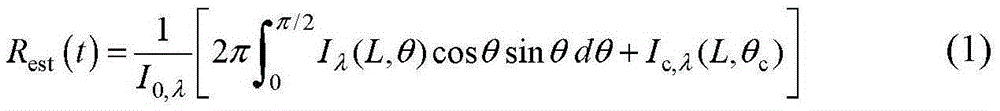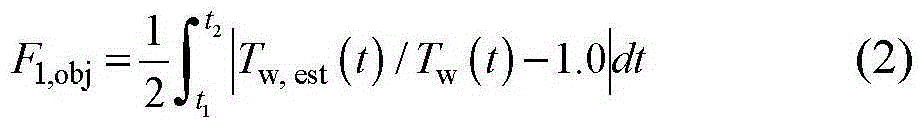Measuring method for simultaneously obtaining temperature-variable thermal conductivity coefficient and absorption coefficient of semi-transparent material
A technology of translucent material and thermal conductivity, applied in the direction of material thermal development, color/spectral property measurement, etc., can solve the problems of radiant thermal physical property result error, measurement error and other problems, and achieve the effect of simple model, high efficiency and sensitivity, and easy theoretical solution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
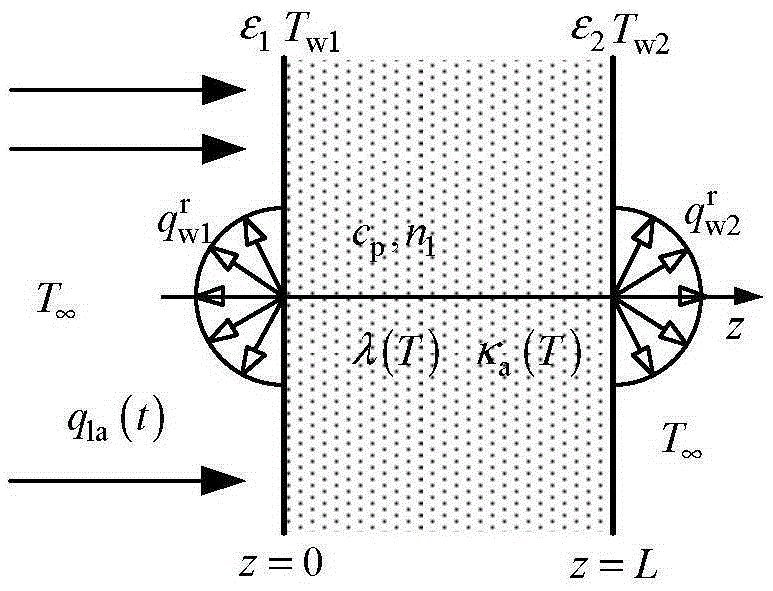
[0026] Specific implementation mode 1. Combination figure 1 Describe this specific embodiment, obtain the measuring method of translucent material temperature change thermal conductivity and absorption coefficient at the same time, the specific operation steps of this method are:
[0027] Step 1, making a sample to be tested with a thickness of L;
[0028] Step two, such as figure 1 As shown, a continuous laser with a wavelength of λ is incident on the left surface of the sample to be tested along the direction perpendicular to the surface of the sample with a thickness of L, and the duration is t seconds; Time-varying temperature T w (t) and radiation intensity R(t);
[0029] Step 3. Use the idea of solving the inverse problem to assume that the absorption coefficient κ of the corresponding wavelength of the sample to be tested varies with temperature a (T)=a 1 +a 2 ·Tmm -1 And the thermal conductivity λ(T)=b that varies with temperature 1 +b 2 TW / (m K); Then, by s...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0043] Specific embodiment 2. This embodiment is a further description of the method for simultaneously obtaining the temperature-related thermal conductivity and absorption coefficient of a translucent medium described in specific embodiment 1. The method for obtaining the temperature field in the calculation domain in step 3 is:
[0044] Using the heat conduction differential equation:
[0045] ρc p ∂ T ∂ t = λ ( T ) ∂ 2 T ∂ z 2 - ∂ q r ∂ z - - - (...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0050] Specific embodiment three. This embodiment is a further description of the method for simultaneously obtaining the temperature-related thermal conductivity and absorption coefficient of a translucent medium described in specific embodiment one. The method for obtaining the radiation field strength in the calculation domain in step three is:
[0051] Using the radiative transfer equation:
[0052] d I ( z , θ ) d z = - κ a I ( z ) + κ a I b ( z ) - - - ( 8 ) ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com