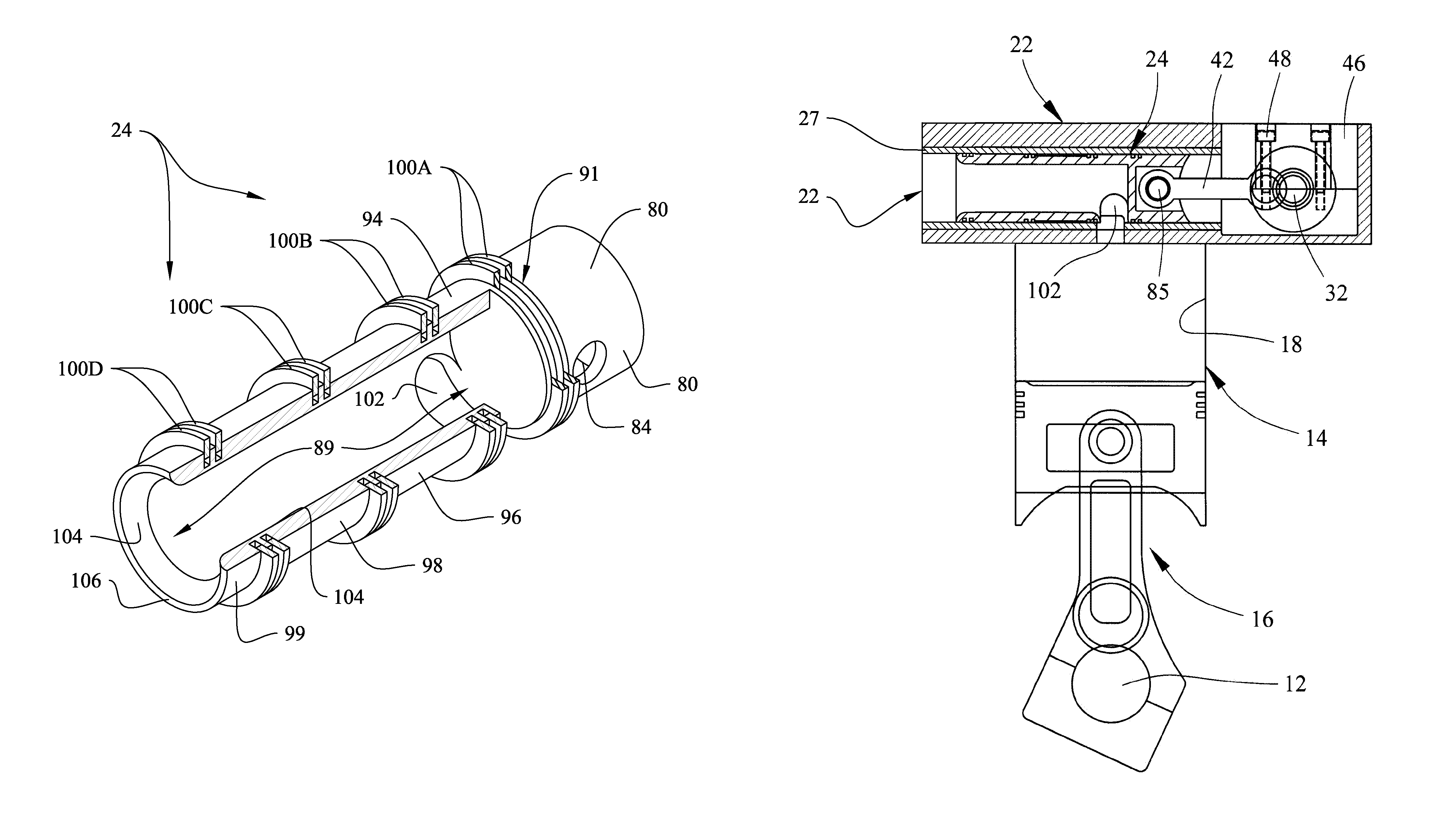
Sliding valve aspiration
ActiveUS8776756B2Reduce frictionEqually distributedMachines/enginesValve camshaftsSpool valveCombustion
Multi-section sleeve valves for internal combustion engines for improved aspiration. An open connecting rod section is separated from an internal, tubular passageway by a closed wall. A port section proximate the wall defines valve ports. A power stroke midsection borders the port section. An oiling section borders the midsection, and an open section adjacent the oiling section is in fluid flow communication with the tubular passageway. The lower-diameter midsection forms a relief annulus between the valve and the tunnel or sleeve in which the valve is disposed. Fluid flow occurs through the valve interior and through ports dynamically positioned above the compression cylinder, proximate aligned sleeve and head ports. Sleeve ports are separated by bridges that maintain valve rings in compression during reciprocation to prevent damage. High pressure gas is confined between axially spaced apart, stepped sealing rings that prevent gases from flowing axially about the valve exterior.
Owner:GRACE CAPITAL PARTNERS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com